Worm infestation
- 1. By: S. Arunkumar, IInd Pharm D, JKKN College of Pharmacy, Kumarpalayam.
- 2. Worm Infestations: Worm Infestation are long-term diseases that produce few symptoms in their early stages and sometimes serious effects at well developed stages or may be quite fatal at times.
- 3. (i) Hook Worm (ii) Ascaris (iii) Pin worms (iv) Whip worm (v) Liver flukes (vi) Tape worm
- 5. Tapeworms : (i) Tapeworms live in human intestines where they feed on the partially-digested food in their hostâs intestines. (ii) It is a fully protected environment and they grow and thrive in these conditions. (iii) Tapeworms are parasitic worms and are most often referred to as just parasites. (iv) They literally survive through their hostâs nutrients. Parasites need hosts to survive.
- 6. Flukes: (i) Flukes are a type of parasitic Flatworm. Flukes get their name from the way they look as they are flat and the word "fluke" comes from a German word "flah" meaning "flat". (ii) Flukes have at least one external sucker, which they use to attach themselves to their host. Some flukes live on the gills, skin or outside of their hosts while others, such as blood flukes that live in humans, live internally in their hosts. (iii) Blood flukes are largely confined to very hot tropical areas such as North Africa and South East Asia and contribute to some extreme health conditions.
- 7. Roundworms: (i) Some of the most common types of Roundworms include Pinworms or Threadworms, Hookworms, Ascaris (a word that literally means âintestinal wormâ) and Heartworms. (ii) Roundworms have hollow bodies and openings at either end and generally grow between 2-5 inches long. Roundworms are very commonly found in pets and animals such as dogs and cats and can be easily passed on to humans. (iii) Roundworms live in salt water, fresh water and the soil. Eating contaminated foods or getting worms from contaminated pets is the most usual way to get roundworms (a category of worms). (iv) Hookworms and pinworms are often the most common types of roundworms found in humans.
- 10. Symptoms: HOOK WORMS: (i) Abdominal pain (ii) Colic (cramping and excessive crying in infants) (iii) Intestinal cramps (iv) Nausea (v) Fever (vi) Blood in your stool (vii) Appetite loss (viii) Itchy rash ASCARIS: (i) Nausea (ii) Vomiting (iii)Irregular stools (iv)Visible worms in the stool (v) Stomach or abdominal pain (vi)Weight loss
- 11. PIN WORMS : (i) Frequent and strong itching of the anal area (ii) Restless sleep due to the itching and discomfort (iii) Pain, rash, or other skin irritation around the anus (iv) The presence of pinworms in the area of your childâs anus (v) The presence of pinworms in stools WHIP WORM: (i) Bloody Diarrhea (ii) Painful or Frequent defecation (iii) Abdominal Pain (iv) Nausea (v) Vomiting (vi) Headaches (vii)Sudden and unexpected weight loss (viii) Fecal incontinence, or the inability to control defecation TAPE WORM : (i) Pain (ii) Unexplained weight loss (iii) Blockage of the intestine (iv) Digestive problems
- 13. Prophylaxis: (i) Cook meat to temperatures of at least 145 degree F for whole cuts of meat and to at least 160 degree F for ground meat. (ii) Then let it rest for at least 3 minutes before carving or eating. (iii) Freeze meat to -4 degrees F for at least 24 hours to kill tapeworm eggs. (iv) When traveling in undeveloped countries, cook fruits and vegetables with boiled or chemically-treated water before eating. (v) Wash hands with soap and hot water before preparing or eating foods.
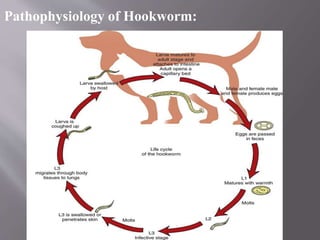
- 16. Pathophysiology:
- 17. Pathophysiology of Liver Fluke:
- 22. What are the Prevention to have taken in case of Worm Infestation?