Goodwill
- 1. Presented by: Presented for: Prajal, Prateekshya, Bidhyabaridhi Sigdel Pravin, Priya, Instructor Rikesh and Rubina Financial Reporting and Analysis
- 2. Example: Net Value of business Business overall is 10 million value is 15 million
- 3. 5 million extra is for Brand Name + The customers + The suppliers + Its workforce = Goodwill
- 4. 5 million extra is for Brand Name + The customers + The suppliers + Its workforce = Goodwill
- 5. 5 million extra is for Brand Name + The customers + The suppliers + Its workforce = Goodwill
- 6. âGoodwill is an intangible asset linked to an established business built over time, as a business gains favorable reputation for maintaining good customers-suppliers relationship and effective branding as it is expected to make profit year after year.â
- 7. 1. Good Public Relation 2. Regular Customers 3. Quality Maintenance 4. Management Skills 5. Location 6. Good Relation with Suppliers 7. Employees
- 8. Good Will (+) Good Will (-)
- 9. Good Will (+) BAD Good Will (-)
- 10. ïĄ Positive Goodwill Cost of Acquisition > Net Book Value of Business Net Assets
- 11. ïĄ Negative Goodwill / Badwill Cost of Acquisition < Net Book Value of Business Net Assets
- 12. 1. Average Profits Method 2. Super Profits Method 3. Capitalization Method
- 13. Goodwill = Average Profits X Number of years of Purchase
- 14. ïĄ Before calculating the average profits the following adjustments should be made in the profits of the firm: a) Any abnormal profits should be deducted from the net profits of that year. b) Any abnormal loss should be added back to the net profits of that year. c) Non-operating incomes e.g. income from investments etc should be deducted from the net profits of that year.
- 15. ïĄ Goodwill is calculated on the basis of Super Profits i.e. the excess of actual profits over the average profits.
- 16. ïĄ For example if the normal rate of return in a particular type of business is 20% and your investment in the business is Rs10,00,000 then your normal profits should be Rs 2,00,000 . But if you earned a net profit of Rs 2,30,000 then Rs 2,30,000 â Rs 2,00,000 = Rs 30,000 are your super profits.
- 17. ïĄ For calculating Goodwill, ï§ Super Profits are multiplied by the number of year of purchase. i. Normal profits = Capital Invested à Normal rate of return/100 ii. Super Profits = Actual profits â Normal Profits iii. Goodwill = Super Profits à No. of years purchased
- 18. 1. Capitalization of Average Profits Method 2. Capitalization of Super Profits Method
- 19. 1. Capitalization of Average Profits Method ï§ Under this method we calculate the average profits and then assess the capital needed for earning such average profits on basis of normal rate of return. such capital is called capitalization value of average profit.
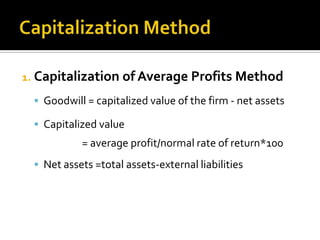
- 20. 1. Capitalization of Average Profits Method ï§ Goodwill = capitalized value of the firm - net assets ï§ Capitalized value = average profit/normal rate of return*100 ï§ Net assets =total assets-external liabilities
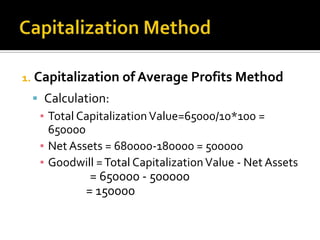
- 21. 1. Capitalization of Average Profits Method ï§ Example: ⊠A firm earns Rs.65000 as its average profits. The usual rate of earnings is 10%.the total assets of the firm amounted to Rs.680000 and liabilities are Rs.180000.
- 22. 1. Capitalization of Average Profits Method ï§ Calculation: ⊠Total Capitalization Value=65000/10*100 = 650000 ⊠Net Assets = 680000-180000 = 500000 ⊠Goodwill = Total Capitalization Value - Net Assets = 650000 - 500000 = 150000
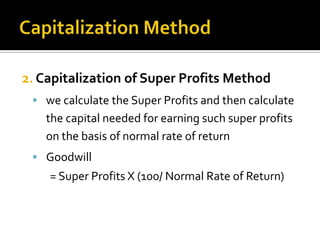
- 23. 2. Capitalization of Super Profits Method ï§ we calculate the Super Profits and then calculate the capital needed for earning such super profits on the basis of normal rate of return ï§ Goodwill = Super Profits X (100/ Normal Rate of Return)
- 24. 2. Capitalization of Super Profits Method ï§ Example: ⊠Verma Brothers earn a profit of Rs. 90,000 with a capital of Rs. 4, 00,000. The normal rate of return in the business is 15%.
- 25. 2. Capitalization of Super Profits Method ï§ Calculation ⊠Normal Profit = Rs. 4, 00,000 x 15/100 = Rs. 60,000 ⊠Super Profit = Rs. 90,000 â Rs. 60,000 = Rs. 30,000 ⊠Goodwill = Super Profit x 100/Normal Rate of Return = Rs. 30,000 x 100/15 = Rs. 2, 00,000