Density Functional Theory
Download as PPTX, PDF4 likes3,088 views
Density functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanics modeling method used in physics and chemistry to investigate the electronic structure of molecules and condensed phases. DFT was awarded the 1998 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. DFT approximates the complex quantum many-body problem by considering electron density as a basic variable instead of wave functions. Common approximations include the local density approximation (LDA) and generalized gradient approximation (GGA), which include additional information about the density gradient. DFT is widely used today due to its good accuracy and scaling better than other computational methods.
1 of 14
Downloaded 51 times



![Mathematical Model
ŌĆó SE: ─żŽł= [T+V+U]Žł= EŽł
ŌĆó T=e kinetic Energy
ŌĆó V=e-N attraction
ŌĆó Electron-electron interaction (U) prevents separation into
single particle wave function for exact solution
ŌĆó (HK)DFT: E=├Ŗ[Žü(ŌåÆv)]
ŌĆó ├Ŗ is a single unique functional, but probably extremely
complex
ŌĆó Approximated functionals](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e45a329a-f368-408e-873f-71889a0e4f38-170119090638/85/Density-Functional-Theory-5-320.jpg)





Recommended
Introduction to density functional theory 



Introduction to density functional theory Sarthak Hajirnis
╠²
This presentation is the introduction to Density Functional Theory, an essential computational approach used by Physicist and Quantum Chemist to study Solid State matter.Dft presentation



Dft presentationSaibalendu Sarkar
╠²
Density functional theory (DFT) provides an alternative approach to calculate properties of molecules by working with electron density rather than wave functions. DFT relies on two theorems linking the ground state energy and electron density. Approximations must be made for the exchange-correlation functional, with popular approximations including LDA, GGA, and hybrid functionals. DFT calculations can determine properties like molecular geometries, energies, vibrational frequencies, and more using software packages. While computationally efficient, DFT has limitations such as its reliance on approximate exchange-correlation functionals.Introduction to DFT Part 2



Introduction to DFT Part 2Mariana M. Odashima
╠²
(If visualization is slow, please try downloading the file.)
Part 2 of a tutorial given in the Brazilian Physical Society meeting, ENFMC. Abstract: Density-functional theory (DFT) was developed 50 years ago, connecting fundamental quantum methods from early days of quantum mechanics to our days of computer-powered science. Today DFT is the most widely used method in electronic structure calculations. It helps moving forward materials sciences from a single atom to nanoclusters and biomolecules, connecting solid-state, quantum chemistry, atomic and molecular physics, biophysics and beyond. In this tutorial, I will try to clarify this pathway under a historical view, presenting the DFT pillars and its building blocks, namely, the Hohenberg-Kohn theorem, the Kohn-Sham scheme, the local density approximation (LDA) and generalized gradient approximation (GGA). I would like to open the black box misconception of the method, and present a more pedagogical and solid perspective on DFT.Density functional theory (DFT) and the concepts of the augmented-plane-wave ...



Density functional theory (DFT) and the concepts of the augmented-plane-wave ...ABDERRAHMANE REGGAD
╠²
Density functional theory (DFT) is a quantum mechanical method used to investigate the electronic structure of materials. The document discusses DFT and the linearized augmented plane wave plus local orbital (LAPW+lo) method implemented in the Wien2k software. Wien2k is widely used to study the properties of solids and surfaces using an all-electron, relativistic, and full-potential DFT approach. The document provides an overview of the theoretical foundations of DFT and LAPW methods as well as examples of applications studied with Wien2k.Materials Modelling: From theory to solar cells (Lecture 1)



Materials Modelling: From theory to solar cells (Lecture 1)cdtpv
╠²
This document provides an overview of a mini-module on materials modelling for solar energy applications. It introduces the lecturers and outlines the course structure, which includes lectures on modelling, interfaces, and multi-scale approaches. It also describes a literature review activity where students will present a research paper using materials modelling in photovoltaics. Recommended textbooks are provided on topics like bonding in solids, computational chemistry, and density functional theory for solids.Density functional theory



Density functional theorysandhya singh
╠²
This document provides an overview of density functional theory (DFT). It discusses the history and development of DFT, including the Hohenberg-Kohn and Kohn-Sham theorems. The document outlines the fundamentals of DFT, including how it uses functionals of electron density rather than wavefunctions to simplify solving the many-body Schrodinger equation. It also describes the self-consistent approach in DFT calculations and provides examples of popular DFT software packages.Dft calculation by vasp



Dft calculation by vaspMIHIR RANJAN SAHOO
╠²
The document discusses density functional theory (DFT) and its implementation in the VASP software. It explains key concepts like the Kohn-Sham approach for approximating the many-body Schrodinger equation and the use of pseudopotentials and plane wave basis sets. It also summarizes some example calculations done in VASP like determining the binding energy of O2, equilibrium lattice constant of Cu, and band structures of Si and graphene. Key input and output files of VASP are also outlined.NANO266 - Lecture 4 - Introduction to DFT



NANO266 - Lecture 4 - Introduction to DFTUniversity of California, San Diego
╠²
UCSD NANO 266 Quantum Mechanical Modelling of Materials and Nanostructures is a graduate class that provides students with a highly practical introduction to the application of first principles quantum mechanical simulations to model, understand and predict the properties of materials and nano-structures. The syllabus includes: a brief introduction to quantum mechanics and the Hartree-Fock and density functional theory (DFT) formulations; practical simulation considerations such as convergence, selection of the appropriate functional and parameters; interpretation of the results from simulations, including the limits of accuracy of each method. Several lab sessions provide students with hands-on experience in the conduct of simulations. A key aspect of the course is in the use of programming to facilitate calculations and analysis.Introduction to DFT Part 1 



Introduction to DFT Part 1 Mariana M. Odashima
╠²
(If visualization is slow, please try downloading the file.)
Part 1 of a tutorial given in the Brazilian Physical Society meeting, ENFMC. Abstract: Density-functional theory (DFT) was developed 50 years ago, connecting fundamental quantum methods from early days of quantum mechanics to our days of computer-powered science. Today DFT is the most widely used method in electronic structure calculations. It helps moving forward materials sciences from a single atom to nanoclusters and biomolecules, connecting solid-state, quantum chemistry, atomic and molecular physics, biophysics and beyond. In this tutorial, I will try to clarify this pathway under a historical view, presenting the DFT pillars and its building blocks, namely, the Hohenberg-Kohn theorem, the Kohn-Sham scheme, the local density approximation (LDA) and generalized gradient approximation (GGA). I would like to open the black box misconception of the method, and present a more pedagogical and solid perspective on DFT.Band structure



Band structurenirupam12
╠²
The document provides an overview of the electronic band structure of solids from both the Sommerfeld and Bloch perspectives. It discusses key concepts such as:
1) Quantum numbers that label the eigenenergies and eigenfunctions of the Hamiltonian.
2) Bloch's theorem which describes the wavefunction of an electron as a plane wave modulated by a periodic function with the periodicity of the crystal lattice.
3) The band structure and energy levels that arise from Bloch's treatment, which has no simple explicit form unlike Sommerfeld's free electron model.
4) Key differences between the Sommerfeld and Bloch approaches regarding concepts like the density of states, Fermi surface, and wavefunctionsDensity Functional Theory.pptx



Density Functional Theory.pptxHassanShah396906
╠²
Density functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanics method used to investigate the electronic structure of many-body systems like molecules and solids. It functions by using functionals of the electron density rather than the many-body wavefunction. This makes calculations more efficient. DFT was developed based on the Hohenberg-Kohn theorems, which established that all ground state properties are uniquely determined by the electron density alone. This allowed modeling systems using functionals of the density rather than attempting to solve the complicated many-electron Schrodinger equation directly. DFT is now widely used in physics, chemistry, and materials science.Density Functional Theory



Density Functional Theorykrishslide
╠²
This document discusses computational methods for theoretical chemistry. It describes how quantum chemical calculations can be used to simulate molecular structures, vibrational frequencies, and spectra. The main computational methods covered are molecular mechanics, semi-empirical quantum chemistry, and ab initio quantum chemistry. Molecular mechanics uses classical physics approximations while quantum chemistry methods solve the Schrodinger equation using different levels of approximation.Perturbation



PerturbationBHAVANAR12
╠²
The document discusses first order perturbation theory. It begins by introducing perturbation theory as an approximate method to solve the Schrodinger equation for complex quantum systems where the Hamiltonian cannot be solved exactly. It then presents the key equations of first order perturbation theory. The first order correction to the energy is given by the expectation value of the perturbation operator over the unperturbed ground state wavefunction. The first order correction to the wavefunction is expressed as a linear combination of unperturbed eigenstates.THE HARTREE FOCK METHOD



THE HARTREE FOCK METHODPremashis Kumar
╠²
In computational physics and Quantum chemistry, the HartreeŌĆōFock (HF) method also known as self consistent method is a method of approximation for the determination of the wave function and the energy of a quantum many-body system or many electron system in a stationary stateApplications of Computational Quantum Chemistry



Applications of Computational Quantum ChemistryUniversity of Kerbala, Faculty of Science, Department of Chemistry
╠²
This presentation introduces an idea about the computational quantum chemistry field and its importance and applications in different ways.Exchange Interaction and their Consequences.pptx



Exchange Interaction and their Consequences.pptxSubhajit Pramanick
╠²
Hello, I am Subhajit Pramanick. I and my classmate, Anannya Sahaw, both presented this ppt in seminar of our Institute, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. The topic of this presentation is on exchange interaction and their consequences. It includes the basic of exchange interaction, the origin of it, classification of it and their discussions etc. We hope you will all enjoy by reading this presentation. Thank you.Intro. to quantum chemistry



Intro. to quantum chemistryRawat DA Greatt
╠²
The document provides an introduction to computational quantum chemistry, including:
- Definitions of computational chemistry and computational quantum chemistry, which focuses on solving the Schrodinger equation for molecules.
- An overview of methods like ab initio quantum chemistry, density functional theory, and approximations like the Born-Oppenheimer approximation and basis set approximations.
- Descriptions of approaches like Hartree-Fock, configuration interaction, M├Ėller-Plesset perturbation theory, and coupled cluster theory for including electron correlation effects.Fermi dirac distribution



Fermi dirac distributionAHSAN HALIMI
╠²
This document introduces the Fermi-Dirac distribution function. It begins by discussing basic concepts like the Fermi level and Fermi energy. It then covers Fermi and Bose statistics, and the postulates of Fermi particles. The derivation of the Fermi-Dirac distribution function is shown, which gives the probability of a quantum state being occupied at a given energy and temperature. Graphs are presented showing how the distribution varies with different temperatures. The classical limit of the distribution is discussed. References are provided at the end.Hartree fock theory



Hartree fock theoryž¦ž│ž¬ž¦ž░ ž¦┘ä┘ü┘Ŗž▓┘Ŗž¦žĪ ž¦┘ä┘å┘ł┘ł┘Ŗž®
╠²
1. Hartree-Fock theory describes molecules using a linear combination of atomic orbitals to approximate molecular orbitals. It treats electrons as independent particles moving in the average field of other electrons.
2. The Hartree-Fock method involves iteratively solving the Fock equations until self-consistency is reached between the input and output orbitals. This approximates electron correlation by including an average electron-electron repulsion term.
3. The Hartree-Fock method satisfies the Pauli exclusion principle through the use of Slater determinants, which are antisymmetric wavefunctions that go to zero when the spatial or spin coordinates of any two electrons are identical.Hydrogen atom



Hydrogen atomAnilkumar Shoibam
╠²
This document summarizes the key steps in solving the time-independent Schrodinger equation for the hydrogen atom using spherical polar coordinates. It separates the equation into three one-dimensional equations for the radial, angular, and azimuthal variables (R(r), ╬ś(╬Ė), ╬”(Žå)). Solving each equation shows they are only satisfied for discrete quantum numbers like angular momentum l and principal quantum number n, resulting in quantization of the hydrogen atom's energy levels.CHAPTER 6 Quantum Mechanics II



CHAPTER 6 Quantum Mechanics IIThepsatri Rajabhat University
╠²
CHAPTER 6 Quantum Mechanics II
6.0 Partial differentials
6.1 The Schr├Čdinger Wave Equation
6.2 Expectation Values
6.3 Infinite Square-Well Potential
6.4 Finite Square-Well Potential
6.5 Three-Dimensional Infinite-Potential Well
6.6 Simple Harmonic Oscillator
6.7 Barriers and Tunneling in some books an extra chapter due to its technical importanceQuantum Hall Effect



Quantum Hall EffectRCC Institute of Information Technology
╠²
The document summarizes a lecture on the quantum Hall effect. It defines the quantum Hall effect as a phenomenon where the resistance of a quantum well system is quantized under low temperature and high magnetic field conditions. It then provides calculations to show that the quantum Hall resistance is quantized and equal to h/q^2, where h is Planck's constant and q is the elementary charge. Finally, it discusses how the quantization occurs due to the formation of discrete energy levels called Landau levels in the presence of a magnetic field.Basics of DFT+U 



Basics of DFT+U Burak Himmetoglu
╠²
1. DFT+U is a method that adds Hubbard corrections to DFT to better account for localized electrons and electronic correlations in transition metal oxides that LDA/GGA cannot describe accurately.
2. It introduces an on-site Coulomb repulsion term U to the energy functional that favors electron localization and integer orbital occupations.
3. The U parameter can be computed using linear response theory by perturbing occupation matrices and evaluating screened response matrices in a supercell calculation.Quantum-Espresso_10_8_14



Quantum-Espresso_10_8_14cjfoss
╠²
Quantum Espresso is a suite of open-source computer codes for electronic structure calculations and materials modeling based on density functional theory and plane waves. It can be used to calculate material properties including ground-state energy, atomic forces, stresses, molecular dynamics, and more. The document provides an introduction and overview of Quantum Espresso, including examples of input files for defining crystal structures, pseudopotentials, k-points, and performing calculations of total energy and phonon frequencies. Convergence of key parameters like the plane wave cutoff energy and k-point sampling is also discussed.Photoelectron spectroscopy



Photoelectron spectroscopytesfayehh
╠²
Photoelectron spectroscopy
- a single photon in/ electron out process
ŌĆó X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
- using soft x-ray (200-2000 eV) radiation to
examine core-levels.
ŌĆó Ultraviolet Photoelectron Spectroscopy (UPS)
- using vacuum UV (10-45 eV) radiation to
examine valence levels.Hartree-Fock Review 



Hartree-Fock Review Inon Sharony
╠²
(This presentation is in .pptx format, and will display well when embedded improperly, such as on the ║▌║▌▀ŻShare site. Please download at your discretion, and be sure to cite your source)
Review of the Hartree-Fock algorithm for the Self-Consistent Field solution of the electronic Schroedinger equation. This talk also serves to highlight some basic points in Quantum Mechanics and Computational Chemistry.
March 21st, 2012Particle in a box- Application of Schrodinger wave equation



Particle in a box- Application of Schrodinger wave equationRawat DA Greatt
╠²
The document summarizes key concepts from quantum chemistry, including:
1) It introduces the historical development of quantum mechanics from classical mechanics and discusses how quantum theory was needed to describe atomic and subatomic phenomena.
2) It then summarizes the particle-like and wave-like properties of light and matter and introduces the Schrodinger equation.
3) The document concludes by presenting the particle-in-a-box model and explaining how solving the Schrodinger equation for this system shows that a particle's energy is quantized into discrete energy levels when confined in a box.Hetero junction



Hetero junctionyoga prabha
╠²
The document discusses heterojunctions and p-n junctions. It defines a heterojunction as the interface between two dissimilar semiconductors with different band gaps. There are three types of heterojunctions based on band alignment: type I where bands straddle, type II where bands are staggered, and type III where there is a broken gap. A p-n heterojunction diode forms when a p-doped and n-doped semiconductor meet; electrons flow from the higher to lower Fermi level side and holes in the opposite direction.K Point Overview



K Point Overviewsiddharth8250
╠²
kPoint is a cloud-based solution for multimedia learning and sharing in fast moving organizations. kPoint enables easy capture of expert knowledge into multimedia kapsules, which provide searchable video and flexible navigation of content for informal learning. kPoint effectively overcomes the barrier for creating and sharing content.BIOS 203: Lecture 2 - introduction to electronic structure theory



BIOS 203: Lecture 2 - introduction to electronic structure theorybios203
╠²
Lecture 2 of BIOS 203 mini-course taught by Heather Kulik at Stanford University. Introduction to electronic structure theory. http://bios203.stanford.edu or email bios203.course@gmail.com for more information.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Introduction to DFT Part 1 



Introduction to DFT Part 1 Mariana M. Odashima
╠²
(If visualization is slow, please try downloading the file.)
Part 1 of a tutorial given in the Brazilian Physical Society meeting, ENFMC. Abstract: Density-functional theory (DFT) was developed 50 years ago, connecting fundamental quantum methods from early days of quantum mechanics to our days of computer-powered science. Today DFT is the most widely used method in electronic structure calculations. It helps moving forward materials sciences from a single atom to nanoclusters and biomolecules, connecting solid-state, quantum chemistry, atomic and molecular physics, biophysics and beyond. In this tutorial, I will try to clarify this pathway under a historical view, presenting the DFT pillars and its building blocks, namely, the Hohenberg-Kohn theorem, the Kohn-Sham scheme, the local density approximation (LDA) and generalized gradient approximation (GGA). I would like to open the black box misconception of the method, and present a more pedagogical and solid perspective on DFT.Band structure



Band structurenirupam12
╠²
The document provides an overview of the electronic band structure of solids from both the Sommerfeld and Bloch perspectives. It discusses key concepts such as:
1) Quantum numbers that label the eigenenergies and eigenfunctions of the Hamiltonian.
2) Bloch's theorem which describes the wavefunction of an electron as a plane wave modulated by a periodic function with the periodicity of the crystal lattice.
3) The band structure and energy levels that arise from Bloch's treatment, which has no simple explicit form unlike Sommerfeld's free electron model.
4) Key differences between the Sommerfeld and Bloch approaches regarding concepts like the density of states, Fermi surface, and wavefunctionsDensity Functional Theory.pptx



Density Functional Theory.pptxHassanShah396906
╠²
Density functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanics method used to investigate the electronic structure of many-body systems like molecules and solids. It functions by using functionals of the electron density rather than the many-body wavefunction. This makes calculations more efficient. DFT was developed based on the Hohenberg-Kohn theorems, which established that all ground state properties are uniquely determined by the electron density alone. This allowed modeling systems using functionals of the density rather than attempting to solve the complicated many-electron Schrodinger equation directly. DFT is now widely used in physics, chemistry, and materials science.Density Functional Theory



Density Functional Theorykrishslide
╠²
This document discusses computational methods for theoretical chemistry. It describes how quantum chemical calculations can be used to simulate molecular structures, vibrational frequencies, and spectra. The main computational methods covered are molecular mechanics, semi-empirical quantum chemistry, and ab initio quantum chemistry. Molecular mechanics uses classical physics approximations while quantum chemistry methods solve the Schrodinger equation using different levels of approximation.Perturbation



PerturbationBHAVANAR12
╠²
The document discusses first order perturbation theory. It begins by introducing perturbation theory as an approximate method to solve the Schrodinger equation for complex quantum systems where the Hamiltonian cannot be solved exactly. It then presents the key equations of first order perturbation theory. The first order correction to the energy is given by the expectation value of the perturbation operator over the unperturbed ground state wavefunction. The first order correction to the wavefunction is expressed as a linear combination of unperturbed eigenstates.THE HARTREE FOCK METHOD



THE HARTREE FOCK METHODPremashis Kumar
╠²
In computational physics and Quantum chemistry, the HartreeŌĆōFock (HF) method also known as self consistent method is a method of approximation for the determination of the wave function and the energy of a quantum many-body system or many electron system in a stationary stateApplications of Computational Quantum Chemistry



Applications of Computational Quantum ChemistryUniversity of Kerbala, Faculty of Science, Department of Chemistry
╠²
This presentation introduces an idea about the computational quantum chemistry field and its importance and applications in different ways.Exchange Interaction and their Consequences.pptx



Exchange Interaction and their Consequences.pptxSubhajit Pramanick
╠²
Hello, I am Subhajit Pramanick. I and my classmate, Anannya Sahaw, both presented this ppt in seminar of our Institute, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. The topic of this presentation is on exchange interaction and their consequences. It includes the basic of exchange interaction, the origin of it, classification of it and their discussions etc. We hope you will all enjoy by reading this presentation. Thank you.Intro. to quantum chemistry



Intro. to quantum chemistryRawat DA Greatt
╠²
The document provides an introduction to computational quantum chemistry, including:
- Definitions of computational chemistry and computational quantum chemistry, which focuses on solving the Schrodinger equation for molecules.
- An overview of methods like ab initio quantum chemistry, density functional theory, and approximations like the Born-Oppenheimer approximation and basis set approximations.
- Descriptions of approaches like Hartree-Fock, configuration interaction, M├Ėller-Plesset perturbation theory, and coupled cluster theory for including electron correlation effects.Fermi dirac distribution



Fermi dirac distributionAHSAN HALIMI
╠²
This document introduces the Fermi-Dirac distribution function. It begins by discussing basic concepts like the Fermi level and Fermi energy. It then covers Fermi and Bose statistics, and the postulates of Fermi particles. The derivation of the Fermi-Dirac distribution function is shown, which gives the probability of a quantum state being occupied at a given energy and temperature. Graphs are presented showing how the distribution varies with different temperatures. The classical limit of the distribution is discussed. References are provided at the end.Hartree fock theory



Hartree fock theoryž¦ž│ž¬ž¦ž░ ž¦┘ä┘ü┘Ŗž▓┘Ŗž¦žĪ ž¦┘ä┘å┘ł┘ł┘Ŗž®
╠²
1. Hartree-Fock theory describes molecules using a linear combination of atomic orbitals to approximate molecular orbitals. It treats electrons as independent particles moving in the average field of other electrons.
2. The Hartree-Fock method involves iteratively solving the Fock equations until self-consistency is reached between the input and output orbitals. This approximates electron correlation by including an average electron-electron repulsion term.
3. The Hartree-Fock method satisfies the Pauli exclusion principle through the use of Slater determinants, which are antisymmetric wavefunctions that go to zero when the spatial or spin coordinates of any two electrons are identical.Hydrogen atom



Hydrogen atomAnilkumar Shoibam
╠²
This document summarizes the key steps in solving the time-independent Schrodinger equation for the hydrogen atom using spherical polar coordinates. It separates the equation into three one-dimensional equations for the radial, angular, and azimuthal variables (R(r), ╬ś(╬Ė), ╬”(Žå)). Solving each equation shows they are only satisfied for discrete quantum numbers like angular momentum l and principal quantum number n, resulting in quantization of the hydrogen atom's energy levels.CHAPTER 6 Quantum Mechanics II



CHAPTER 6 Quantum Mechanics IIThepsatri Rajabhat University
╠²
CHAPTER 6 Quantum Mechanics II
6.0 Partial differentials
6.1 The Schr├Čdinger Wave Equation
6.2 Expectation Values
6.3 Infinite Square-Well Potential
6.4 Finite Square-Well Potential
6.5 Three-Dimensional Infinite-Potential Well
6.6 Simple Harmonic Oscillator
6.7 Barriers and Tunneling in some books an extra chapter due to its technical importanceQuantum Hall Effect



Quantum Hall EffectRCC Institute of Information Technology
╠²
The document summarizes a lecture on the quantum Hall effect. It defines the quantum Hall effect as a phenomenon where the resistance of a quantum well system is quantized under low temperature and high magnetic field conditions. It then provides calculations to show that the quantum Hall resistance is quantized and equal to h/q^2, where h is Planck's constant and q is the elementary charge. Finally, it discusses how the quantization occurs due to the formation of discrete energy levels called Landau levels in the presence of a magnetic field.Basics of DFT+U 



Basics of DFT+U Burak Himmetoglu
╠²
1. DFT+U is a method that adds Hubbard corrections to DFT to better account for localized electrons and electronic correlations in transition metal oxides that LDA/GGA cannot describe accurately.
2. It introduces an on-site Coulomb repulsion term U to the energy functional that favors electron localization and integer orbital occupations.
3. The U parameter can be computed using linear response theory by perturbing occupation matrices and evaluating screened response matrices in a supercell calculation.Quantum-Espresso_10_8_14



Quantum-Espresso_10_8_14cjfoss
╠²
Quantum Espresso is a suite of open-source computer codes for electronic structure calculations and materials modeling based on density functional theory and plane waves. It can be used to calculate material properties including ground-state energy, atomic forces, stresses, molecular dynamics, and more. The document provides an introduction and overview of Quantum Espresso, including examples of input files for defining crystal structures, pseudopotentials, k-points, and performing calculations of total energy and phonon frequencies. Convergence of key parameters like the plane wave cutoff energy and k-point sampling is also discussed.Photoelectron spectroscopy



Photoelectron spectroscopytesfayehh
╠²
Photoelectron spectroscopy
- a single photon in/ electron out process
ŌĆó X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
- using soft x-ray (200-2000 eV) radiation to
examine core-levels.
ŌĆó Ultraviolet Photoelectron Spectroscopy (UPS)
- using vacuum UV (10-45 eV) radiation to
examine valence levels.Hartree-Fock Review 



Hartree-Fock Review Inon Sharony
╠²
(This presentation is in .pptx format, and will display well when embedded improperly, such as on the ║▌║▌▀ŻShare site. Please download at your discretion, and be sure to cite your source)
Review of the Hartree-Fock algorithm for the Self-Consistent Field solution of the electronic Schroedinger equation. This talk also serves to highlight some basic points in Quantum Mechanics and Computational Chemistry.
March 21st, 2012Particle in a box- Application of Schrodinger wave equation



Particle in a box- Application of Schrodinger wave equationRawat DA Greatt
╠²
The document summarizes key concepts from quantum chemistry, including:
1) It introduces the historical development of quantum mechanics from classical mechanics and discusses how quantum theory was needed to describe atomic and subatomic phenomena.
2) It then summarizes the particle-like and wave-like properties of light and matter and introduces the Schrodinger equation.
3) The document concludes by presenting the particle-in-a-box model and explaining how solving the Schrodinger equation for this system shows that a particle's energy is quantized into discrete energy levels when confined in a box.Hetero junction



Hetero junctionyoga prabha
╠²
The document discusses heterojunctions and p-n junctions. It defines a heterojunction as the interface between two dissimilar semiconductors with different band gaps. There are three types of heterojunctions based on band alignment: type I where bands straddle, type II where bands are staggered, and type III where there is a broken gap. A p-n heterojunction diode forms when a p-doped and n-doped semiconductor meet; electrons flow from the higher to lower Fermi level side and holes in the opposite direction.Viewers also liked (20)
K Point Overview



K Point Overviewsiddharth8250
╠²
kPoint is a cloud-based solution for multimedia learning and sharing in fast moving organizations. kPoint enables easy capture of expert knowledge into multimedia kapsules, which provide searchable video and flexible navigation of content for informal learning. kPoint effectively overcomes the barrier for creating and sharing content.BIOS 203: Lecture 2 - introduction to electronic structure theory



BIOS 203: Lecture 2 - introduction to electronic structure theorybios203
╠²
Lecture 2 of BIOS 203 mini-course taught by Heather Kulik at Stanford University. Introduction to electronic structure theory. http://bios203.stanford.edu or email bios203.course@gmail.com for more information.Wannier90: Band Structures, Tips and Tricks



Wannier90: Band Structures, Tips and TricksJonathan Skelton
╠²
An updated tutorial on using Wannier90 with the VASP code for electronic-structure calculations. Includes tips on how to build VASP with Wannier90 support, how to use the VASP-to-Wannier90 interface, and a worked example of calculating the electronic band structure and density of states of SnS2 using the PBE and HSE06 functionals and the GW routines.vasp-gpu on Balena: Usage and Some Benchmarks



vasp-gpu on Balena: Usage and Some BenchmarksJonathan Skelton
╠²
A presentation looking at the parallelisation of the Vienna ab initio Simulation Package (VASP) code, how to optimise performance and scaling by tuning the input control tags, and some initial experience with the NVIDIA GPU (CUDA) port of the code, including compiling, running jobs, and some initial benchmark results.Phonons & Phonopy: Pro Tips (2015)



Phonons & Phonopy: Pro Tips (2015)Jonathan Skelton
╠²
An overview of the Phonopy (and Phono3py) lattice-dynamics codes, covering features, examples, applications and troubleshooting (2014 presentation updated for 2015).Density-Functional Tight-Binding (DFTB) as fast approximate DFT method - An i...



Density-Functional Tight-Binding (DFTB) as fast approximate DFT method - An i...Stephan Irle
╠²
This presentation was given April 27, 2013 at Ibaraki University in Mito, Japan (Professor Seiji Mori's group). The presentation does not claim to give a complete overview of the complex field of DFTB parameterization, but rather focuses on the method's central approximations and discusses its performance in various applications.VASP: Some Accumulated Wisdom



VASP: Some Accumulated WisdomJonathan Skelton
╠²
Some "accumulated wisdom" from several years of using the Vienna ab initio Simulation Package (VASP) code for computational modelling. Includes tips on convergence and parallelisation.NANO266 - Lecture 5 - Exchange-Correlation Functionals



NANO266 - Lecture 5 - Exchange-Correlation FunctionalsUniversity of California, San Diego
╠²
UCSD NANO 266 Quantum Mechanical Modelling of Materials and Nanostructures is a graduate class that provides students with a highly practical introduction to the application of first principles quantum mechanical simulations to model, understand and predict the properties of materials and nano-structures. The syllabus includes: a brief introduction to quantum mechanics and the Hartree-Fock and density functional theory (DFT) formulations; practical simulation considerations such as convergence, selection of the appropriate functional and parameters; interpretation of the results from simulations, including the limits of accuracy of each method. Several lab sessions provide students with hands-on experience in the conduct of simulations. A key aspect of the course is in the use of programming to facilitate calculations and analysis.Lecture3



Lecture3Heather Kulik
╠²
Lecture 3: Introduction to Quantum Chemical Simulation graduate course taught at MIT in Fall 2014 by Heather Kulik. This course covers: wavefunction theory, density functional theory, force fields and molecular dynamics and sampling.NANO266 - Lecture 3 - Beyond the Hartree-Fock Approximation



NANO266 - Lecture 3 - Beyond the Hartree-Fock ApproximationUniversity of California, San Diego
╠²
UCSD NANO 266 Quantum Mechanical Modelling of Materials and Nanostructures is a graduate class that provides students with a highly practical introduction to the application of first principles quantum mechanical simulations to model, understand and predict the properties of materials and nano-structures. The syllabus includes: a brief introduction to quantum mechanics and the Hartree-Fock and density functional theory (DFT) formulations; practical simulation considerations such as convergence, selection of the appropriate functional and parameters; interpretation of the results from simulations, including the limits of accuracy of each method. Several lab sessions provide students with hands-on experience in the conduct of simulations. A key aspect of the course is in the use of programming to facilitate calculations and analysis.dft



dftNejeh Ferjani
╠²
The document discusses a two-day training on design for testability using Synopsys' DFT Compiler and TetraMAX tools. Day 1 covers basic DFT concepts and techniques including scan path insertion and memory wrappers using DFT Compiler. Day 2 focuses on TetraMAX for fault simulation, modeling memories, and debugging problems.VASP And Wannier90: A Quick Tutorial



VASP And Wannier90: A Quick TutorialJonathan Skelton
╠²
A basic tutorial on using Wannier90 with the VASP code. Includes a brief overview of Wannier functions, tips on how to build VASP with Wannier90 support, and how to use the VASP/Wannier90 interface to compute an HSE06 band structure and perform some other Wannier90 post processing.NANO266 - Lecture 2 - The Hartree-Fock Approach



NANO266 - Lecture 2 - The Hartree-Fock ApproachUniversity of California, San Diego
╠²
UCSD NANO 266 Quantum Mechanical Modelling of Materials and Nanostructures is a graduate class that provides students with a highly practical introduction to the application of first principles quantum mechanical simulations to model, understand and predict the properties of materials and nano-structures. The syllabus includes: a brief introduction to quantum mechanics and the Hartree-Fock and density functional theory (DFT) formulations; practical simulation considerations such as convergence, selection of the appropriate functional and parameters; interpretation of the results from simulations, including the limits of accuracy of each method. Several lab sessions provide students with hands-on experience in the conduct of simulations. A key aspect of the course is in the use of programming to facilitate calculations and analysis.NANO266 - Lecture 6 - Molecule Properties from Quantum Mechanical Modeling



NANO266 - Lecture 6 - Molecule Properties from Quantum Mechanical ModelingUniversity of California, San Diego
╠²
UCSD NANO 266 Quantum Mechanical Modelling of Materials and Nanostructures is a graduate class that provides students with a highly practical introduction to the application of first principles quantum mechanical simulations to model, understand and predict the properties of materials and nano-structures. The syllabus includes: a brief introduction to quantum mechanics and the Hartree-Fock and density functional theory (DFT) formulations; practical simulation considerations such as convergence, selection of the appropriate functional and parameters; interpretation of the results from simulations, including the limits of accuracy of each method. Several lab sessions provide students with hands-on experience in the conduct of simulations. A key aspect of the course is in the use of programming to facilitate calculations and analysis.NANO266 - Lecture 13 - Ab initio molecular dyanmics



NANO266 - Lecture 13 - Ab initio molecular dyanmicsUniversity of California, San Diego
╠²
UCSD NANO 266 Quantum Mechanical Modelling of Materials and Nanostructures is a graduate class that provides students with a highly practical introduction to the application of first principles quantum mechanical simulations to model, understand and predict the properties of materials and nano-structures. The syllabus includes: a brief introduction to quantum mechanics and the Hartree-Fock and density functional theory (DFT) formulations; practical simulation considerations such as convergence, selection of the appropriate functional and parameters; interpretation of the results from simulations, including the limits of accuracy of each method. Several lab sessions provide students with hands-on experience in the conduct of simulations. A key aspect of the course is in the use of programming to facilitate calculations and analysis.Application of density functional theory (dft),



Application of density functional theory (dft),Katerina Makarova
╠²
This document discusses using density functional theory, electron spin resonance, and nuclear magnetic resonance to study the properties and degradation of endocrine-disrupting compounds when exposed to chemical oxidizers. Specifically, it examines how estrogens, xenoestrogens, bisphenol A, and hydroquinone break down and react when exposed to oxidizers like hydroxyl radicals, acetate radicals, and methyl radicals. The goal is to better understand how these endocrine disruptors can be broken down during advanced oxidation processes.Quantum calculations and calculational chemistry



Quantum calculations and calculational chemistrynazanin25
╠²
This document discusses computational chemistry and different methods for calculating molecular structure and properties using computers. It describes two main approaches: molecular mechanics, which views molecules as collections of atoms and calculates potential energy based on bonding parameters; and quantum mechanics, which uses the Schrodinger equation and approximations like Born-Oppenheimer and molecular orbital theory. Specific quantum methods discussed include semi-empirical, ab initio, and density functional theory. Popular computational programs and visualization software are also listed.Lecture7



Lecture7Heather Kulik
╠²
Lecture 8: Introduction to Quantum Chemical Simulation graduate course taught at MIT in Fall 2014 by Heather Kulik. This course covers: wavefunction theory, density functional theory, force fields and molecular dynamics and sampling.Dft and its applications



Dft and its applicationsAgam Goel
╠²
The document discusses the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) and its applications. It provides an overview of DFT and how it represents a signal in the frequency domain. It then describes the fast Fourier transform (FFT) algorithm, which efficiently computes the DFT. The document outlines algorithms to compute the inverse DFT and circular convolution using the DFT. It includes MATLAB code implementations of DFT, inverse DFT, FFT, and circular convolution. Graphs are shown comparing computation times of the algorithms.NANO266 - Lecture 6 - Molecule Properties from Quantum Mechanical Modeling



NANO266 - Lecture 6 - Molecule Properties from Quantum Mechanical ModelingUniversity of California, San Diego
╠²
Similar to Density Functional Theory (20)
Quantum Chemistry II



Quantum Chemistry IIbaoilleach
╠²
This document summarizes several quantum mechanics methods for calculating molecular properties, including semi-empirical, density functional theory (DFT), and correlation methods. It discusses how semi-empirical methods approximate integrals to speed up calculations compared to Hartree-Fock. DFT is described as an alternative to wavefunction methods that uses the electron density. Popular DFT functionals and how they include exchange and correlation are outlined. Geometry optimization and vibrational frequency calculations are also summarized.finland.ppt



finland.pptRAMARATHI2
╠²
This document discusses challenges and open questions in nuclear density functional theory (DFT). It begins by providing background on DFT and how it has been applied to nuclei using approximations like the local density approximation. It then discusses questions around improving the nuclear energy density functional, including justifying terms from microscopic theory, improving treatment of pairing and beyond-mean-field correlations, and incorporating dynamics. The document concludes by emphasizing the need for focused theoretical efforts, international collaborations, and new experimental data to help address open questions in nuclear DFT.SCF methods, basis sets, and integrals part III



SCF methods, basis sets, and integrals part IIIAkefAfaneh2
╠²
Some DFT implementations (such as Octopus) attempt to describe the molecular
KohnŌĆōSham orbitals on a real-space grid.
ŌĆó A 3D simulation box is chosen together with a grid spacing, for example 0.5 a0. Then,
a grid in 3D is constructed and the SCF equations are solved on the grid.
ŌĆó This is different from an MO-LCAO expansion in numerical AOs!
ŌĆó Pseudopotentials are inevitable for real-space grid methods, but they are not required
when numerical AOs are used.
ŌĆó A great advantage of the use of numerical AOs as in DMol3 is that the method is free
of the basis-set superposition error (BSSE).
ŌĆó Because exact atomic orbitals are used, the atoms in a molecule cannot improve
their orbitals arti’¼ücially using basis functions from other atoms.02 - Ab initio Methods converted into ww



02 - Ab initio Methods converted into wwWalidHarb2
╠²
This document summarizes different computational chemistry methods, including ab initio methods that are derived directly from theoretical principles without experimental data. It describes the Hartree-Fock approximation and how it breaks the many-electron Schrodinger equation into simpler one-electron equations. It also discusses the limitations of Hartree-Fock in accounting for electron correlation and summarizes post-Hartree-Fock methods like Moller-Plesset perturbation theory and configuration interaction that include electron correlation.BoltzTrap webinar116_David_J_Singh.pdf



BoltzTrap webinar116_David_J_Singh.pdfDrSanjaySingh13
╠²
BoltzTraP is a software tool that uses linearized Boltzmann transport theory to calculate electronic transport properties from first-principles band structures. It can calculate properties like electrical conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and electronic thermal conductivity. The document discusses applications of BoltzTraP to analyze transport properties of metals and thermoelectric materials. Key applications highlighted include analyzing anisotropy, resistivity temperature dependence, and optimizing the electronic structure of materials for high thermoelectric performance.Intro-QM-Chem.ppt



Intro-QM-Chem.pptsami97008
╠²
This document provides an introduction to computational quantum chemistry. It defines computational chemistry as using mathematical approximations and computer programs to solve chemical problems based on quantum mechanics. Specifically, computational quantum chemistry focuses on solving the Schr├Čdinger equation for molecular systems using approximations like the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. It discusses how computational methods can be used to calculate various molecular properties and motivates the need for approximations due to the inability to exactly solve the Schr├Čdinger equation for complex molecules. The document then provides an overview of common computational methods like Hartree-Fock, configuration interaction, M├Ėller-Plesset perturbation theory, and coupled cluster theory.Intro-QM-Chem.ppt



Intro-QM-Chem.pptAkramLaKilo1
╠²
This document provides an introduction to computational quantum chemistry. It defines computational chemistry as using mathematical approximations and computer programs to solve chemical problems based on quantum mechanics. Specifically, computational quantum chemistry focuses on solving the Schr├Čdinger equation for molecular systems using approximations like the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. It also discusses methods for approximating the wavefunction like Hartree-Fock, configuration interaction, and density functional theory as well as expanding the molecular orbitals in a basis set of atomic orbitals.Density Functional Theory (DFT) Overview.pptx



Density Functional Theory (DFT) Overview.pptxmomnaqayyum01
╠²
Density Functional Theory (DFT) is a powerful computational method used to study the electronic structure of molecules and materials by focusing on electron density rather than the many-body wave function. DFT is preferred due to its efficiency, accuracy, and versatility, making it applicable in diverse fields like material design, catalysis, and drug discovery. When applied to the HŌééO molecule, DFT accurately predicts its molecular geometry, bond angles, and bond lengths, and provides insights into its electron density distribution, which reveals its polar nature. DFT simplifies the study of many-particle systems by reducing the problem to a manageable form, allowing for efficient calculations of large systems. The Born-Oppenheimer approximation further simplifies DFT by treating nuclear and electronic motions separately, significantly reducing the computational cost. At its core, the Hohenberg-Kohn theorem provides the theoretical foundation of DFT, stating that all properties of a quantum system can be determined by its electron density, making it a cornerstone of modern computational chemistry and materials science. In this PPT, we have explained the fundamentals of Density Functional Theory (DFT), its importance, and its application to the HŌééO molecule, along with key concepts like electron density, many-particle systems, the Born-Oppenheimer approximation, and the Hohenberg-Kohn theorem, highlighting its relevance in modern computational chemistry.lecture1-230501075743-146580ac computational chemistry .ppt



lecture1-230501075743-146580ac computational chemistry .pptDrSyedZulqarnainHaid
╠²
This document provides an overview of density functional theory (DFT) and its applications in computational chemistry and solid state physics. It begins with recommended books and websites on the topic. It then outlines the theoretical framework of DFT, including the Hohenberg-Kohn and Kohn-Sham theorems which simplify the many-body Schrodinger equation. The document discusses practical considerations for implementing DFT calculations including input/output files, pseudopotentials, and exchange-correlation functionals. It also introduces concepts from solid state physics like reciprocal space, band structure calculations, and plane wave basis sets which are important for DFT simulations of bulk materials and surfaces.lecture1.ppt



lecture1.pptAvneeshKumar164042
╠²
Ahhh baby jaan good morning sweet dreams my dear wife my love you too my jaan ho tum dimag me kuch kuch bhi nhi kiya h na to bol dena discharge ho gaya hai na aaj kal kya kr rhi hu me
lecture1-230501075743-142343456580ac.ppt



lecture1-230501075743-142343456580ac.pptzulqarnain199841
╠²
density fucntional theory
Hohen kohn sham equationsQuantum Chemistry



Quantum Chemistrybaoilleach
╠²
This document provides an overview of quantum mechanics (QM) calculation methods. It discusses molecular mechanics, wavefunction methods, electron density methods, including correlation, Hartree-Fock theory, semi-empirical methods, density functional theory, and their relative speed and accuracy. Key aspects that can be calculated using these methods are also listed, such as molecular orbitals, electron density, geometry, energies, spectroscopic properties, and more. Basis sets and handling open-shell systems in calculations are also covered.Hartree method ppt physical chemistry



Hartree method ppt physical chemistryalikhan1414
╠²
easy slides to understand the hartree method in basic physical chemistry of BS_6th semester in Pakistani universities. ap-physics-b-review-modern-physics



ap-physics-b-review-modern-physicscjsmann
╠²
1. The document provides an overview and review of topics covered on the AP Physics B exam related to modern physics, including the photoelectric effect, Bohr model of the atom, and nuclear physics.
2. It describes Einstein's explanation of the photoelectric effect involving photons and how it resolved issues not explained by classical wave theory.
3. It also explains the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, including Bohr's assumptions and how it leads to quantized electron orbits that can explain atomic emission spectra.Interaction of small molecules with grapheen supported on metal substrates: A...



Interaction of small molecules with grapheen supported on metal substrates: A...MIHIR RANJAN SAHOO
╠²
here we study how band structure changes in graphene on Ni(111) substrate and also binding energy of water on graphene/metal interface.Single Particle Appoximation Final Pres.pptx



Single Particle Appoximation Final Pres.pptxkhalilpcsir
╠²
Many Body Problems topic About Perturbation Theory Single Particle Aproximation, it Defination Working , advantgaes Limittation Future aspects , Mathemtical Formulas about Many Body Problems topic About Perturbation Theory Single Particle Aproximation, Detail of Similicity in Quantam phyisics Methods Interaction of small molecules with grapheen supported on metal substrates: A...



Interaction of small molecules with grapheen supported on metal substrates: A...MIHIR RANJAN SAHOO
╠²
Density Functional Theory
- 1. Density Functional Theory 1998 Nobel Chemistry Walter Kohn + John A. Pople Presenter: Wei-Ting Chen
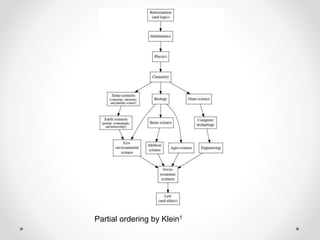
- 2. Partial ordering by Klein1
- 3. History ŌĆó Atomic chemistry 1800s ŌĆó Rutherford-Bohr model for quantum physical interpretation with electron shells. ŌĆó Molecular orbital theory in 1933 ŌĆó Early 1950ŌĆÖs computer development fueled computational QM
- 4. Motivation ŌĆó Electron is the main factor for a lot of the properties of matter ŌĆó Nanoscience, our device are scaling down ŌĆó DFT application saves experimental probing ŌĆó DFT was used in solid state physics since 1970s, but has great potentials if applicable for chemistry ŌĆó Exact wave function solution is unsolvable for many electron systems
- 5. Mathematical Model ŌĆó SE: ─żŽł= [T+V+U]Žł= EŽł ŌĆó T=e kinetic Energy ŌĆó V=e-N attraction ŌĆó Electron-electron interaction (U) prevents separation into single particle wave function for exact solution ŌĆó (HK)DFT: E=├Ŗ[Žü(ŌåÆv)] ŌĆó ├Ŗ is a single unique functional, but probably extremely complex ŌĆó Approximated functionals
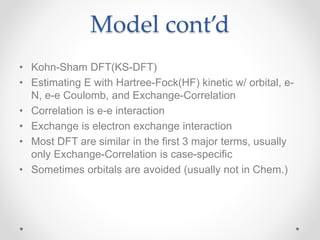
- 6. Model contŌĆÖd ŌĆó Kohn-Sham DFT(KS-DFT) ŌĆó Estimating E with Hartree-Fock(HF) kinetic w/ orbital, e- N, e-e Coulomb, and Exchange-Correlation ŌĆó Correlation is e-e interaction ŌĆó Exchange is electron exchange interaction ŌĆó Most DFT are similar in the first 3 major terms, usually only Exchange-Correlation is case-specific ŌĆó Sometimes orbitals are avoided (usually not in Chem.)
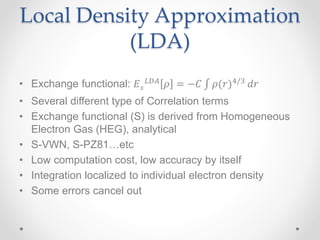
- 7. Local Density Approximation (LDA) ŌĆó Exchange functional: ØÉĖ Øæź ØÉ┐ØÉĘØÉ┤ Ø£ī = ŌłÆØÉČ Ø£ī(Øæ¤)4/3 ØææØæ¤ ŌĆó Several different type of Correlation terms ŌĆó Exchange functional (S) is derived from Homogeneous Electron Gas (HEG), analytical ŌĆó S-VWN, S-PZ81ŌĆ”etc ŌĆó Low computation cost, low accuracy by itself ŌĆó Integration localized to individual electron density ŌĆó Some errors cancel out
- 8. Graphite imaging with Imaging PS vs LDA. by Heske et al3
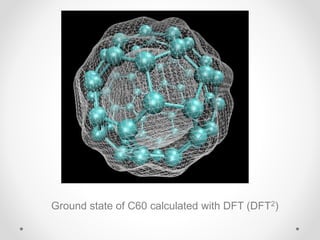
- 9. Ground state of C60 calculated with DFT (DFT2)
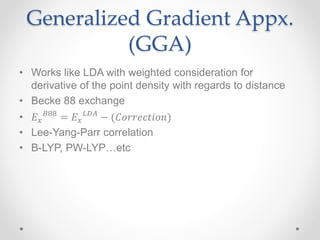
- 10. Generalized Gradient Appx. (GGA) ŌĆó Works like LDA with weighted consideration for derivative of the point density with regards to distance ŌĆó Becke 88 exchange ŌĆó ØÉĖ Øæź ØÉĄ88 = ØÉĖ Øæź ØÉ┐ØÉĘØÉ┤ ŌłÆ (ØÉČØæ£Øæ¤Øæ¤ØæÆØæÉØæĪØæ¢Øæ£Øæø) ŌĆó Lee-Yang-Parr correlation ŌĆó B-LYP, PW-LYPŌĆ”etc
- 11. Comparison ŌĆó DFT doesnŌĆÖt have hierarchy since it is not variational ŌĆó DFT also doesnŌĆÖt have single convergence ŌĆó HF and Coupled Cluster Theory are single convergence ŌĆó Coupled Cluster works by perturbation, can always go to higher accuracy ŌĆó Vanilla DFT=n^3, HF=n^4, CC=n^7
- 12. Limitations ŌĆó DFT not very accurate for dynamics due to activation energy being a bit off (a few kcal/mol) ŌĆó Modification to KS-DFT can be made to accommodate for far out electrons using ad hoc diffuse integrals and asymptotic correction. ŌĆó Often have to be used with other methods (usually no longer ab initio)
- 13. Current DFT ŌĆó Since KS-DFT is partially HF dependent most HF programs adopted DFT add-ons (i.e. Gaussian) ŌĆó Figuring out optical properties of Chromophores ŌĆó Structure-property relationships ŌĆó Design to property parameters
- 14. Sources 1. ŌĆØIs chemistry ŌĆśThe Central ScienceŌĆÖ? How are different sciences related? Co- citations, reductionism, emergence, and posetsŌĆØ Alexandru T. Balaban, Douglas J. Klein Scientometrics 2006, 69, 615-637. 2. Density Functional Theory. (2015, September 22). Retrieved October 18, 2015, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Density_functional_theory 3. Heske, C., Treusch, R., Himpsel, F., Kakar, S., Terminello, L., Weyer, H., & Shirley, E. (1999). Band widening in graphite. Phys. Rev. B Physical Review B, 4680-4684.




