Hba1 c
- 2. Be serious Doctor 1. I am making India the capital of the world shortly ! 2. Already I have a bigŌĆ” family of 200 millions on the globe. 3. I am happily troubling 12% urban and 8.2% of rural Indians. 4. In my name I am sweet but my effects are very hot ! 5. I am not easily controlled (< 45%)
- 3. Dr.E.P.Joslin ŌĆ£The greatest burden on doctors will be not the management of diabetes, but the associated macro and micro- vascular complications of it.ŌĆØ ..1926 ŌĆ£The goal of therapy in diabetes should be to make serious efforts to keep the blood sugar levels as close normal as possible.ŌĆØ ŌĆ”.. 1929
- 4. HbA1c: the blood test with a memory What is HbA1c? Hemoglobin is a protein that makes your red blood cells red-colored. When hemoglobin picks up glucose from your bloodstream, the hemoglobin becomes glycosylated. Glycosylated hemoglobin is HbA1c. The HbA1c test measures the percentage of HbA1c in your bloodŌĆö a number that corresponds to your average blood glucose for the previous 3 months. HbA1c in your bloodstream.
- 5. Different types of Glycation products are formed from the HbA0depending on the carbohydrate moiety ŌĆō namely ’ā║ HbA1a1 - Fr 1,6 diphos ŌĆōN-term. valine ’ā║ HbA1a2 - Gl 6 phos ŌĆōN-terminal valine ’ā║ HbA1b - Other CHO ŌĆō N-term. valine ’ā║ HbA1c - Glucose ŌĆōN-terminal valine Normally less than 6% of Hb is HbA1c Glycated Hb - GHb (Previously called glycosylated Hb.)
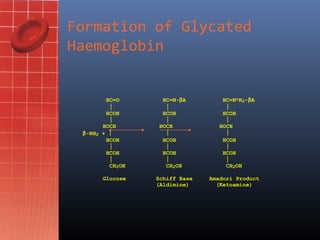
- 7. Formation of Glycated Haemoglobin HC=O HC=N-╬▓A HC=N+H2-╬▓A ’Ż” ’Ż” ’Ż” HCOH HCOH HCOH ’Ż” ’Ż” ’Ż” HOCH HOCH HOCH ╬▓-NH2 + ’Ż” ’Ż” ’Ż” HCOH HCOH HCOH ’Ż” ’Ż” ’Ż” HCOH HCOH HCOH ’Ż” ’Ż” ’Ż” CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH Glucose Schiff Base Amadori Product (Aldimine) (Ketoamine)
- 8. HbA1c: Historical Aspects 1962: Huisman and Dozy Increases in minor fractions of haemoglobin in four diabetic patients treated with tolbutamide. 1968: Rahbar ŌĆśDiabetic haemoglobin componentŌĆÖ found in 49 Iranian diabetic patients. 1968: Rahbar Component the same structure as the previously described HbA1c
- 9. HbA1c: Historical Aspects HbA1c correlated with: ’é¦ Plasma ŌĆśglucose bracketsŌĆÖ Koenig RJ et al. N Engl J Med 1976; 295: 417-420 ’é¦ Daily mean plasma glucose Gonen B et al. Lancet 1977; ii; 734-737 ’é¦ 24 hour urinary glucose excretions Gabbay KH et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1977; 44: 859-864 ’é¦ Glucose control over past 6-8 weeks Goldstein D et al. Clin Chem 1986; 32(Suppl): B64-70
- 11. Reference values of HbA1c 1. Less than 6% - Normal 2. 6 to 7% - Good control of DM 3. 7 to 9% - Unsatisfactory control 4. More than 9% - Very poor control Values depend on the method of estimation They vary from lab to lab.
- 12. Estimation of HbA1c ’é¦ There are many methods of estimation ’é¦ HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) ŌĆō Gold standard. ’é¦ Immuno-turbimetric meth. ŌĆō HbA1cAb ’é¦ Affinity chromatography ’é¦ Electrophoretic methods ’é¦ Method based on chemical reactions.
- 13. Lowering Hb A1c reduces risk of complications How well it measures ?
- 14. Dr.Sarma@works
- 15. UKPDS: Risk of Macro and Microvascular Complications UKPDS Group. BMJ 2000;321:405-412
- 16. DCCT: Risk of Microvascular Complications DCCT Group. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329: 977-86
- 17. Correlation of MPG - HbA1c Mean Plasma Glucose = (33.3 x HbA1C%) - 86 (Nathan et. al. NEJM, vol. 310, No 6, Feb 9, 1994) HbA1C % 5 7 9 11 Mean BG mg % 80.5 147.1 213.7 280.3
- 18. Dr.Sarma@works
- 19. Dr.Sarma@works
- 20. Advantages of HbA1c ŌĆó Index of long-term control over 120 days and not a snap shot like PG ŌĆó Can be done at any time of day ŌĆó Not influenced by diet, exercise, emotional disturbances on test day ŌĆó Useful index in clinical trials ŌĆó Useful if missed drugs / default diet ŌĆó Useful in DD of stress hyperglycemia
- 21. Limitations of HbA1c ŌĆó Cannot be an emergency room test to titrate Insulin or OHA dosage ŌĆó Cannot register hypoglycemia ŌĆó More sensitive to sin than repentance ŌĆō if it is elevated it confirms poor control, if it is boarder line, it cannot assure good control in the recent past. ŌĆó Not sensitive enough for use in GDM ŌłĆŌåō Anaemia, Uraemia, Pregnancy