1 of 33
Download to read offline
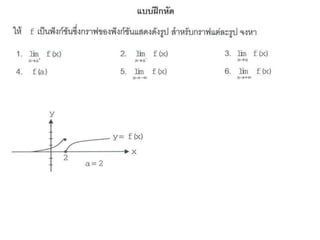
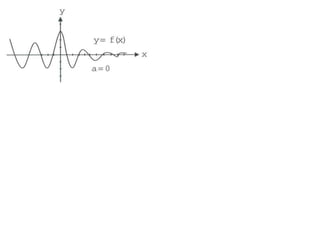
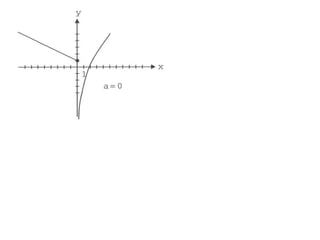
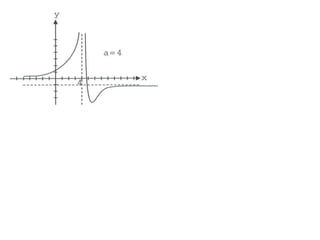






















Ad
Recommended
การเคลื่อนที่แบบหมุน
การเคลื่อนที่แบบหมุนthanakit553
��
1. The document discusses circular motion and kinematic equations relating displacement, velocity, acceleration, and other variables. It defines relationships between angular displacement, angular velocity, linear velocity, tangential acceleration, and angular acceleration.
2. Equations are provided relating angular displacement to angular velocity and time, linear velocity to angular velocity and radius, and tangential acceleration to angular acceleration and radius.
3. The kinematic relationships for circular motion allow one to calculate variables like velocity, acceleration, and displacement given information about rotation, radius, and time.งา�Ȩ��ละพลังงาน
งา�Ȩ��ละพลังงานthanakit553
��
1) The document discusses work (W) in physics and defines it as the product of an applied force (F) and the distance (s) over which it acts (W=Fs).
2) Several examples are provided to demonstrate calculating work done by various constant and non-constant forces.
3) The concept of net work is introduced as the sum of individual works done by each force acting on an object.More Related Content
Viewers also liked (20)
การเคลื่อนที่แบบหมุน
การเคลื่อนที่แบบหมุนthanakit553
��
1. The document discusses circular motion and kinematic equations relating displacement, velocity, acceleration, and other variables. It defines relationships between angular displacement, angular velocity, linear velocity, tangential acceleration, and angular acceleration.
2. Equations are provided relating angular displacement to angular velocity and time, linear velocity to angular velocity and radius, and tangential acceleration to angular acceleration and radius.
3. The kinematic relationships for circular motion allow one to calculate variables like velocity, acceleration, and displacement given information about rotation, radius, and time.งา�Ȩ��ละพลังงาน
งา�Ȩ��ละพลังงานthanakit553
��
1) The document discusses work (W) in physics and defines it as the product of an applied force (F) and the distance (s) over which it acts (W=Fs).
2) Several examples are provided to demonstrate calculating work done by various constant and non-constant forces.
3) The concept of net work is introduced as the sum of individual works done by each force acting on an object.More from เซิฟ กิ๊ฟ ติวเตอร์ (20)
4.1โปรเจกไทล์
4.1โปรเจกไทล์เซิฟ กิ๊ฟ ติวเตอร์
��
พี่เซิฟ เกียรตินิยมปิโตรเคมี ปริญญาโทฟิสิกส์ ม.ศิลปากร
เซิฟ กิ๊ฟ ติวเตอร์ นครปฐม 0874073625Ad
