1 of 79
Download to read offline
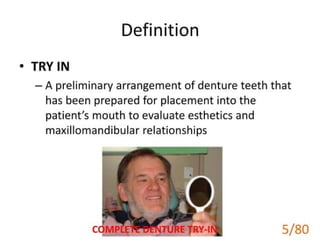
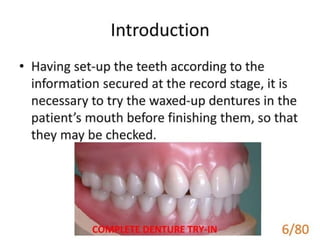


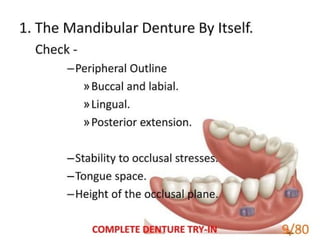
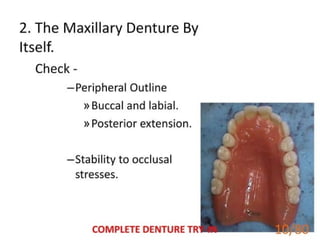










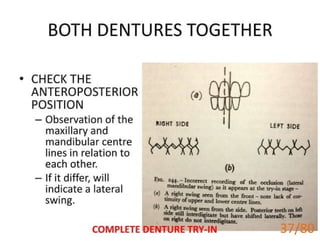












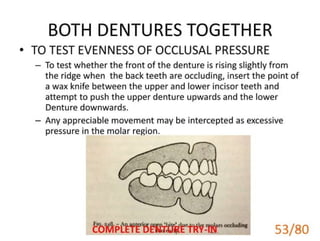

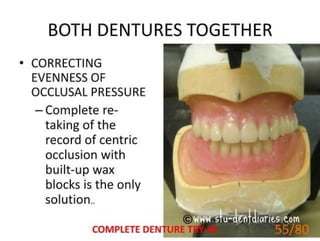



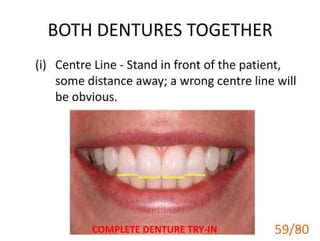



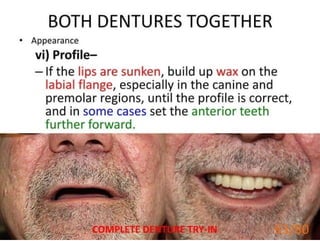











Ad
Recommended
INDIRECT RETAINERS (1).ppthgkj,jxgc.hi/;kl
INDIRECT RETAINERS (1).ppthgkj,jxgc.hi/;klmanjulikatyagi
╠²
The document presents an overview of removable partial dentures, detailing their components, classifications, and the role of indirect retainers in preventing displacement of distal extension bases. It emphasizes the significance of proper placement and design of indirect retainers for effective function regarding fulcrum lines and the mechanics of retention. The conclusion suggests that while some areas provide auxiliary support, nothing is more effective than proper tooth support for these dental prosthetics.lect dental-polymers.pptghm,./fghjkdnmkjhhjhj
lect dental-polymers.pptghm,./fghjkdnmkjhhjhjmanjulikatyagi
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of dental polymers, including their classifications, types of resins used in dentistry, and various applications such as denture bases and cavity filling materials. It details the polymerization process, including initiation, propagation, and termination stages, and elaborates on the physical properties and behavior of these materials under different conditions. Key types of polymers discussed include thermoplastics, thermosets, and various copolymers, with emphasis on their compositional and structural characteristics.allceramiccrownpreparationseminar-150409204437-conversion-gate01-converted.pptx
allceramiccrownpreparationseminar-150409204437-conversion-gate01-converted.pptxmanjulikatyagi
╠²
This document discusses all ceramic crown preparation, outlining its definition, advantages, and disadvantages. It details indications, contraindications, and specific preparation techniques needed for optimal esthetics and strength, including necessary tooth reductions and precautions to avoid fractures. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of preparation finishing to ensure the durability of the ceramic restoration.rpd ppt.pptxdfghjkl;;tyuioghjnmvbnmbnmnm
rpd ppt.pptxdfghjkl;;tyuioghjnmvbnmbnmnmmanjulikatyagi
╠²
The document outlines the classification and definitions of removable partial dentures (RPD) within the field of prosthodontics, emphasizing their role in restoring oral function and aesthetics. It details various types of RPDs, indications for their use, and established classification systems such as Kennedy's and Applegate's, which help dentists communicate design needs effectively. Additionally, it describes criteria and classifications for assessing partial and complete edentulism based on diagnostic findings.denture base resin 3.pptxfghjklhgsdfghfj
denture base resin 3.pptxfghjklhgsdfghfjmanjulikatyagi
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive history of denture base materials used in dentistry, tracing their evolution from ancient times to contemporary practices. It discusses various materials such as wood, bone, ivory, porcelain, vulcanite, and acrylic, explaining their advantages and disadvantages in relation to functionality and aesthetics. Additionally, it details significant developments in dental materials and polymerization processes, culminating in the widespread use of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) in modern dentures.common oral diseases of gingiva.pptx fcg
common oral diseases of gingiva.pptx fcgmanjulikatyagi
╠²
The document discusses various common oral diseases affecting the gingiva, including gingivitis, periodontitis, and gingival enlargement caused by factors such as pregnancy, medications, and hereditary conditions. It highlights specific conditions like inflammatory gingival enlargement and leukemia-induced gingival enlargement. Additionally, it addresses florid pregnancy gingivitis as a notable related condition.KERATOCYSTIC ODONTOGENIC TUMOR.ppt uploaded
KERATOCYSTIC ODONTOGENIC TUMOR.ppt uploadedmanjulikatyagi
╠²
Mrs. Chandrakala, a 35-year-old housewife, presents with pain and swelling in the right mid face, which has progressively worsened over the last three days after prior episodes. Examination and imaging suggest an impacted tooth associated with an infected keratocystic odontogenic tumor, requiring enucleation and treatment of the affected area. The diagnosis indicates a good prognosis with appropriate treatment and follow-up.diagnosis of bleeding and clotting disorders.pptx
diagnosis of bleeding and clotting disorders.pptxmanjulikatyagi
╠²
El documento aborda los trastornos hemorr├Īgicos y de coagulaci├│n, describiendo sus mecanismos normales y las clases de anomal├Łas que pueden causar un aumento en la tendencia a sangrar. Se enfatiza la importancia del diagn├│stico preciso y reconocimiento temprano de estos trastornos, junto con las consideraciones de manejo para los pacientes dentales. Incluye un resumen de pruebas diagn├│sticas clave y diferencias cl├Łnicas entre los tipos de trastornos hemorr├Īgicos.MAXILLOFACIAL MATERIALS.ppt on dental materials
MAXILLOFACIAL MATERIALS.ppt on dental materialsmanjulikatyagi
╠²
This document provides an overview of maxillofacial prosthetic materials. It begins with definitions of key terms and discusses the history of maxillofacial prosthetics from ancient times to recent developments. Common materials used for extraoral maxillofacial prostheses are then reviewed, including their ideal properties, types, advantages, and limitations. Key materials discussed are acrylic resin, vinyl polymers, polyurethane elastomers, and silicone elastomers. Considerations for material selection and limitations of current materials are also presented.full mouth rehabilitation ppt including all
full mouth rehabilitation ppt including allmanjulikatyagi
╠²
The document discusses concepts and philosophies related to full mouth rehabilitation. It defines full mouth rehabilitation as restoring the form and function of the masticatory apparatus as close to normal as possible. Occlusion plays a key role in establishing synchronous harmony between teeth, TMJ, and muscles of mastication. The selection of the proper occlusal scheme is important for prosthetic rehabilitation. Various philosophies and concepts are discussed, including gnathological concept, mutually protected occlusion, group function, balanced occlusion, Pankey-Mann-Schuyler philosophy, and Hobo's twin table technique. Cusp shape factors, amount of disocclusion, and influences on disocclusion are also covered.zirconia in dentistry adv and disadvantages
zirconia in dentistry adv and disadvantagesmanjulikatyagi
╠²
This document provides an overview of zirconia and its use in dentistry. It begins with the history of ceramics and introduces zirconia as a modern ceramic material. Key points about zirconia include its high strength, fracture toughness and biocompatibility. The document discusses the various crystal phases of zirconia and why it is preferred over other materials. Applications of zirconia in dentistry are summarized, including crowns, bridges, implants, orthodontic brackets and more. The integration of zirconia with digital technologies like CAD/CAM is also mentioned.lect dental-polymers.ppt including heat and cold
lect dental-polymers.ppt including heat and coldmanjulikatyagi
╠²
This document summarizes key information about dental polymers, including the types of resins used in dentistry, how they are classified, and the polymerization process. It discusses the main categories of polymers as thermoplastic and thermoset, and how polymerization occurs through addition and condensation reactions. The stages of polymerization - initiation, propagation and termination - are outlined. Factors that can inhibit polymerization and the physical properties of polymers related to deformation, rheology, solvation and thermal behavior are also summarized.TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT DISORDERS AND ITS PROSTHETIC MANAGEMENT (2) [Repaired...
TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT DISORDERS AND ITS PROSTHETIC MANAGEMENT (2) [Repaired...manjulikatyagi
╠²
Temporomandibular disorders (TMD) are the most common non tooth-related chronic orofacial pain conditions. Diagnosis requires a multidisciplinary approach due to the complex nature of each case. TMDs can be classified into masticatory muscle disorders, temporomandibular joint disorders, chronic mandibular hypomobility, and growth disorders. Common causes include trauma, inflammation, systemic diseases, and prolonged immobilization. Management involves both conservative and definitive treatment depending on the specific disorder.Mechanical_properties_of_dental_material.pptx
Mechanical_properties_of_dental_material.pptxmanjulikatyagi
╠²
This document discusses various mechanical properties that are important for evaluating dental materials, including their ability to withstand forces in the oral cavity. It defines key terms like stress, strain, elastic limit, yield strength, toughness, ductility and describes how these properties are measured. Properties like elastic modulus, resilience and strength values are important for determining a material's stiffness, ability to absorb forces without permanent deformation, and maximum stress before failure. Understanding these mechanical behaviors can help select appropriate materials for different dental applications and restorations.PRINCIPLES OF TOOTH PREPARATION ppt given
PRINCIPLES OF TOOTH PREPARATION ppt givenmanjulikatyagi
╠²
The document discusses principles of tooth preparation for fixed partial dentures. It covers objectives like reducing tooth structure for retention while preserving healthy tooth structure. Principles include conservative preparation with minimal taper and preservation of tooth structure. Margin placement should be supragingival when possible. Margin designs like chamfer and shoulder are described. Tooth preparation creates retention and resistance for fixed restorations.DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING OF EDENTULOUS PATIENTS (2).ppt
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING OF EDENTULOUS PATIENTS (2).pptmanjulikatyagi
╠²
This document discusses the diagnosis and treatment planning process for edentulous patients requiring complete dentures. It emphasizes the importance of a thorough patient assessment involving medical history, clinical examinations, diagnostic procedures and observations. The goal is to understand the patient's physical and psychological condition to determine a treatment plan that meets their expectations. A proper diagnosis recognizes any issues, formulates an appropriate plan, carries out necessary examinations and interprets the results. This process requires developing trust with the patient and familiarizing oneself with their overall oral condition to achieve successful complete denture therapy.Biomechanics of Ed state.pptx
Biomechanics of Ed state.pptxmanjulikatyagi
╠²
This document discusses the biomechanics of edentulism and complete denture support. Key points include:
- Loss of teeth results in loss of periodontal ligament support and alterations to the mechanisms of force transmission during functions like chewing.
- Complete dentures rely on mucosal support over a much smaller area compared to periodontal ligaments. They are also subject to residual ridge resorption over time.
- Chewing forces are significantly lower with complete dentures versus natural dentition. Movement patterns during functions like chewing are similar but dentures cannot substitute fully for natural teeth.biomaterials in dental implants.ppt
biomaterials in dental implants.pptmanjulikatyagi
╠²
This document discusses biomaterials used in dental implants. It begins by introducing various biomaterial options for implants, including metals, ceramics, polymers, and natural materials. It then discusses the history of biomaterial development, starting with ancient attempts to replace teeth and progressing to modern materials like titanium. The document also covers important properties to consider when selecting and evaluating biomaterials, such as mechanical strength, biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and how materials can be modified.dentalceramicsppt-.pptx
dentalceramicsppt-.pptxmanjulikatyagi
╠²
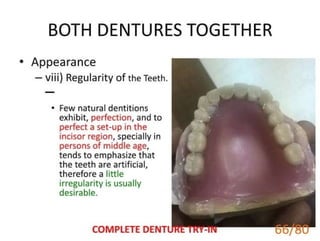
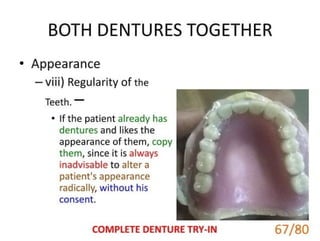
This document discusses dental ceramics. It defines ceramics as inorganic, non-metallic materials that are crystalline in nature and formed from compounds of metallic and nonmetallic elements. Dental ceramics are characterized by properties like biocompatibility, esthetic potential, hardness, and chemical inertness. They can be crystalline or amorphous and are classified based on factors like firing temperature, processing method, and microstructure. Common types used in dentistry include feldspathic porcelain, aluminous porcelain, and glass ceramics. Dental ceramics have various applications and are indicated for uses like crowns, veneers, and fixed dental prostheses depending on their composition and properties.ceramics.ppt
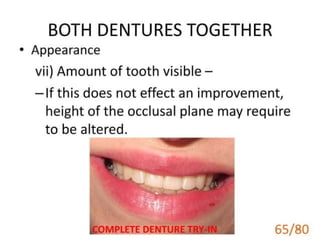
ceramics.pptmanjulikatyagi
╠²
Ceramics are inorganic, non-metallic materials formed from chemical and biochemical stable substances. Dental ceramics contain a glassy matrix reinforced by crystalline structures such as leucite, alumina, and silica. Dental porcelains are composed of feldspar, silica, and kaolin, which are blended and fired to form the ceramic. Metal-ceramic restorations consist of a metal coping covered with opaque, dentin, and enamel porcelain layers that are bonded to the metal through mechanical interlocking and chemical bonding between metal oxide layers and the ceramic.Soldering and welding.pptx
Soldering and welding.pptxmanjulikatyagi
╠²
Soldering and welding are processes to join metal components. Soldering involves melting a filler metal below the melting points of the components being joined. Welding directly melts the components together without a filler. Common types of soldering include soft, hard, and brazing based on the filler metal temperature. Welding techniques include spot welding, laser welding, and tungsten inert gas welding. Key factors for a strong joint include clean surfaces, proper temperature, timing, and gap width between components. Defects like porosity or distortion can weaken the joint if processes are not followed correctly.elastic impression materials.ppt
elastic impression materials.pptmanjulikatyagi
╠²
1. The document discusses different types of elastic impression materials used in dentistry including their history, properties, and recent advances.
2. The main elastic impression materials discussed are elastomers/rubber base materials like polysulfides, condensation silicones, addition silicones, and polyethers.
3. Recent advances include visible light cured impression materials which offer controlled working times and excellent properties but require special trays and can be difficult to cure in all areas.Diet and Nutrition.ppt
Diet and Nutrition.pptmanjulikatyagi
╠²
This document discusses diet and nutrition as they relate to oral health and prosthodontic treatment. It defines key terms like diet, nutrition, and balanced diet. It describes the major nutrients - carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, vitamins, minerals, and water. It discusses dietary requirements and recommendations for different age groups, especially the elderly. It emphasizes the importance of adequate protein, vitamin, mineral and calcium intake for dental patients, especially those undergoing prosthodontic treatment. It provides dietary guidelines for new denture wearers.Flashcards Animais brasileiros Ilustrado Verde.pdf
Flashcards Animais brasileiros Ilustrado Verde.pdfPriscilaRibeiro803210
╠²
Jogo com animais brasileirosGazetteer of Russia. Part: Populated places A-F.pdf
Gazetteer of Russia. Part: Populated places A-F.pdfpeivhau
╠²
Detailed gazetteer of cities, towns and villages of Russia. Census results. Name changes. Incorporations. Latitudes and longitudes. More Related Content
More from manjulikatyagi (20)
rpd ppt.pptxdfghjkl;;tyuioghjnmvbnmbnmnm
rpd ppt.pptxdfghjkl;;tyuioghjnmvbnmbnmnmmanjulikatyagi
╠²
The document outlines the classification and definitions of removable partial dentures (RPD) within the field of prosthodontics, emphasizing their role in restoring oral function and aesthetics. It details various types of RPDs, indications for their use, and established classification systems such as Kennedy's and Applegate's, which help dentists communicate design needs effectively. Additionally, it describes criteria and classifications for assessing partial and complete edentulism based on diagnostic findings.denture base resin 3.pptxfghjklhgsdfghfj
denture base resin 3.pptxfghjklhgsdfghfjmanjulikatyagi
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive history of denture base materials used in dentistry, tracing their evolution from ancient times to contemporary practices. It discusses various materials such as wood, bone, ivory, porcelain, vulcanite, and acrylic, explaining their advantages and disadvantages in relation to functionality and aesthetics. Additionally, it details significant developments in dental materials and polymerization processes, culminating in the widespread use of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) in modern dentures.common oral diseases of gingiva.pptx fcg
common oral diseases of gingiva.pptx fcgmanjulikatyagi
╠²
The document discusses various common oral diseases affecting the gingiva, including gingivitis, periodontitis, and gingival enlargement caused by factors such as pregnancy, medications, and hereditary conditions. It highlights specific conditions like inflammatory gingival enlargement and leukemia-induced gingival enlargement. Additionally, it addresses florid pregnancy gingivitis as a notable related condition.KERATOCYSTIC ODONTOGENIC TUMOR.ppt uploaded
KERATOCYSTIC ODONTOGENIC TUMOR.ppt uploadedmanjulikatyagi
╠²
Mrs. Chandrakala, a 35-year-old housewife, presents with pain and swelling in the right mid face, which has progressively worsened over the last three days after prior episodes. Examination and imaging suggest an impacted tooth associated with an infected keratocystic odontogenic tumor, requiring enucleation and treatment of the affected area. The diagnosis indicates a good prognosis with appropriate treatment and follow-up.diagnosis of bleeding and clotting disorders.pptx
diagnosis of bleeding and clotting disorders.pptxmanjulikatyagi
╠²
El documento aborda los trastornos hemorr├Īgicos y de coagulaci├│n, describiendo sus mecanismos normales y las clases de anomal├Łas que pueden causar un aumento en la tendencia a sangrar. Se enfatiza la importancia del diagn├│stico preciso y reconocimiento temprano de estos trastornos, junto con las consideraciones de manejo para los pacientes dentales. Incluye un resumen de pruebas diagn├│sticas clave y diferencias cl├Łnicas entre los tipos de trastornos hemorr├Īgicos.MAXILLOFACIAL MATERIALS.ppt on dental materials
MAXILLOFACIAL MATERIALS.ppt on dental materialsmanjulikatyagi
╠²
This document provides an overview of maxillofacial prosthetic materials. It begins with definitions of key terms and discusses the history of maxillofacial prosthetics from ancient times to recent developments. Common materials used for extraoral maxillofacial prostheses are then reviewed, including their ideal properties, types, advantages, and limitations. Key materials discussed are acrylic resin, vinyl polymers, polyurethane elastomers, and silicone elastomers. Considerations for material selection and limitations of current materials are also presented.full mouth rehabilitation ppt including all
full mouth rehabilitation ppt including allmanjulikatyagi
╠²
The document discusses concepts and philosophies related to full mouth rehabilitation. It defines full mouth rehabilitation as restoring the form and function of the masticatory apparatus as close to normal as possible. Occlusion plays a key role in establishing synchronous harmony between teeth, TMJ, and muscles of mastication. The selection of the proper occlusal scheme is important for prosthetic rehabilitation. Various philosophies and concepts are discussed, including gnathological concept, mutually protected occlusion, group function, balanced occlusion, Pankey-Mann-Schuyler philosophy, and Hobo's twin table technique. Cusp shape factors, amount of disocclusion, and influences on disocclusion are also covered.zirconia in dentistry adv and disadvantages
zirconia in dentistry adv and disadvantagesmanjulikatyagi
╠²
This document provides an overview of zirconia and its use in dentistry. It begins with the history of ceramics and introduces zirconia as a modern ceramic material. Key points about zirconia include its high strength, fracture toughness and biocompatibility. The document discusses the various crystal phases of zirconia and why it is preferred over other materials. Applications of zirconia in dentistry are summarized, including crowns, bridges, implants, orthodontic brackets and more. The integration of zirconia with digital technologies like CAD/CAM is also mentioned.lect dental-polymers.ppt including heat and cold
lect dental-polymers.ppt including heat and coldmanjulikatyagi
╠²
This document summarizes key information about dental polymers, including the types of resins used in dentistry, how they are classified, and the polymerization process. It discusses the main categories of polymers as thermoplastic and thermoset, and how polymerization occurs through addition and condensation reactions. The stages of polymerization - initiation, propagation and termination - are outlined. Factors that can inhibit polymerization and the physical properties of polymers related to deformation, rheology, solvation and thermal behavior are also summarized.TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT DISORDERS AND ITS PROSTHETIC MANAGEMENT (2) [Repaired...
TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT DISORDERS AND ITS PROSTHETIC MANAGEMENT (2) [Repaired...manjulikatyagi
╠²
Temporomandibular disorders (TMD) are the most common non tooth-related chronic orofacial pain conditions. Diagnosis requires a multidisciplinary approach due to the complex nature of each case. TMDs can be classified into masticatory muscle disorders, temporomandibular joint disorders, chronic mandibular hypomobility, and growth disorders. Common causes include trauma, inflammation, systemic diseases, and prolonged immobilization. Management involves both conservative and definitive treatment depending on the specific disorder.Mechanical_properties_of_dental_material.pptx
Mechanical_properties_of_dental_material.pptxmanjulikatyagi
╠²
This document discusses various mechanical properties that are important for evaluating dental materials, including their ability to withstand forces in the oral cavity. It defines key terms like stress, strain, elastic limit, yield strength, toughness, ductility and describes how these properties are measured. Properties like elastic modulus, resilience and strength values are important for determining a material's stiffness, ability to absorb forces without permanent deformation, and maximum stress before failure. Understanding these mechanical behaviors can help select appropriate materials for different dental applications and restorations.PRINCIPLES OF TOOTH PREPARATION ppt given
PRINCIPLES OF TOOTH PREPARATION ppt givenmanjulikatyagi
╠²
The document discusses principles of tooth preparation for fixed partial dentures. It covers objectives like reducing tooth structure for retention while preserving healthy tooth structure. Principles include conservative preparation with minimal taper and preservation of tooth structure. Margin placement should be supragingival when possible. Margin designs like chamfer and shoulder are described. Tooth preparation creates retention and resistance for fixed restorations.DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING OF EDENTULOUS PATIENTS (2).ppt
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING OF EDENTULOUS PATIENTS (2).pptmanjulikatyagi
╠²
This document discusses the diagnosis and treatment planning process for edentulous patients requiring complete dentures. It emphasizes the importance of a thorough patient assessment involving medical history, clinical examinations, diagnostic procedures and observations. The goal is to understand the patient's physical and psychological condition to determine a treatment plan that meets their expectations. A proper diagnosis recognizes any issues, formulates an appropriate plan, carries out necessary examinations and interprets the results. This process requires developing trust with the patient and familiarizing oneself with their overall oral condition to achieve successful complete denture therapy.Biomechanics of Ed state.pptx
Biomechanics of Ed state.pptxmanjulikatyagi
╠²
This document discusses the biomechanics of edentulism and complete denture support. Key points include:
- Loss of teeth results in loss of periodontal ligament support and alterations to the mechanisms of force transmission during functions like chewing.
- Complete dentures rely on mucosal support over a much smaller area compared to periodontal ligaments. They are also subject to residual ridge resorption over time.
- Chewing forces are significantly lower with complete dentures versus natural dentition. Movement patterns during functions like chewing are similar but dentures cannot substitute fully for natural teeth.biomaterials in dental implants.ppt
biomaterials in dental implants.pptmanjulikatyagi
╠²
This document discusses biomaterials used in dental implants. It begins by introducing various biomaterial options for implants, including metals, ceramics, polymers, and natural materials. It then discusses the history of biomaterial development, starting with ancient attempts to replace teeth and progressing to modern materials like titanium. The document also covers important properties to consider when selecting and evaluating biomaterials, such as mechanical strength, biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and how materials can be modified.dentalceramicsppt-.pptx
dentalceramicsppt-.pptxmanjulikatyagi
╠²
This document discusses dental ceramics. It defines ceramics as inorganic, non-metallic materials that are crystalline in nature and formed from compounds of metallic and nonmetallic elements. Dental ceramics are characterized by properties like biocompatibility, esthetic potential, hardness, and chemical inertness. They can be crystalline or amorphous and are classified based on factors like firing temperature, processing method, and microstructure. Common types used in dentistry include feldspathic porcelain, aluminous porcelain, and glass ceramics. Dental ceramics have various applications and are indicated for uses like crowns, veneers, and fixed dental prostheses depending on their composition and properties.ceramics.ppt
ceramics.pptmanjulikatyagi
╠²
Ceramics are inorganic, non-metallic materials formed from chemical and biochemical stable substances. Dental ceramics contain a glassy matrix reinforced by crystalline structures such as leucite, alumina, and silica. Dental porcelains are composed of feldspar, silica, and kaolin, which are blended and fired to form the ceramic. Metal-ceramic restorations consist of a metal coping covered with opaque, dentin, and enamel porcelain layers that are bonded to the metal through mechanical interlocking and chemical bonding between metal oxide layers and the ceramic.Soldering and welding.pptx
Soldering and welding.pptxmanjulikatyagi
╠²
Soldering and welding are processes to join metal components. Soldering involves melting a filler metal below the melting points of the components being joined. Welding directly melts the components together without a filler. Common types of soldering include soft, hard, and brazing based on the filler metal temperature. Welding techniques include spot welding, laser welding, and tungsten inert gas welding. Key factors for a strong joint include clean surfaces, proper temperature, timing, and gap width between components. Defects like porosity or distortion can weaken the joint if processes are not followed correctly.elastic impression materials.ppt
elastic impression materials.pptmanjulikatyagi
╠²
1. The document discusses different types of elastic impression materials used in dentistry including their history, properties, and recent advances.
2. The main elastic impression materials discussed are elastomers/rubber base materials like polysulfides, condensation silicones, addition silicones, and polyethers.
3. Recent advances include visible light cured impression materials which offer controlled working times and excellent properties but require special trays and can be difficult to cure in all areas.Diet and Nutrition.ppt
Diet and Nutrition.pptmanjulikatyagi
╠²
This document discusses diet and nutrition as they relate to oral health and prosthodontic treatment. It defines key terms like diet, nutrition, and balanced diet. It describes the major nutrients - carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, vitamins, minerals, and water. It discusses dietary requirements and recommendations for different age groups, especially the elderly. It emphasizes the importance of adequate protein, vitamin, mineral and calcium intake for dental patients, especially those undergoing prosthodontic treatment. It provides dietary guidelines for new denture wearers.Recently uploaded (10)
Flashcards Animais brasileiros Ilustrado Verde.pdf
Flashcards Animais brasileiros Ilustrado Verde.pdfPriscilaRibeiro803210
╠²
Jogo com animais brasileirosGazetteer of Russia. Part: Populated places A-F.pdf
Gazetteer of Russia. Part: Populated places A-F.pdfpeivhau
╠²
Detailed gazetteer of cities, towns and villages of Russia. Census results. Name changes. Incorporations. Latitudes and longitudes. cambios_emocionales en los traumas presentes en adolescentes
cambios_emocionales en los traumas presentes en adolescentesvivianyarenivallecil
╠²
cambios emocionalesAylanmadan olinadigan soliq.2025 yil.pdf
Aylanmadan olinadigan soliq.2025 yil.pdfilxomislomov2020
╠²
soliqlar. Aylanmadan olinadigan soliq.soliq 2025.Qarshi davlat texnika universiteti.soliq stavkalari 2025 y. O'zR soliq kodeksi.Prezentatsiya 2025. yąĮą░ą║ą░ąĘ ą┐čĆąŠ ąĘą░čĆą░čģčāą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅą┤ąŠ 1 ą║ą╗ą░čüčā kg72 2025
ąĮą░ą║ą░ąĘ ą┐čĆąŠ ąĘą░čĆą░čģčāą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅą┤ąŠ 1 ą║ą╗ą░čüčā kg72 2025AleksSaf
╠²
ąĮą░ą║ą░ąĘ ą┐čĆąŠ ąĘą░čĆą░čģčāą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅą┤ąŠ 1 ą║ą╗ą░čüčā 2025Gazetteer of Russia. Part: Populated places G-Krasno.pdf
Gazetteer of Russia. Part: Populated places G-Krasno.pdfpeivhau
╠²
Detailed gazetteer of cities, towns and villages of Russia. Census results. Name changes. Incorporations. Latitudes and longitudes.pdf-p-classtruncatedtext-module-lineclamped-85ulhh-style-max-lines5topik-tema...
pdf-p-classtruncatedtext-module-lineclamped-85ulhh-style-max-lines5topik-tema...Ifa Nofalia
╠²
bjbij jknkj knlk ml ko k lk lkmk k kmpom kmp kl pk km op lk ok p m k k ,l pom l pmfpoasfmasmfp om k kmp kla fpmpaf pkokmp pmppmpa fkmpo l pmo l pamfomaf afpomopafa pompo kmapofma poAd