Business Simulation "Global Management Challenge"
Download as pptx, pdf1 like653 views
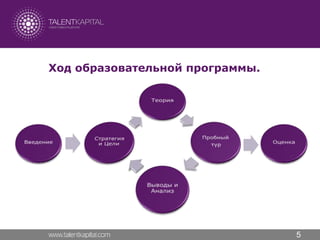
Бизнес-симуляция «Комплексное управление развитием компании» помогает участникам научиться формировать и следовать стратегии компании, выработать понимание сложности и многогранности процессов управления крупной международной или национальной компанией в динамичной и конкурентной среде.
1 of 16
Downloaded 27 times















Ad
Recommended
E Gov Indicators Regions Metodika V1
E Gov Indicators Regions Metodika V1Victor Gridnev
Ã˝
МЕТОДИКА - составления рейтинга уровня использования технологий «электронного правительства» в органах исполнительной власти субъектов Российской ФедерацииRevolucii tvoie prezentacii
Revolucii tvoie prezentaciidan voronov
Ã˝
–•–æ—Ä–æ—à–∞—è —Å–∏—Å—Ç–µ–º–∞ –¥–ª—è –æ—Å–Ω–æ–≤—ã –ø—Ä–µ–∑–µ–Ω—Ç–∞—Ü–∏–∏Brand Resources
Brand Resourceschjuncu
Ã˝
–í –±–æ–ª—å—à–∏–Ω—Å—Ç–≤–µ —Å–ª—É—á–∞–µ–≤ –ª—é–¥–∏ –Ω–µ –∑–Ω–∞—é—Ç —Ç–æ–≥–æ, —á–µ–º –≤–ª–∞–¥–µ—é—Ç. –£ –≤–∞—Å –µ—Å—Ç—å –æ–≥—Ä–æ–º–Ω—ã–µ —Ä–µ—Å—É—Ä—Å—ã, –∫–æ—Ç–æ—Ä—ã–µ –º–æ–∂–Ω–æ –∞–∫—Ç–∏–≤–∏–∑–∏—Ä–æ–≤–∞—Ç—å, –ø–æ—á—Ç–∏ –Ω–µ —Ç—Ä–∞—Ç—è –¥–µ–Ω–µ–≥. –¢–µ–º –±–æ–ª–µ–µ –∫–æ–≥–¥–∞ —Å—Ä–µ–¥—Å—Ç–≤ –Ω–µ —Ö–≤–∞—Ç–∞–µ—Ç –∏ –±—é–¥–∂–µ—Ç—ã –Ω–∞ –∫–æ–º–º—É–Ω–∏–∫–∞—Ü–∏—é –ø—Ä–∏—Ö–æ–¥–∏—Ç—Å—è —É—Ä–µ–∑–∞—Ç—å.
Сейчас самое время раскрыть потенциал бренда! Прочтите брошюру “Скрытые ресурсы вашего бренда”. В ней вы найдете полезные рекомендации, за которыми стоит реальный опыт.Business Simulations
Business SimulationsTalent Kapital
Ã˝
Бизнес-симуляция – это одна из самых эффективных образовательных технологий, разработанная на основе концепции «обучение на практике», которое обеспечивает 75% усвоения знаний и навыков участников программы.
–ë–∏–∑–Ω–µ—Å-—Å–∏–º—É–ª—è—Ü–∏–∏ –º–æ–¥–µ–ª–∏—Ä—É—é—Ç —Ä–µ–∞–ª—å–Ω—ã–µ –±–∏–∑–Ω–µ—Å-—Å–∏—Ç—É–∞—Ü–∏–∏, –ø—Ä–∏ —ç—Ç–æ–º –Ω–µ –ø–æ–¥–≤–µ—Ä–≥–∞—è –∫–æ–º–ø–∞–Ω–∏—é –Ω–∞—Å—Ç–æ—è—â–µ–º—É —Ä–∏—Å–∫—É –≤ –≤–∏–¥–µ —Ñ–∏–Ω–∞–Ω—Å–æ–≤—ã—Ö –ø–æ—Å–ª–µ–¥—Å—Ç–≤–∏–π. –£—á–∞—Å—Ç–Ω–∏–∫–∞–º –ø—Ä–µ–¥–æ—Å—Ç–∞–≤–ª—è–µ—Ç—Å—è –≤–æ–∑–º–æ–∂–Ω–æ—Å—Ç—å –ø—Ä–æ–±–æ–≤–∞—Ç—å, –ø—Ä–æ–∏–≥—Ä—ã–≤–∞—Ç—å, –ø—Ä–æ–±–æ–≤–∞—Ç—å –µ—â–µ —Ä–∞–∑, –¥–æ—Å—Ç–∏–≥–∞—Ç—å —Ü–µ–ª–µ–π –∏ –¥–µ–ª–∞—Ç—å –≤—ã–≤–æ–¥—ã.–º–µ—Ç–æ–¥–∏–∫–∞ –æ—Ü–µ–Ω–∫–∏ –¥–µ—è—Ç–µ–ª—å–Ω–æ—Å—Ç–∏ –æ—Ä–≥–∞–Ω–æ–≤ –∏—Å–ø–æ–ª–Ω–∏—Ç–µ–ª—å–Ω–æ–π –≤–ª–∞—Å—Ç–∏ —Å—É–±—ä–µ–∫—Ç–æ–≤ —Ä—Ñ
–º–µ—Ç–æ–¥–∏–∫–∞ –æ—Ü–µ–Ω–∫–∏ –¥–µ—è—Ç–µ–ª—å–Ω–æ—Å—Ç–∏ –æ—Ä–≥–∞–Ω–æ–≤ –∏—Å–ø–æ–ª–Ω–∏—Ç–µ–ª—å–Ω–æ–π –≤–ª–∞—Å—Ç–∏ —Å—É–±—ä–µ–∫—Ç–æ–≤ —Ä—ÑVictor Gridnev
Ã˝
–ú–µ—Ç–æ–¥–∏–∫–∞ –æ—Ü–µ–Ω–∫–∏ –¥–µ—è—Ç–µ–ª—å–Ω–æ—Å—Ç–∏ –æ—Ä–≥–∞–Ω–æ–≤ –∏—Å–ø–æ–ª–Ω–∏—Ç–µ–ª—å–Ω–æ–π –≤–ª–∞—Å—Ç–∏ —Å—É–±—ä–µ–∫—Ç–æ–≤ —Ä—Ñ–ö–æ–Ω—Ü–µ–ø—Ü–∏—è —Ä–µ–æ—Ä–≥–∞–Ω–∏–∑–∞—Ü–∏–∏ –°–≤—è–∑—å–∏–Ω–≤–µ—Å—Ç–∞
–ö–æ–Ω—Ü–µ–ø—Ü–∏—è —Ä–µ–æ—Ä–≥–∞–Ω–∏–∑–∞—Ü–∏–∏ –°–≤—è–∑—å–∏–Ω–≤–µ—Å—Ç–∞Ilya Ponomarev
Ã˝
–ö–æ–Ω—Ü–µ–ø—Ü–∏—è —Ä–µ–æ—Ä–≥–∞–Ω–∏–∑–∞—Ü–∏–∏ –°–≤—è–∑—å–∏–Ω–≤–µ—Å—Ç–∞–ü—Ä–æ–≥—Ä–∞–º–º–∞ –ª–æ—è–ª—å–Ω–æ—Å—Ç–∏
–ü—Ä–æ–≥—Ä–∞–º–º–∞ –ª–æ—è–ª—å–Ω–æ—Å—Ç–∏vseneshtiak
Ã˝
–î–∞–Ω–Ω–∞—è –ø—Ä–µ–∑–µ–Ω—Ç–∞—Ü–∏—è –∫—Ä–∞—Ç–∫–æ –æ–ø–∏—Å—ã–≤–∞–µ—Ç –ø—Ä–æ—Ü–µ—Å—Å —Ä–∞–∑—Ä–∞–±–æ—Ç–∫–∏ –∏ –≤–Ω–µ–¥—Ä–µ–Ω–∏—è –ø—Ä–æ–≥—Ä–∞–º–º—ã –ª–æ—è–ª—å–Ω–æ—Å—Ç–∏ –Ω–∞ –ø—Ä–∏–º–µ—Ä–µ –∫–æ–º–ø–∞–Ω–∏–∏ –û–û–û "–§—Ä–µ–π–º".
This presentation briefly describes loaylty program development and installation process on the example of Frame Company Ltd.Design Matters
Design MattersConstantin Kichinsky
Ã˝
Design Matters, –ö–æ–Ω—Å—Ç–∞–Ω—Ç–∏–Ω –ì–æ—Ä—Å–∫–∏–π, –ö–ª—É–± MAInfo.ru–ö–û–¢ - –ù–æ–≤–∞—è –ü–ª–æ—â–∞–¥—å
–ö–û–¢ - –ù–æ–≤–∞—è –ü–ª–æ—â–∞–¥—åguest4f99c3
Ã˝
–ü—Ä–æ–µ–∫—Ç—ã "–ö–æ–º–ø–ª–µ–∫—Å–Ω–æ–≥–æ –û—Å–≤–æ–µ–Ω–∏—è –¢–µ—Ä—Ä–∏—Ç–æ—Ä–∏–π". –ù–æ–≤–∞—è –ü–ª–æ—â–∞–¥—å.Design Lecture
Design LectureConstantin Kichinsky
Ã˝
–õ–µ–∫—Ü–∏—è –ö–æ–Ω—Å—Ç–∞–Ω—Ç–∏–Ω–∞ –ì–æ—Ä—Å–∫–æ–≥–æ –ø–æ —Ä–∞–∑—Ä–∞–±–æ—Ç–∫–µ –ø–æ–ª—å–∑–æ–≤–∞—Ç–µ–ª—å—Å–∫–∏—Ö –∏–Ω—Ç–µ—Ä—Ñ–µ–π—Å–æ–≤ –≤ —Ä–∞–º–∫–∞—Ö –∫—É—Ä—Å–∞ –ø–æ –û–û–ü. –ö–∞—Ñ. –í—ã—á–∏—Å–ª–∏—Ç–µ–ª—å–Ω–∞—è –º–∞—Ç–µ–º–∞—Ç–∏–∫–∞ –∏ –ø—Ä–æ–≥—Ä–∞–º–º–∏—Ä–æ–≤–∞–Ω–∏–µ, –ú–ê–ò.Etarget Bulgaria - Automotive Case Study
Etarget Bulgaria - Automotive Case StudyEtarget
Ã˝
–ö–∞–∫ –°—É–∑—É–∫–∏ –∏–∑–ø–æ–ª–∑–≤–∞ –ï—Ç–∞—Ä–≥–µ—Ç? –í–∏–∂—Ç–µ –∫–∞–∫–≤–æ –æ–∑–Ω–∞—á–∞–≤–∞ —É—Å–ø–µ—Ö –≤ –ï—Ç–∞—Ä–≥–µ—Ç –∏ –∫–∞–∫ –¥–∞ –≥–æ –∏–∑–ø–æ–ª–∑–≤–∞—Ç–µ –∑–∞ –≤–∞—à–∞—Ç–∞ —Ñ–∏—Ä–º–∞.–∫–∞–∫ –≤—ã–±—Ä–∞—Ç—å –ø—Ä–æ—Ñ–µ—Å—Å–∏—é
–∫–∞–∫ –≤—ã–±—Ä–∞—Ç—å –ø—Ä–æ—Ñ–µ—Å—Å–∏—é–ê–ª–∏–Ω–∞ –í–µ—Ç—Ä–æ–≤–∞
Ã˝
–∫–∞–∫ –≤—ã–±—Ä–∞—Ç—å –ø—Ä–æ—Ñ–µ—Å—Å–∏—é—Å–∏–Ω—é—à–∫–∏–Ω
—Å–∏–Ω—é—à–∫–∏–ΩMoscow State University, Political Sciences Department, Communication Group G3
Ã˝
–í. –°–∏–Ω—é—à–∫–∏–Ω. –¢–µ—Ö–Ω–æ–ª–æ–≥–∏–∏ —Ä–∞–±–æ—Ç—ã —Å–æ –°–ú–ò –≤ –ø–æ–ª–∏—Ç–∏—á–µ—Å–∫–∏—Ö –∫–∞–º–ø–∞–Ω–∏—è—Ö.–ü—Ä–æ–µ–∫—Ç –ø–æ—Å—Ç–∞–Ω–æ–≤–ª–µ–Ω–∏—è –ü—Ä–∞–≤–∏—Ç–µ–ª—å—Å—Ç–≤–∞ –†–§ –ø–æ –ú–§–¶ 30 04 09
–ü—Ä–æ–µ–∫—Ç –ø–æ—Å—Ç–∞–Ω–æ–≤–ª–µ–Ω–∏—è –ü—Ä–∞–≤–∏—Ç–µ–ª—å—Å—Ç–≤–∞ –†–§ –ø–æ –ú–§–¶ 30 04 09Victor Gridnev
Ã˝
–ü—Ä–æ–µ–∫—Ç –ø–æ—Å—Ç–∞–Ω–æ–≤–ª–µ–Ω–∏—è –ü—Ä–∞–≤–∏—Ç–µ–ª—å—Å—Ç–≤–∞ –†–æ—Å—Å–∏–π—Å–∫–æ–π –§–µ–¥–µ—Ä–∞—Ü–∏–∏
¬´–û –Ω–µ–∫–æ—Ç–æ—Ä—ã—Ö –º–µ—Ä–∞—Ö –ø–æ –ø–æ–≤—ã—à–µ–Ω–∏—é –∫–∞—á–µ—Å—Ç–≤–∞ –≥–æ—Å—É–¥–∞—Ä—Å—Ç–≤–µ–Ω–Ω—ã—Ö –∏
–º—É–Ω–∏—Ü–∏–ø–∞–ª—å–Ω—ã—Ö —É—Å–ª—É–≥ –Ω–∞ –±–∞–∑–µ –º–Ω–æ–≥–æ—Ñ—É–Ω–∫—Ü–∏–æ–Ω–∞–ª—å–Ω—ã—Ö —Ü–µ–Ω—Ç—Ä–æ–≤
предоставления государственных (муниципальных) услуг»SimBrand Marketing Management Simulation
SimBrand Marketing Management SimulationTalent Kapital
Ã˝
Обучающая маркетинговая программа “SimBrand – Управление Маркетингом”, в основе которой лежит использование бизнес-симуляции. Бизнес-симуляцию SimBrand используют для отработки профессиональных для маркетологов навыков и компетенций бизнес-школы Wharton, Nangyang Technical University, McGrawHill и др., а также международные компании, среди которых Coca Cola, Oracle, Pirelli, Nokia, MTС, Вымпелком.Presentation by Vadim Prasov
Presentation by Vadim Prasovworkshop-moscow
Ã˝
–î–æ–∫—É–º–µ–Ω—Ç –æ–±—Å—É–∂–¥–∞–µ—Ç –ø–æ–¥—Ö–æ–¥—ã –∫ —É–ø—Ä–∞–≤–ª–µ–Ω–∏—é –ø–µ—Ä—Å–æ–Ω–∞–ª–æ–º –≤ —Ä–æ—Å—Å–∏–π—Å–∫–∏—Ö –≥–æ—Å—Ç–∏–Ω–∏—Ü–∞—Ö, –≤—ã–¥–µ–ª—è—è —á–µ—Ç—ã—Ä–µ —Ç–∏–ø–∞ —Å–æ—Ç—Ä—É–¥–Ω–∏–∫–æ–≤ –∏ —Å–æ–æ—Ç–≤–µ—Ç—Å—Ç–≤—É—é—â–∏–µ –∏–º —Å—Ç–∞–Ω–¥–∞—Ä—Ç—ã –æ–±—Å–ª—É–∂–∏–≤–∞–Ω–∏—è. –¢–∞–∫–∂–µ —Ä–∞—Å—Å–º–∞—Ç—Ä–∏–≤–∞—é—Ç—Å—è —ç—Ñ—Ñ–µ–∫—Ç–∏–≤–Ω–æ–µ —É–ø—Ä–∞–≤–ª–µ–Ω–∏–µ, –æ—Ä–≥–∞–Ω–∏–∑–∞—Ü–∏—è —Ç—Ä—É–¥–∞, —Å–∏—Å—Ç–µ–º—ã –º–æ—Ç–∏–≤–∞—Ü–∏–∏, –æ–±—É—á–µ–Ω–∏—è –∏ –∞—Ç—Ç–µ—Å—Ç–∞—Ü–∏–∏, –∞ —Ç–∞–∫–∂–µ –ø–æ–∫–∞–∑–∞—Ç–µ–ª–∏ —ç—Ñ—Ñ–µ–∫—Ç–∏–≤–Ω–æ—Å—Ç–∏. –í –∫–æ–Ω—Ü–µ –æ—Ç–º–µ—á–µ–Ω—ã –∞–Ω—Ç–∏–∫—Ä–∏–∑–∏—Å–Ω—ã–µ –º–µ—Ä—ã –¥–ª—è –ø–æ–≤—ã—à–µ–Ω–∏—è –ø—Ä–æ–∏–∑–≤–æ–¥–∏—Ç–µ–ª—å–Ω–æ—Å—Ç–∏ –∏ —É–ª—É—á—à–µ–Ω–∏—è –∫–æ—Ä–ø–æ—Ä–∞—Ç–∏–≤–Ω–æ–π –∫—É–ª—å—Ç—É—Ä—ã.–ì–ª—è–Ω–µ—Ü ‚Ññ 29 (–Ω–æ—è–±—Ä—å 2014)
–ì–ª—è–Ω–µ—Ü ‚Ññ 29 (–Ω–æ—è–±—Ä—å 2014)gorodche
Ã˝
В журнале «Глянец» представлено эксклюзивное интервью с финалисткой проекта «Голос» Наргиз Закировой, обсуждаются достижения футболиста Евгения Макеева и его потенциальный переход в берлинскую команду «Герта». Также в числе новостей о celebrity – мнения известных личностей о разных событиях и их взаимодействие с общественностью, включая персональные аспекты жизни Маргариты Гусевой, заместителя председателя городской думы Череповца, которая делится планами на третий ребенок и карьеру. Журнал подробно охватывает события, связанные с культурой, спортом и личными историями известных россиян.More Related Content
What's hot (19)
–ö–æ–Ω—Ü–µ–ø—Ü–∏—è —Ä–µ–æ—Ä–≥–∞–Ω–∏–∑–∞—Ü–∏–∏ –°–≤—è–∑—å–∏–Ω–≤–µ—Å—Ç–∞
–ö–æ–Ω—Ü–µ–ø—Ü–∏—è —Ä–µ–æ—Ä–≥–∞–Ω–∏–∑–∞—Ü–∏–∏ –°–≤—è–∑—å–∏–Ω–≤–µ—Å—Ç–∞Ilya Ponomarev
Ã˝
–ö–æ–Ω—Ü–µ–ø—Ü–∏—è —Ä–µ–æ—Ä–≥–∞–Ω–∏–∑–∞—Ü–∏–∏ –°–≤—è–∑—å–∏–Ω–≤–µ—Å—Ç–∞–ü—Ä–æ–≥—Ä–∞–º–º–∞ –ª–æ—è–ª—å–Ω–æ—Å—Ç–∏
–ü—Ä–æ–≥—Ä–∞–º–º–∞ –ª–æ—è–ª—å–Ω–æ—Å—Ç–∏vseneshtiak
Ã˝
–î–∞–Ω–Ω–∞—è –ø—Ä–µ–∑–µ–Ω—Ç–∞—Ü–∏—è –∫—Ä–∞—Ç–∫–æ –æ–ø–∏—Å—ã–≤–∞–µ—Ç –ø—Ä–æ—Ü–µ—Å—Å —Ä–∞–∑—Ä–∞–±–æ—Ç–∫–∏ –∏ –≤–Ω–µ–¥—Ä–µ–Ω–∏—è –ø—Ä–æ–≥—Ä–∞–º–º—ã –ª–æ—è–ª—å–Ω–æ—Å—Ç–∏ –Ω–∞ –ø—Ä–∏–º–µ—Ä–µ –∫–æ–º–ø–∞–Ω–∏–∏ –û–û–û "–§—Ä–µ–π–º".
This presentation briefly describes loaylty program development and installation process on the example of Frame Company Ltd.Design Matters
Design MattersConstantin Kichinsky
Ã˝
Design Matters, –ö–æ–Ω—Å—Ç–∞–Ω—Ç–∏–Ω –ì–æ—Ä—Å–∫–∏–π, –ö–ª—É–± MAInfo.ru–ö–û–¢ - –ù–æ–≤–∞—è –ü–ª–æ—â–∞–¥—å
–ö–û–¢ - –ù–æ–≤–∞—è –ü–ª–æ—â–∞–¥—åguest4f99c3
Ã˝
–ü—Ä–æ–µ–∫—Ç—ã "–ö–æ–º–ø–ª–µ–∫—Å–Ω–æ–≥–æ –û—Å–≤–æ–µ–Ω–∏—è –¢–µ—Ä—Ä–∏—Ç–æ—Ä–∏–π". –ù–æ–≤–∞—è –ü–ª–æ—â–∞–¥—å.Design Lecture
Design LectureConstantin Kichinsky
Ã˝
–õ–µ–∫—Ü–∏—è –ö–æ–Ω—Å—Ç–∞–Ω—Ç–∏–Ω–∞ –ì–æ—Ä—Å–∫–æ–≥–æ –ø–æ —Ä–∞–∑—Ä–∞–±–æ—Ç–∫–µ –ø–æ–ª—å–∑–æ–≤–∞—Ç–µ–ª—å—Å–∫–∏—Ö –∏–Ω—Ç–µ—Ä—Ñ–µ–π—Å–æ–≤ –≤ —Ä–∞–º–∫–∞—Ö –∫—É—Ä—Å–∞ –ø–æ –û–û–ü. –ö–∞—Ñ. –í—ã—á–∏—Å–ª–∏—Ç–µ–ª—å–Ω–∞—è –º–∞—Ç–µ–º–∞—Ç–∏–∫–∞ –∏ –ø—Ä–æ–≥—Ä–∞–º–º–∏—Ä–æ–≤–∞–Ω–∏–µ, –ú–ê–ò.Etarget Bulgaria - Automotive Case Study
Etarget Bulgaria - Automotive Case StudyEtarget
Ã˝
–ö–∞–∫ –°—É–∑—É–∫–∏ –∏–∑–ø–æ–ª–∑–≤–∞ –ï—Ç–∞—Ä–≥–µ—Ç? –í–∏–∂—Ç–µ –∫–∞–∫–≤–æ –æ–∑–Ω–∞—á–∞–≤–∞ —É—Å–ø–µ—Ö –≤ –ï—Ç–∞—Ä–≥–µ—Ç –∏ –∫–∞–∫ –¥–∞ –≥–æ –∏–∑–ø–æ–ª–∑–≤–∞—Ç–µ –∑–∞ –≤–∞—à–∞—Ç–∞ —Ñ–∏—Ä–º–∞.–∫–∞–∫ –≤—ã–±—Ä–∞—Ç—å –ø—Ä–æ—Ñ–µ—Å—Å–∏—é
–∫–∞–∫ –≤—ã–±—Ä–∞—Ç—å –ø—Ä–æ—Ñ–µ—Å—Å–∏—é–ê–ª–∏–Ω–∞ –í–µ—Ç—Ä–æ–≤–∞
Ã˝
–∫–∞–∫ –≤—ã–±—Ä–∞—Ç—å –ø—Ä–æ—Ñ–µ—Å—Å–∏—é—Å–∏–Ω—é—à–∫–∏–Ω
—Å–∏–Ω—é—à–∫–∏–ΩMoscow State University, Political Sciences Department, Communication Group G3
Ã˝
–í. –°–∏–Ω—é—à–∫–∏–Ω. –¢–µ—Ö–Ω–æ–ª–æ–≥–∏–∏ —Ä–∞–±–æ—Ç—ã —Å–æ –°–ú–ò –≤ –ø–æ–ª–∏—Ç–∏—á–µ—Å–∫–∏—Ö –∫–∞–º–ø–∞–Ω–∏—è—Ö.–ü—Ä–æ–µ–∫—Ç –ø–æ—Å—Ç–∞–Ω–æ–≤–ª–µ–Ω–∏—è –ü—Ä–∞–≤–∏—Ç–µ–ª—å—Å—Ç–≤–∞ –†–§ –ø–æ –ú–§–¶ 30 04 09
–ü—Ä–æ–µ–∫—Ç –ø–æ—Å—Ç–∞–Ω–æ–≤–ª–µ–Ω–∏—è –ü—Ä–∞–≤–∏—Ç–µ–ª—å—Å—Ç–≤–∞ –†–§ –ø–æ –ú–§–¶ 30 04 09Victor Gridnev
Ã˝
–ü—Ä–æ–µ–∫—Ç –ø–æ—Å—Ç–∞–Ω–æ–≤–ª–µ–Ω–∏—è –ü—Ä–∞–≤–∏—Ç–µ–ª—å—Å—Ç–≤–∞ –†–æ—Å—Å–∏–π—Å–∫–æ–π –§–µ–¥–µ—Ä–∞—Ü–∏–∏
¬´–û –Ω–µ–∫–æ—Ç–æ—Ä—ã—Ö –º–µ—Ä–∞—Ö –ø–æ –ø–æ–≤—ã—à–µ–Ω–∏—é –∫–∞—á–µ—Å—Ç–≤–∞ –≥–æ—Å—É–¥–∞—Ä—Å—Ç–≤–µ–Ω–Ω—ã—Ö –∏
–º—É–Ω–∏—Ü–∏–ø–∞–ª—å–Ω—ã—Ö —É—Å–ª—É–≥ –Ω–∞ –±–∞–∑–µ –º–Ω–æ–≥–æ—Ñ—É–Ω–∫—Ü–∏–æ–Ω–∞–ª—å–Ω—ã—Ö —Ü–µ–Ω—Ç—Ä–æ–≤
предоставления государственных (муниципальных) услуг»SimBrand Marketing Management Simulation
SimBrand Marketing Management SimulationTalent Kapital
Ã˝
Обучающая маркетинговая программа “SimBrand – Управление Маркетингом”, в основе которой лежит использование бизнес-симуляции. Бизнес-симуляцию SimBrand используют для отработки профессиональных для маркетологов навыков и компетенций бизнес-школы Wharton, Nangyang Technical University, McGrawHill и др., а также международные компании, среди которых Coca Cola, Oracle, Pirelli, Nokia, MTС, Вымпелком.Проект постановления Правительства РФ по МФЦ 30 04 09
–ü—Ä–æ–µ–∫—Ç –ø–æ—Å—Ç–∞–Ω–æ–≤–ª–µ–Ω–∏—è –ü—Ä–∞–≤–∏—Ç–µ–ª—å—Å—Ç–≤–∞ –†–§ –ø–æ –ú–§–¶ 30 04 09Victor Gridnev
Ã˝
Viewers also liked (8)
Presentation by Vadim Prasov
Presentation by Vadim Prasovworkshop-moscow
Ã˝
–î–æ–∫—É–º–µ–Ω—Ç –æ–±—Å—É–∂–¥–∞–µ—Ç –ø–æ–¥—Ö–æ–¥—ã –∫ —É–ø—Ä–∞–≤–ª–µ–Ω–∏—é –ø–µ—Ä—Å–æ–Ω–∞–ª–æ–º –≤ —Ä–æ—Å—Å–∏–π—Å–∫–∏—Ö –≥–æ—Å—Ç–∏–Ω–∏—Ü–∞—Ö, –≤—ã–¥–µ–ª—è—è —á–µ—Ç—ã—Ä–µ —Ç–∏–ø–∞ —Å–æ—Ç—Ä—É–¥–Ω–∏–∫–æ–≤ –∏ —Å–æ–æ—Ç–≤–µ—Ç—Å—Ç–≤—É—é—â–∏–µ –∏–º —Å—Ç–∞–Ω–¥–∞—Ä—Ç—ã –æ–±—Å–ª—É–∂–∏–≤–∞–Ω–∏—è. –¢–∞–∫–∂–µ —Ä–∞—Å—Å–º–∞—Ç—Ä–∏–≤–∞—é—Ç—Å—è —ç—Ñ—Ñ–µ–∫—Ç–∏–≤–Ω–æ–µ —É–ø—Ä–∞–≤–ª–µ–Ω–∏–µ, –æ—Ä–≥–∞–Ω–∏–∑–∞—Ü–∏—è —Ç—Ä—É–¥–∞, —Å–∏—Å—Ç–µ–º—ã –º–æ—Ç–∏–≤–∞—Ü–∏–∏, –æ–±—É—á–µ–Ω–∏—è –∏ –∞—Ç—Ç–µ—Å—Ç–∞—Ü–∏–∏, –∞ —Ç–∞–∫–∂–µ –ø–æ–∫–∞–∑–∞—Ç–µ–ª–∏ —ç—Ñ—Ñ–µ–∫—Ç–∏–≤–Ω–æ—Å—Ç–∏. –í –∫–æ–Ω—Ü–µ –æ—Ç–º–µ—á–µ–Ω—ã –∞–Ω—Ç–∏–∫—Ä–∏–∑–∏—Å–Ω—ã–µ –º–µ—Ä—ã –¥–ª—è –ø–æ–≤—ã—à–µ–Ω–∏—è –ø—Ä–æ–∏–∑–≤–æ–¥–∏—Ç–µ–ª—å–Ω–æ—Å—Ç–∏ –∏ —É–ª—É—á—à–µ–Ω–∏—è –∫–æ—Ä–ø–æ—Ä–∞—Ç–∏–≤–Ω–æ–π –∫—É–ª—å—Ç—É—Ä—ã.–ì–ª—è–Ω–µ—Ü ‚Ññ 29 (–Ω–æ—è–±—Ä—å 2014)
–ì–ª—è–Ω–µ—Ü ‚Ññ 29 (–Ω–æ—è–±—Ä—å 2014)gorodche
Ã˝
В журнале «Глянец» представлено эксклюзивное интервью с финалисткой проекта «Голос» Наргиз Закировой, обсуждаются достижения футболиста Евгения Макеева и его потенциальный переход в берлинскую команду «Герта». Также в числе новостей о celebrity – мнения известных личностей о разных событиях и их взаимодействие с общественностью, включая персональные аспекты жизни Маргариты Гусевой, заместителя председателя городской думы Череповца, которая делится планами на третий ребенок и карьеру. Журнал подробно охватывает события, связанные с культурой, спортом и личными историями известных россиян.Overview of transfer pricing
Overview of transfer pricingCA Yash Jagati
Ã˝
Controlled
transaction
A Inc.
(USA)
Uncontrolled
transaction
B Inc.
(USA)
$10
A Ltd.
(India)
C Ltd.
(India)
GM 20%
$8
Customers
Customers
1) Transfer pricing refers to the prices charged for transactions between associated enterprises, and aims to ensure they are consistent with prices charged between independent parties (arm's length principle).
2) India introduced transfer pricing provisions to prevent profit shifting by multinational enterprises from high tax to low tax jurisdictions.
3) The key concepts are arm's length price, transfer price, uncontrolled transactions, controlled transactionsIntroduction to Transfer Pricing
Introduction to Transfer PricingEd Morris
Ã˝
The document is a comprehensive introduction to transfer pricing, outlining its significance, U.S. regulations, and key concepts such as the arm's length standard and various testing methods. It discusses recent developments and hot topics related to transfer pricing, including audit triggers and best practices for compliance. Presented by Ed Morris from Clifton Gunderson, the document emphasizes the importance of thorough documentation and proactive planning in managing transfer pricing risks.Transfer pricing concept and practice
Transfer pricing concept and practiceTechnip
Ã˝
The document outlines the concept and practice of transfer pricing, highlighting its definition, regulatory impact, and adjustments necessary for compliance. It explains how mis-pricing between related parties can lead to significant tax avoidance and capital flight, and details the regulatory framework introduced by the Finance Act for international and specified domestic transactions. Additionally, it emphasizes documentation requirements, methods for determining arm's length prices, and strategies for taxpayers to align with regulations.Transfer Pricing
Transfer PricingAsia Pacific Marketing Institute
Ã˝
Transfer pricing refers to the prices charged for goods and services transferred between divisions of a multinational company operating across international borders. The objectives of transfer pricing include reducing taxes, managing cash flows, and avoiding conflicts with governments. Common transfer pricing methods are market-based prices, cost-based prices, and negotiated prices. Transfer pricing allows companies to shift profits between countries to minimize taxes but also presents challenges in terms of performance measurement and conflicts with tax authorities.6. transfer pricing
6. transfer pricingKAMALIYA PANKAJ
Ã˝
Transfer pricing refers to the prices charged for goods and services transferred between divisions within the same company. There are several approaches to setting transfer prices, including using market prices, cost-based prices, negotiated prices, or administered prices set by a rule. The objectives of transfer pricing are to provide accurate performance measurement for each division, encourage goal congruence between divisions, and mimic external market prices. Key considerations include using transfer prices that motivate optimal sourcing and production decisions for the entire company.Ad
Recently uploaded (10)
Aylanmadan olinadigan soliq.2025 yil.pdf
Aylanmadan olinadigan soliq.2025 yil.pdfilxomislomov2020
Ã˝
soliqlar. Aylanmadan olinadigan soliq.soliq 2025.Qarshi davlat texnika universiteti.soliq stavkalari 2025 y. O'zR soliq kodeksi.Prezentatsiya 2025. y–Ω–∞–∫–∞–∑ –ø—Ä–æ –∑–∞—Ä–∞—Ö—É–≤–∞–Ω–Ω—è–¥–æ 1 –∫–ª–∞—Å—É kg72 2025
–Ω–∞–∫–∞–∑ –ø—Ä–æ –∑–∞—Ä–∞—Ö—É–≤–∞–Ω–Ω—è–¥–æ 1 –∫–ª–∞—Å—É kg72 2025AleksSaf
Ã˝
–Ω–∞–∫–∞–∑ –ø—Ä–æ –∑–∞—Ä–∞—Ö—É–≤–∞–Ω–Ω—è–¥–æ 1 –∫–ª–∞—Å—É 2025Flashcards Animais brasileiros Ilustrado Verde.pdf
Flashcards Animais brasileiros Ilustrado Verde.pdfPriscilaRibeiro803210
Ã˝
Jogo com animais brasileirosGazetteer of Russia. Part: Populated places G-Krasno.pdf
Gazetteer of Russia. Part: Populated places G-Krasno.pdfpeivhau
Ã˝
Detailed gazetteer of cities, towns and villages of Russia. Census results. Name changes. Incorporations. Latitudes and longitudes.pdf-p-classtruncatedtext-module-lineclamped-85ulhh-style-max-lines5topik-tema...
pdf-p-classtruncatedtext-module-lineclamped-85ulhh-style-max-lines5topik-tema...Ifa Nofalia
Ã˝
bjbij jknkj knlk ml ko k lk lkmk k kmpom kmp kl pk km op lk ok p m k k ,l pom l pmfpoasfmasmfp om k kmp kla fpmpaf pkokmp pmppmpa fkmpo l pmo l pamfomaf afpomopafa pompo kmapofma pocambios_emocionales en los traumas presentes en adolescentes
cambios_emocionales en los traumas presentes en adolescentesvivianyarenivallecil
Ã˝
cambios emocionalesGazetteer of Russia. Part: Populated places A-F.pdf
Gazetteer of Russia. Part: Populated places A-F.pdfpeivhau
Ã˝
Detailed gazetteer of cities, towns and villages of Russia. Census results. Name changes. Incorporations. Latitudes and longitudes. Ad
