Carbon Dating 2.pptx
- 1. Carbon Dating Presented by, Sachin K 1st year M.sc Dos in Molecular Biology Guided by, Ms B.M Ranjitha Dept of Molecular Biology
- 2. Content âĒ Introduction âĒ History âĒ Carbon Dating âĒ Principle of carbon dating âĒ Life Cycle Of Carbon 14 âĒ Methods of carbon dating âĒ Application âĒ Summary
- 3. INTRODUCTION âĒ All carbon atoms have 6 protons in the nucleus,but the nucleus may also contain 6, 7, or 8 neutrons. âĒ Their are 3 naturally occuring isotopes of carbon on earth, 1.carbon-12 : Stable nucleous (99% of all natural carbon) 2.carbon -13 : Stable nucleous (1%) 3.Carbon -14 : Unstable radioactive isotopes (Wher 1 in 1012 carbon atoms in the atomosphere is C-14)
- 4. History âĒ The carbon-14 method was developed by the American physicist Willard Frank Libby and his team in 1946 at the University of Chicago. âĒ He determined the half life to be 5568 years Âą 30 years and it is popularly known as libby half life. âĒ This half life has later been re-determind by Godwin as 5730 Âą 40 years which is known as the Cambridge half life. âĒ In 1960, Mr. Willard F. Libby was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in recognition of his efforts to develop radiocarbon dating.
- 5. Carbon dating It is one of the form of Radiometric dating and also refered as Radiocarbon dating or carbon-14 dating. âĒ This method used for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
- 6. Principle âĒ Carbon 14 is continually being formed in the upper atmosphere by the effect of cosmic ray neutrons on nitrogen 14 atoms. It is rapidly oxidized in air to form carbon dioxide and enters the global carbon cycle. âĒ Plants and animals assimilate carbon 14 from carbon dioxide throughout their lifetimes. When they die, they stop exchanging carbon with the biosphere and their carbon 14 content then starts to decrease at a rate determined by the law of radioactive decay. âĒ Radiocarbon dating is essentially a method designed to measure residual radioactivity.
- 7. Life Cycle Of Carbon 14
- 8. Marine cycle
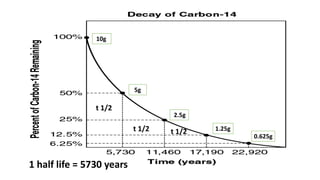
- 9. Contd.... âĒ Animals get their C-14 dose from the food that they consume. âĒ When the organism (or a tissue) dies absorption of C-14 ceases and the amount of C-14 gradually decays.. âĒ The half-life of the decay of C-14 to nitrogen is 5730 years so the concentration halves every 5730 years. âĒ HALF-LIFE : The time taken for half a radioactive sample to decay into something else. âĒ Radioactive carbon (C-14) Îē decays to nitrogen (N14) by emitting an electron (eâ) and an antineutrino ( v-) with no mass or charge.
- 10. 10g 5g 2.5g 1.25g 0.625g 1 half life = 5730 years t 1/2 t 1/2 t 1/2
- 11. Carbon dating in laboratory
- 12. Methods of measuring C-14 There are two basic methods, 1. Radiometric : Radiometric dating method is used to detect beta particles from the decay of carbon 14 atoms. using a gas proportional counter (a form of Geiger counter) or a liquid scintillation counter. âĒ It is cheap and It takes about a month to achieve satisfactory statistics. 2. AMS (Accelerator mass spectrometer): Accelerator mass spectrometers count the number of carbon 14 atoms present in the sample. âĒ It is expensive and it takes about a week. âĒ It requires only about a gram. âĒ It is a good method for dating specific samples.
- 13. Accelerator mass spectrometer at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, California Liquid Scintillation conter
- 14. Application âĒCarbon dating is useful to archeologists when they need to know the approximate date of a fossil or any other object. âĒcarbon dating is used to find the ages of trees, mummies, fossils, or other organic material âĒCarbon-14 is used to study the passage of carbon dating photosynthesis in plants.
- 15. contd.... âĒ Radiocarbon dating of sacred mummies from ancient Egypt. âĒ Radiocarbon dating can be used to date carbon containing pigment like charcoal, it was even useful in dating cave paintings. âĒ Samples that have been radiocarbon dated since the inception of the method include, âĒ charcoal, wood, twigs, seeds, bones, shells, leather, peat âĒ lake mud, soil, hair, pottery, pollen âĒ wall paintings, corals, blood residues, fabrics âĒ paper or parchment, resins, and water.
- 16. Contd.... Ancientin ink : Iceman Otzi has worldâs oldest tattoos (Chinchoro mummy) âĒ 61 tattoos on the Icemanâs body. Ancient Quran manuscript (1,500 years old)
- 17. contd.... Prehistoric horse decorates the walls of lascaux Cave in France. (40.000BC to 8000 BC ) Burial site with items dug up from the Sanauli site in Baghpa (3800 yrs old)
- 18. Limitation âĒ This technique used only for dating organic material âĒ It cannot be used to date rocks (except carbonacious rocks) âĒ Maximum age limit for C-14 dating is 52,000 to 62,000 years. âĒ Several physical, chemical, and biological processes can cause contamination. âĒ Carbon exchange between the sample and the atmosphere is a common cause of contamination in bone, wood, and shell samples.
- 19. Measurement and reporting dates âĒ The radiocarbon measurement is termed as conventional radiocarbon age (CRA). âĒ Uncalibrated radiocarbon measurements are usually reported in years BP(Before present) where 0 (zero), BP is defined as AD 1950. âĒ BP notation is also used in other dating techniques but is defined differently, as in the case of thermoluminescence dating, where BP is defined as AD 1980. âĒ Half-life used in carbon dating calculations is 5568 years, the value worked out by chemist Willard Libby, and not the more accurate value of 5730 years, Although it is less accurate.(to avoide inconsistencies or errors when comparing carbon-14 test )
- 20. Summary âĒ C-14 method is used for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon. âĒ The half-life of the decay of C-14 to nitrogen 14 is 5730 years so the concentration halves every 5730 years. âĒ When the organism (or a tissue) dies absorption of C-14 ceases, and the amount of C-14 gradually decays in every half life. âĒ carbon dating is used to find the ages of trees, mummies, fossils, or other organic materials.
- 21. Thank you