Carter matariki
- 1. Taatai Arorangi: Matariki and the New Year âĒ Traditionally MÄori, and many other cultures, used the night sky and the stars to tell the time and seasons. âĒ They also used them as they navigated the oceans. âĒ The tohunga kÅkÅrangi would watch for the rise of Matariki just before dawn.
- 2. Matariki and the New Year âĒ Stories and legends were ways of passing knowledge from generation to generation. âĒ Even if the cause was not understood the story explained observed events. âĒ There may be many versions of a similar story. âĒ Here is one story of Matariki
- 4. âĒ The rising of Matariki the Maori New âĒ Matariki was also a time Year and signalled a time for to turn to the future, connecting, giving thanks to the land, welcoming the new sea and sky, a time for the community to come together to generation to the world farewell those departed and and planning for the year acknowledge the year gone. ahead. âĒ Matariki could be added âĒ It is universal to Maori and Pakeha, to our celebrations because we all live with the opposite calendar. It provides us seasons to the Northern hemisphere. with something that's unique.
- 5. âĒ The crops were planted according to the appearance of the Matariki star cluster. âĒ If the stars were clear and bright, it was a sign of a favourable and productive season ahead, and planting would begin in September. âĒ If the stars appeared hazy and closely bunched together, a cold winter was in store and planting was put off until October.
- 6. âĒ The Matariki were honoured by the Maori. The heliacal rising of that asterism was greeted by women with song and dance. âĒ In other areas the cosmic rising of Rigel marked the beginning of the new year with a similar festival marking the event.
- 7. The Helical rising of the Stars
- 8. âĒ New star patterns become visible as we travel around the Sun. âĒ Matariki is in Taurus
- 9. Heliacal risings occur after a star has been behind the Sun for a time and it is just returning to visibility. One morning, just before dawn, the star rises after its absence behind the Sun and is seen for a moment, then lost in the rising Sunâs glare. That one special morning is called the star's heliacal rising.
- 10. Circumpolar stars will NOT work! âĒ Not all stars have heliacal risings because some stars are always above the horizon and are called circumpolar stars. âĒ Only certain stars rise, flash and twinkle in the pre- dawn glow.
- 11. El NiÃąo or La NiÃąa- watch out! âĒ Clear, bright stars = a good season. âĒ Hazy and bunched together= cold winter, planting delayed. âĒ The upper atmosphere may indicate long term weather conditions. âĒ Astute, practiced observers can see the difference from year to year. âĒ Can you?
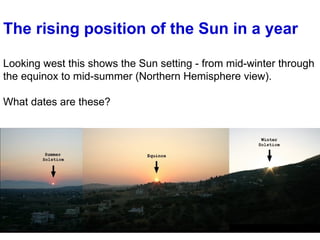
- 12. The rising position of the Sun in a year Looking west this shows the Sun setting - from mid-winter through the equinox to mid-summer (Northern Hemisphere view). What dates are these?
- 13. The Pleiades/Matariki star cluster facts âĒ A cluster of around 1000 stars that are about 440 light years away (our Sun is 8 light minutes away) âĒ The blue color is caused by blue light being scattered by dust. âĒMerope, one of the brightest stars in the Pleiades- where the âĒ The stars in the nebulosity is caused by a chance Pleiades are young- encounter between an open star 100 million years old - cluster and a molecular cloud. about 1/50th the age of our Sun
- 14. âĒ 29.5 days makes a âMoonthâ âĒ Maori followed a lunar calendar: Te Maramataka âĒ New Moon is when the Moon is between Sun and the Earth âĒ First quarter is when it has moved one fourth of itâs way around the Earth - but it looks like a semi-circle and many call it a âhalf Moonâ! âĒ Full Moon comes half way through the cycle (Sun, Earth & Moon Alignment. âĒ 29.5 days is not a factor of 365- which is why our months are a mix from 28 day to 31 day lengths In the Southern Hemisphere the sunlit part moves from the left to the right. C O D (C first quarter, O full Moon, D last quarter)
- 15. Calendars, clocks and Time âĒ How many trips around the Sun have you made? âĒ What season were you born in?
- 16. How many days, weeks, and âmoonthsâ have you lived through? How do you know?
- 17. Is it easy to count how many Moon cycles you have lived through? Is it years x12 or years x13 ? So how many Moonths old are you?
- 18. Near, Far and IN-between.
Editor's Notes
- For MÄori, this time signified remembrance, fertility and celebration.
- For MÄori, this time signified remembrance, fertility and celebration.
- Christmas was always the celebration of the winter solstice, Easter the spring equinox. Iwi (tribes) marked the New Year by when Matariki or other stars, such as Puanga (Rigel), or Takurua (Sirius) were first seen, or on the day of the first new Moon after they had risen .
- The blue colour is now thought to be a gas cloud the Pleiades have drifted into -previously thought to be the tell-tale leftover gas from their formation. Young stars at only 100 million years old!
- Kapa Haka festival???
- Explain the zodiac is where the moving objects of the solar system are found.
- Slightly doctored photo of heliacal rising.
- An equal area can never be seen from here just as those people at 40 ° N can never see the Southern Cross
- Clear, bright stars = a good season. Hazy and bunched together= cold winter, planting delayed. Whatever method chosen there will always be an element of randomness! Modern meteorology not always accurate.
- Actually this photo is for the morning in the Northern hemisphere
- Light travels at 300,000 kms per second.
- Could there be a better time interval on the calendar for a âmoonthâ?
- Look out for eclipsed Moon morning 16 th June 2011.
- Perigee and Apogee, solar and lunar eclipses are different.