Ct temporal bone
- 1. Moderator: Dr Pankaj Kumar Presenter: Dr Yasha Gupta Department of ENT Dr Baba Saheb Ambedkar Hospital.
- 2. WHY?? âĒ Identify anatomy âĒ Operative planning âĒ Risk assessment âĒ Informed consent
- 3. Informations âĒ Aeration âĒ Position of dura, Facial Nerve and Vessels âĒ Labyrinth âĒ Extension of disease âĒ Evidence of previous surgery
- 4. Planes of scanning ï Axial ï 30 Degrees to anthropological base line ï Parallel to lateral SCC. ï Best displays inner & middle ear. ï Sections parallel to the hard Palate ï Coronal plane ï patient head extended in prone or supine with 105 degree ï plane is perpendicular to the lateral SCC ï Sections are parallel to posterior wall of maxillary sinus ï Saggital plane 4 105 0 30
- 5. Planes âĒ PÃķschl plane approximates the plane of the sSCC âĒ Stenvers plane is perpendicular to both the axial plane and the PÃķschl plane
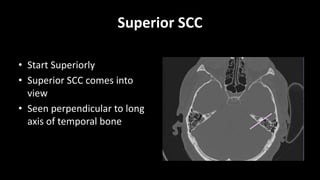
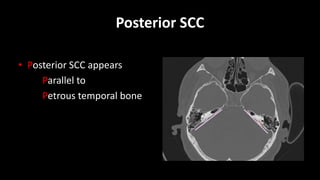
- 6. AXIAL CUTS âĒ Superior SCC âĒ Posterior SCC âĒ Vestibular aqueduct âĒ IAC âĒ Facial âĒ LSCC
- 7. Superior SCC âĒ Start Superiorly âĒ Superior SCC comes into view âĒ Seen perpendicular to long axis of temporal bone
- 8. Posterior SCC âĒ Posterior SCC appears Parallel to Petrous temporal bone
- 9. Vestibular Aqueduct âĒ Vestibular aqueduct Veers Ventrally Onto the posterior cranial fossa surface of Temporal bone
- 11. Inernal Auditory Canal âĒ It is next to appear âĒ All structures anterior to it are cochlear âĒ Posterior to it are vestibular
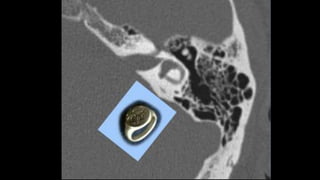
- 14. Lateral SCC âĒ Signet ring appearance
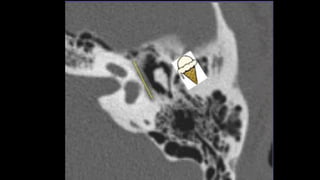
- 17. Ossicles âĒ Ice cream cone appearance
- 19. âĒ The ice-cream cone sign represents the normal appearance of the malleus and incus on an axial high-resolution CT scan (HRCT) image of the temporal bone . âĒ The ball (scoop) of the ice cream is formed by the head of malleus and the cone is formed by the body of the incus. âĒ The space between the ice-cream cone and the scutum is called Prussak's space.
- 21. Cochlea âĒ Stack of coins
- 23. CORONAL
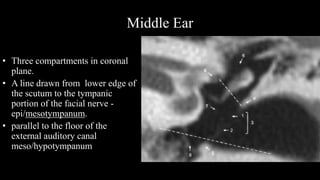
- 24. Middle Ear âĒ Three compartments in coronal plane. âĒ A line drawn from lower edge of the scutum to the tympanic portion of the facial nerve - epi/mesotympanum. âĒ parallel to the floor of the external auditory canal meso/hypotympanum
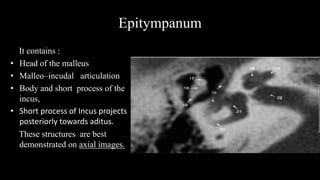
- 25. Epitympanum It contains : âĒ Head of the malleus âĒ Malleoâincudal articulation âĒ Body and short process of the incus, âĒ Short process of Incus projects posteriorly towards aditus. These structures are best demonstrated on axial images.
- 26. âĒ Tegment tympani â roof of epitympanum â barrier between middle cranial fossa and middle ear cavity. âĒ Best evaluated on coronal images
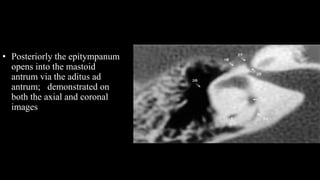
- 27. âĒ Posteriorly the epitympanum opens into the mastoid antrum via the aditus ad antrum; demonstrated on both the axial and coronal images
- 28. Mesotympanum âĒ The mesotympanum contains the ossicular chain âĒ Oval and round window âĒ Long process of the Incus âĒ Stapes âĒ Handle of Malleus âĒ Facial nerve Canal
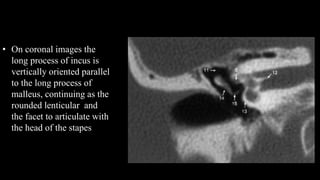
- 29. âĒ On coronal images the long process of incus is vertically oriented parallel to the long process of malleus, continuing as the rounded lenticular and the facet to articulate with the head of the stapes
- 30. âĒ The stapes hub and crura are best demonstrated on axial images at the level of the oval window âĒ The stapes footplate sits in the oval window niche and cannot always be discretely identified on CT.