Cysts of oral regions
- 1. Cysts In The Oral Cavity Regions By: Naz Noori Burhan Oral surgery 5th Grade Group E
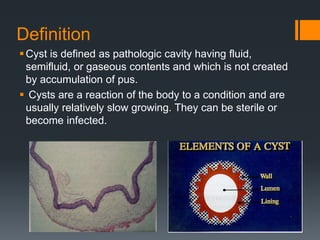
- 2. Definition ï§ Cyst is defined as pathologic cavity having fluid, semifluid, or gaseous contents and which is not created by accumulation of pus. ï§ Cysts are a reaction of the body to a condition and are usually relatively slow growing. They can be sterile or become infected.
- 3. TYPES OF CYSTS ï§ TRUE CYSTS: that which is lined by epithelium e.g dentigerous cyst, radicular cyst etc. ï§ PSEUDO CYSTS: not lined by epithelium, e.g. Solitary bone cyst, Aneurismal bone cyst etc
- 4. Classification Cysts of oral region Epithelial Lined Odontogenic Developmental Inflammatory Non Non Epithelial odontogenic Lined
- 5. Frequency Of Epithelial Cysts Of Oral Region 52.30% 5.60% 8% 11.60% 18.10% 4.20% SHEAR 2006 Radicular cyst Dentigerous cyst Odontogenic keratocyst Residual cyst Paradental cyst Unclassified odontogenic cysts
- 6. CLASSIFICATION OF JAW CYSTS: A.ODONTOGENIC: ï§ DEVELOPMENTAL ïž Odontogenic keratocyst. ïž Dentigerous cyst. ïž Eruption cyst. ïž Gingival cyst of infants. ïž Gingival cyst of adults. ïž Lateral periodontal cyst. ïž Calcifying odontogenic cyst. ïž Glandular odontogenic cyst. ï§ INFLAMMATORY ïžRadicular. ïž Residual. ïž Paradental. B.NON ODONTOGENIC ïž Nasopalatine duct. ïž Nasolabial cyst. ïž Globulomaxi l lary cyst.
- 7. Radicular ( Periapical ) cyst ï§ The most common odontogenic cyst of inflammatory origin. ï§ Related to apex of non-vital tooth. More common in anterior of maxilla , small cyst asymptomatic . ï§ Pain if infected with sinus ï§ Paresthesia and pathological fracture Differential diagnosis: ï§ Periapical granuloma. ï§ Periapical abscess . ï§ Cementblastoma. ï§ Traumatic bone cyst .
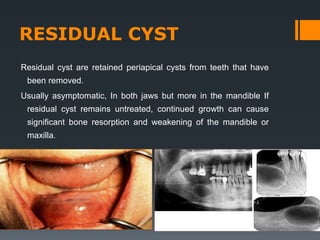
- 8. RESIDUAL CYST Residual cyst are retained periapical cysts from teeth that have been removed. Usually asymptomatic, In both jaws but more in the mandible If residual cyst remains untreated, continued growth can cause significant bone resorption and weakening of the mandible or maxilla.
- 9. Paradental cyst ï§ A cyst of inflammatory origin- occurring on lateral aspect of root of partially erupted mandibular 3rd molar with an associated history of pericoronitis ï§ Age: 20-40 years ï§ Tooth is vital ï§ Facial swelling ï§ Facial sinus in some cases
- 10. Odontogenic kerato cyst ï§ OKC is a cyst containing keratin and lined with keratinized epithelium. ï§ OKCâs arises from cell rests of the dental lamina. ï§ Ocure at any age More frequently in males than in females,. ï§ Mandible: posterior portion of body & ramus. ï§ Maxila: 3rd molar area.
- 11. DENTIGEROUS CYST ï§ Defined as cyst originating after crown of a tooth is completely formed, by accumulation of fluid between reduced dental epithelium and tooth substance. ï§ Encloses crown of impacted / unerupted tooth and is attached to its neck. ï§ Dentigerous cyst occurring in soft tissues, instead of bone. ï§ Mandibular 3rd molar, maxillary canine and maxillary 3rd molars.
- 12. 3 types: Central Lateral Circumfe rential
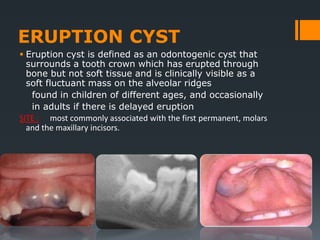
- 13. ERUPTION CYST ï§ Eruption cyst is defined as an odontogenic cyst that surrounds a tooth crown which has erupted through bone but not soft tissue and is clinically visible as a soft fluctuant mass on the alveolar ridges found in children of different ages, and occasionally in adults if there is delayed eruption SITE : most commonly associated with the first permanent, molars and the maxillary incisors.
- 14. GINGIVAL CYST ï§ A small developmental odontogenic cyst of the gingival soft tissue derived from the rests of the dental lamina ï§ Slowly enlarging, well circumscribed painless swelling. ï§ on facial aspect of free / attached gingiva and gingival papilla. ï§ Site: mandibular bicuspid/cuspid/incisor area. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS: ï§ Lateral periodontal cyst.
- 15. Lateral periodontal cyst ï§ Uncommon intra-osseous odontogenic cyst similar to gingival cyst of adult ï§ Itâs derived from rest of dental lamina ï§ Lateral to the root surface of erupted tooth Differential diagnosis: Middle age patient ,Both mandible and maxilla Canine and premolar of mandible ,Near the crest of ridge Asymptomatic, May produce bone expansion and pain Tooth is vital .Cyst less than 1 cm.
- 16. Nasopalatine (FISSURAL CYSTS) ï§ Nasopalatine canal usually contains remnants of the nasopalatine duct, a primitive organ of smell, and the nasopalatine vessels and nerves. forms in the nasopalatine canal,, Pressure of cyst on adjacent nasopalatine nerve may cause burning sensation or numbness over palatal mucosa. ï§ Asymptomatic ï§ If extends posteriorly involving hard palate ï§(MEDIAN PALATAL CYST) ï§ if expands anteriorly between central incisors,destroying or expanding labial plate of bone and causing teeth to diverge MEDIAN ANTERI OR MAXILLARY CYST
- 17. Nasopalatine
- 18. Simple/Solitary Bone Cyst ï§Traumatic bone cyst , or hemorrhagic bone cyst. ï§ Children and adolescent, Mandibular premolar and molar ,rarely in maxilla ï§ Painless swelling ,Round radio-lucent and less sharply defined ï§ Bony wall lined by thin loose C.T.
- 19. Treatment ï§ Cysts of the jaws are treated in one of the following four basic methods: (1) Enucleation, (2) Marsupialization, (3) A staged combination of the two procedures, and (4) Enucleation with curettage.
- 20. 1. Enucleation ï§ Enucleation: This technique involves complete removal of the cystic sac and healing of the wound by primary intention. This is the most satisfactory method of treatment of a cyst and is indicated in all cases where cysts are involved, whose wall may be removed without damaging adjacent teeth and other anatomic structures. ï§The surgical procedure for treatment of a cyst with enucleation includes the following steps: 1. Reflection of a mucoperiosteal flap. 2. Removal of bone and exposure of part of the cyst. 3. Enucleation of the cystic sac. 4. Care of the wound and suturing.
- 21. Enuculation
- 22. Surgical removal the of the cyst
- 23. 2.Marsupialization ï§ This method is usually employed for the removal of large cysts by opening a surgical window above the lesion. ï§ A circular incision is made, which includes the mucoperiosteum, the underlying perforated (usually) bone, and the respective wall of the cystic sac. ï§ Then the contents of the cyst are evacuated, and interrupted sutures are placed around the periphery of the cyst , suturing the mucoperiosteum and the cystic wall together. ï§ Afterwards, the cystic cavity is irrigated with saline solution and packed with iodoform gauze.
- 24. Technique of Marsupiaiization ï§1) Anesthesia. ï§2) Aspiration. ï§3) Incision. ï§4) Removal of bone. ï§5) Removal of cystic lining specimen. ï§6) Visual examination of residual cystic lining. ï§7) Irrigation of cystic cavity. ï§8) Suturing Cystic lining sutured with the edge of oral mucosa.
- 25. Marsupialization method. Circular incision includes mucosa and periosteum. Exposure of buccal cortical plate and removal of portion of bone with round bur Exposure of cyst after removal of bone Suturing of wound margins with cystic wall Packing of cystic cavity with iodoform gauze Cystic cavity after insertion of gauze
- 26. Marsupialization
- 27. Refrences ï§ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cysts_of_the_jaws ï§ http://www.gorlingroup.org/jupgrade/index.php/about-gorlin-syndrome/ 11-jaw-cysts ï§ http://www.slideshare.net/makkahguys/jaw-bone-chttp:// www.slideshare.net/JanmiPascual/cysts-of-oral-region- 5?related=1yst ï§ https://www.bestdentistguide.com/oral-cysts