Delphine Bard HSE
0 likes304 views
Working safely with Nanomaterials in R&D laboratories: an update.
1 of 23
Download to read offline




















Ad
Recommended
10.4 Rossbach
10.4 RossbachKate Jones
╠²
- The study examined the uptake and elimination of permethrin in 30 male volunteers who wore permethrin-treated clothing for forestry workers for 8 hours on three separate occasions under different conditions.
- Biomonitoring of urine samples found that permethrin exposure peaked 8-16 hours after use and could be detected for up to 144 hours, with an average elimination half-life of 30 hours. Over 50% of subjects exceeded environmental reference values after one-time use.
- Internal exposure increased with hot/humid conditions and physical activity, likely due to higher dermal absorption from increased skin perfusion and sweat. Accumulation may occur with daily use.Wendy Jones Loughborough University
Wendy Jones Loughborough UniversityKate Jones
╠²
Working safely with Nanomaterials in R&D laboratories: an update.Pieter van Broekhuizen IVAM
Pieter van Broekhuizen IVAMKate Jones
╠²
Working safely with Nanomaterials in R&D laboratories: an update.John Mackenzie Thomas Swan
John Mackenzie Thomas SwanKate Jones
╠²
Working safely with Nanomaterials in R&D laboratories: an update.Claire Wienburg University of Bristol
Claire Wienburg University of BristolKate Jones
╠²
Working safely with Nanomaterials in R&D laboratories: an update.Stewart Kowalczyk
Stewart KowalczykKate Jones
╠²
This document summarizes research on the disposal and impacts of chlorinated solvents in a local community. It finds that up to 6.8 ppb of chlorinated benzene was found in 26 homes near known disposal sites for chlorinated solvents. Testing of residents found elevated levels of urinary markers indicating early kidney dysfunction in over half of participants, though follow up testing showed improvement. While exposure to chlorinated benzene can cause kidney damage, other pollution sources may have also contributed to local renal disease rates. The document reviews the toxicology of chlorinated benzene and differences in risk assessments between regulatory agencies.Kalin
KalinKate Jones
╠²
This document discusses the use of comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography with time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GCxGC TOFMS) for environmental forensics analysis. It introduces GCxGC TOFMS, describing how it provides improved separation of compounds compared to traditional GC. Applications discussed include analysis of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in bird tissues to determine geographic origin, and analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in coal tar samples to identify the type of distillation process and determine the source. Statistical methods are applied to GCxGC TOFMS data from coal tar samples to accurately classify unknown samples. The document concludes the technique is effective for environmental forensicsPaton
PatonKate Jones
╠²
This document discusses fractionating hydrocarbons for hazard and risk assessment through chemical and biological analysis. It describes extracting oil from contaminated soils and peat for analysis, and using extraction, fractionation, and indicator compounds to assess risks to human health and the environment from weathered petroleum hydrocarbons. Biological assays on the extracts include tests with microbes, plants, earthworms, and models to predict human and environmental exposure and toxicity.Stuart
StuartKate Jones
╠²
This document summarizes emerging organic groundwater contaminants and their transformation products. It defines emerging contaminants as anthropogenic organic compounds and their transformation products that are increasingly detected due to changes in chemical use, advances in analysis, and improved monitoring. Many emerging contaminants come from sources like wastewater discharge, manure/sludge application, and septic tanks. Common emerging contaminant groups discussed include pesticides, pharmaceuticals, personal care products, industrial compounds, and hormones. The document examines the pathways these contaminants take to groundwater and the processes controlling their subsurface migration. It also provides examples of specific contaminants frequently detected in UK groundwater and discusses their degradation.Weber
WeberKate Jones
╠²
The document summarizes the development of the Environmental Fate Simulator (EFS), a tool being created by the US Environmental Protection Agency to predict the degradation pathways of organic chemicals in groundwater. The EFS will integrate process science, cheminformatics applications, and modeling software to provide physicochemical properties and simulate reaction pathways of chemicals in various environmental media and conditions. It is being developed to help evaluate thousands of chemicals where limited data currently exists. The EFS will automate the simulation of chemical fate through various environmental scenarios to support exposure and risk assessments.Boxall
BoxallKate Jones
╠²
Pharmaceuticals are released into the environment through sewage sludge applied to agricultural soils. Studies have detected various pharmaceuticals in sewage sludge samples at concentrations that could potentially affect soil organisms. Laboratory studies show some pharmaceuticals can accumulate in earthworm tissues. Modeling indicates factors like a drug's properties, soil characteristics, and organism type influence bioaccumulation. While risks to human health are generally low, certain levels of pharmaceutical exposure may subtly affect non-target species like invertebrates through mechanisms related to a drug's mode of action. Further research is still needed to fully understand pharmaceutical impacts on terrestrial environments.11.3 Smolders
11.3 SmoldersKate Jones
╠²
This document summarizes a human biomonitoring study that collected all urine samples from 8 participants over a continuous 6-day period. Biomarkers for metals and organic compounds were measured to understand intra- and inter-individual variability in biomarker concentrations and determine optimal urine sampling strategies. Biomarker levels varied within and between individuals depending on compound half-life and exposure frequency from personal care products. High intra-individual variability was observed for biomarkers with short half-lives like methyl paraben, while cadmium showed low variability. The study provides insights into interpreting biomarker measurements from single spot samples versus multiple samples over time.7.3 Smolders
7.3 SmoldersKate Jones
╠²
The document discusses a study that measured biomarkers in mothers and children across 17 European countries. The study aimed to perform human biomonitoring in a harmonized way to obtain reliable and comparable data. The document examines whether differences in environmental concentrations and lifestyle factors can explain differences in biomarker levels among countries. It finds that cadmium levels correlated with air emissions and food quality, mercury levels correlated with fish consumption, and cotinine levels in non-smokers correlated with strength of anti-smoking laws. However, limitations included a lack of representative national data and differences in data quality among countries. Continued efforts are needed to improve interpretation through more harmonized datasets.A.2 Galea
A.2 GaleaKate Jones
╠²
This document summarizes a study methodology that aims to determine pesticide exposure levels in residents living near agricultural land through the analysis of urine samples. The study recruited farmers and residents across 3 regions in the UK. Urine samples were collected from residents on a weekly basis, as well as 1-2 days after pesticide spray events to compare metabolite levels within and outside the spraying season. The study also aims to compare measured urinary levels to exposure estimates from regulatory risk assessments. Over 3,000 urine samples were collected in total. Statistical analysis of the results will help evaluate current risk assessment methods and estimate long-term pesticide exposure levels for residents.1.4 Leng
1.4 LengKate Jones
╠²
1. A sensitive analytical method was developed to detect MDA-Val-Hyd, a specific biomarker for exposure to MDI, in human blood.
2. Application of the method to workers exposed to MDI found the biomarker present in their blood, demonstrating its ability to measure MDI exposure levels.
3. Background levels of MDA-Val-Hyd were found to be below detection limits in unexposed individuals and those with only low inhalation exposure to MDI.6.4 Leng
6.4 LengKate Jones
╠²
This document summarizes research on determining exposure to the plasticizer bis(2-propylheptyl)phthalate (DPHP) in the general population. Researchers developed analytical methods to measure DPHP metabolite levels in human urine using GC-MS and LC-MS/MS. A human elimination study found the main metabolites were excreted within 48 hours, with 24% of the dose detected. Further studies detected DPHP metabolites in some general population urine samples at low levels, showing evidence of widespread exposure.9.3 Cocker
9.3 CockerKate Jones
╠²
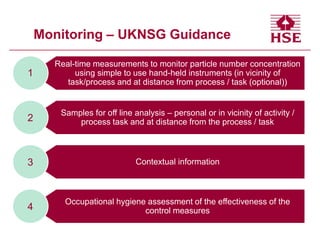
This document discusses biological monitoring (BM) guidance values and their uses and requirements. It provides the following key points:
1) BM is a tool for assessing exposure that is used by occupational health providers, hygienists, employers, researchers and regulators to evaluate compliance, exposure controls, and identify potential health issues.
2) Guidance values are set by various organizations using different methods, and the same substance may have different values. Exceeding a value indicates exposure controls should be examined and exposure reduced.
3) Requirements for BM include ethics, appropriate sample matrices, analytes related to toxicity, and validated analytical methods. Guidance values also require data linking BM levels to exposure, health effects, andB.1 Laitinen
B.1 LaitinenKate Jones
╠²
This study analyzed fire fighters' multiple exposures to perfluoroalkyl acids (PFCs) and 2-butoxyethanol found in aqueous film-forming foams (AFFFs). The study aimed to analyze PFC profiles in used foam, assess firefighter exposure, and evaluate eight AFFFs. Serum samples before and after training sessions found increased excretion of PFOA, PFNA, PFHxS, and PFOS in firefighters. Urinary samples also showed exposure to 2-butoxyethanol exceeding limits for the general population. The study concluded that firefighter exposure to PFCs was higher than the general population and increased during training. PFHxS showed the highest increase, making it1.2 Mraz
1.2 MrazKate Jones
╠²
This document discusses protein adducts as biomarkers of exposure to alkylating agents. It begins by introducing protein adducts and globin adducts specifically as surrogate biomarkers for DNA adducts. The document then details a research plan to test the hypothesis that globin adducts undergo degradation, producing free amino acid adducts that are excreted in urine and could serve as non-invasive biomarkers of exposure. Initial results are presented demonstrating the successful synthesis of model amino acid adducts and detection of some administered adducts and their metabolites in rat urine. Further research is planned to study the fate of native globin adducts in vivo.11.1 Koch
11.1 KochKate Jones
╠²
This document summarizes a study that aimed to validate biomarkers in urine for assessing exposure to N-ethyl-2pyrrolidone (NEP). The study identified and characterized two metabolites of NEP - 5-HNEP and 2-HESI - that are analogous to known metabolites of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone. Three men were given a single oral dose of NEP and their urine was collected over 4 days to analyze metabolite levels. The study determined elimination kinetics, metabolic conversion factors, and concluded that the metabolites can be used in human biomonitoring studies to assess occupational and environmental exposure to NEP. However, 5-HNEP alone may underestimate exposure compared to11.2 Fustinoni
11.2 FustinoniKate Jones
╠²
This study compared the use of hair and urine samples to biomonitor exposure to the herbicide terbutylazine (TBA) in agricultural workers and rural residents. The researchers found that (1) desethylterbutylazine (DET) in urine samples collected after exposure and before the next shift is a biomarker for short-term TBA exposure, (2) TBA can be detected in human hair and levels increase with repeated exposure, and (3) hair TBA detected exposure in rural residents not seen in urine, suggesting hair may be a better indicator of long-term low-level exposure. The study demonstrates the potential for hair and urine samples to biomonitor both short and long-term pesticideScience Holiday Homework (interesting slide )
Science Holiday Homework (interesting slide )aryanxkohli88
╠²
science holiday homework
good for childrenDeath in Sleep Apnea: Who and How It Kills
Death in Sleep Apnea: Who and How It KillsRichard Castriotta
╠²
Evaluation of mortality in obstructive sleep apnea.More Related Content
More from Kate Jones (20)
John Mackenzie Thomas Swan
John Mackenzie Thomas SwanKate Jones
╠²
Working safely with Nanomaterials in R&D laboratories: an update.Claire Wienburg University of Bristol
Claire Wienburg University of BristolKate Jones
╠²
Working safely with Nanomaterials in R&D laboratories: an update.Stewart Kowalczyk
Stewart KowalczykKate Jones
╠²
This document summarizes research on the disposal and impacts of chlorinated solvents in a local community. It finds that up to 6.8 ppb of chlorinated benzene was found in 26 homes near known disposal sites for chlorinated solvents. Testing of residents found elevated levels of urinary markers indicating early kidney dysfunction in over half of participants, though follow up testing showed improvement. While exposure to chlorinated benzene can cause kidney damage, other pollution sources may have also contributed to local renal disease rates. The document reviews the toxicology of chlorinated benzene and differences in risk assessments between regulatory agencies.Kalin
KalinKate Jones
╠²
This document discusses the use of comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography with time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GCxGC TOFMS) for environmental forensics analysis. It introduces GCxGC TOFMS, describing how it provides improved separation of compounds compared to traditional GC. Applications discussed include analysis of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in bird tissues to determine geographic origin, and analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in coal tar samples to identify the type of distillation process and determine the source. Statistical methods are applied to GCxGC TOFMS data from coal tar samples to accurately classify unknown samples. The document concludes the technique is effective for environmental forensicsPaton
PatonKate Jones
╠²
This document discusses fractionating hydrocarbons for hazard and risk assessment through chemical and biological analysis. It describes extracting oil from contaminated soils and peat for analysis, and using extraction, fractionation, and indicator compounds to assess risks to human health and the environment from weathered petroleum hydrocarbons. Biological assays on the extracts include tests with microbes, plants, earthworms, and models to predict human and environmental exposure and toxicity.Stuart
StuartKate Jones
╠²
This document summarizes emerging organic groundwater contaminants and their transformation products. It defines emerging contaminants as anthropogenic organic compounds and their transformation products that are increasingly detected due to changes in chemical use, advances in analysis, and improved monitoring. Many emerging contaminants come from sources like wastewater discharge, manure/sludge application, and septic tanks. Common emerging contaminant groups discussed include pesticides, pharmaceuticals, personal care products, industrial compounds, and hormones. The document examines the pathways these contaminants take to groundwater and the processes controlling their subsurface migration. It also provides examples of specific contaminants frequently detected in UK groundwater and discusses their degradation.Weber
WeberKate Jones
╠²
The document summarizes the development of the Environmental Fate Simulator (EFS), a tool being created by the US Environmental Protection Agency to predict the degradation pathways of organic chemicals in groundwater. The EFS will integrate process science, cheminformatics applications, and modeling software to provide physicochemical properties and simulate reaction pathways of chemicals in various environmental media and conditions. It is being developed to help evaluate thousands of chemicals where limited data currently exists. The EFS will automate the simulation of chemical fate through various environmental scenarios to support exposure and risk assessments.Boxall
BoxallKate Jones
╠²
Pharmaceuticals are released into the environment through sewage sludge applied to agricultural soils. Studies have detected various pharmaceuticals in sewage sludge samples at concentrations that could potentially affect soil organisms. Laboratory studies show some pharmaceuticals can accumulate in earthworm tissues. Modeling indicates factors like a drug's properties, soil characteristics, and organism type influence bioaccumulation. While risks to human health are generally low, certain levels of pharmaceutical exposure may subtly affect non-target species like invertebrates through mechanisms related to a drug's mode of action. Further research is still needed to fully understand pharmaceutical impacts on terrestrial environments.11.3 Smolders
11.3 SmoldersKate Jones
╠²
This document summarizes a human biomonitoring study that collected all urine samples from 8 participants over a continuous 6-day period. Biomarkers for metals and organic compounds were measured to understand intra- and inter-individual variability in biomarker concentrations and determine optimal urine sampling strategies. Biomarker levels varied within and between individuals depending on compound half-life and exposure frequency from personal care products. High intra-individual variability was observed for biomarkers with short half-lives like methyl paraben, while cadmium showed low variability. The study provides insights into interpreting biomarker measurements from single spot samples versus multiple samples over time.7.3 Smolders
7.3 SmoldersKate Jones
╠²
The document discusses a study that measured biomarkers in mothers and children across 17 European countries. The study aimed to perform human biomonitoring in a harmonized way to obtain reliable and comparable data. The document examines whether differences in environmental concentrations and lifestyle factors can explain differences in biomarker levels among countries. It finds that cadmium levels correlated with air emissions and food quality, mercury levels correlated with fish consumption, and cotinine levels in non-smokers correlated with strength of anti-smoking laws. However, limitations included a lack of representative national data and differences in data quality among countries. Continued efforts are needed to improve interpretation through more harmonized datasets.A.2 Galea
A.2 GaleaKate Jones
╠²
This document summarizes a study methodology that aims to determine pesticide exposure levels in residents living near agricultural land through the analysis of urine samples. The study recruited farmers and residents across 3 regions in the UK. Urine samples were collected from residents on a weekly basis, as well as 1-2 days after pesticide spray events to compare metabolite levels within and outside the spraying season. The study also aims to compare measured urinary levels to exposure estimates from regulatory risk assessments. Over 3,000 urine samples were collected in total. Statistical analysis of the results will help evaluate current risk assessment methods and estimate long-term pesticide exposure levels for residents.1.4 Leng
1.4 LengKate Jones
╠²
1. A sensitive analytical method was developed to detect MDA-Val-Hyd, a specific biomarker for exposure to MDI, in human blood.
2. Application of the method to workers exposed to MDI found the biomarker present in their blood, demonstrating its ability to measure MDI exposure levels.
3. Background levels of MDA-Val-Hyd were found to be below detection limits in unexposed individuals and those with only low inhalation exposure to MDI.6.4 Leng
6.4 LengKate Jones
╠²
This document summarizes research on determining exposure to the plasticizer bis(2-propylheptyl)phthalate (DPHP) in the general population. Researchers developed analytical methods to measure DPHP metabolite levels in human urine using GC-MS and LC-MS/MS. A human elimination study found the main metabolites were excreted within 48 hours, with 24% of the dose detected. Further studies detected DPHP metabolites in some general population urine samples at low levels, showing evidence of widespread exposure.9.3 Cocker
9.3 CockerKate Jones
╠²
This document discusses biological monitoring (BM) guidance values and their uses and requirements. It provides the following key points:
1) BM is a tool for assessing exposure that is used by occupational health providers, hygienists, employers, researchers and regulators to evaluate compliance, exposure controls, and identify potential health issues.
2) Guidance values are set by various organizations using different methods, and the same substance may have different values. Exceeding a value indicates exposure controls should be examined and exposure reduced.
3) Requirements for BM include ethics, appropriate sample matrices, analytes related to toxicity, and validated analytical methods. Guidance values also require data linking BM levels to exposure, health effects, andB.1 Laitinen
B.1 LaitinenKate Jones
╠²
This study analyzed fire fighters' multiple exposures to perfluoroalkyl acids (PFCs) and 2-butoxyethanol found in aqueous film-forming foams (AFFFs). The study aimed to analyze PFC profiles in used foam, assess firefighter exposure, and evaluate eight AFFFs. Serum samples before and after training sessions found increased excretion of PFOA, PFNA, PFHxS, and PFOS in firefighters. Urinary samples also showed exposure to 2-butoxyethanol exceeding limits for the general population. The study concluded that firefighter exposure to PFCs was higher than the general population and increased during training. PFHxS showed the highest increase, making it1.2 Mraz
1.2 MrazKate Jones
╠²
This document discusses protein adducts as biomarkers of exposure to alkylating agents. It begins by introducing protein adducts and globin adducts specifically as surrogate biomarkers for DNA adducts. The document then details a research plan to test the hypothesis that globin adducts undergo degradation, producing free amino acid adducts that are excreted in urine and could serve as non-invasive biomarkers of exposure. Initial results are presented demonstrating the successful synthesis of model amino acid adducts and detection of some administered adducts and their metabolites in rat urine. Further research is planned to study the fate of native globin adducts in vivo.11.1 Koch
11.1 KochKate Jones
╠²
This document summarizes a study that aimed to validate biomarkers in urine for assessing exposure to N-ethyl-2pyrrolidone (NEP). The study identified and characterized two metabolites of NEP - 5-HNEP and 2-HESI - that are analogous to known metabolites of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone. Three men were given a single oral dose of NEP and their urine was collected over 4 days to analyze metabolite levels. The study determined elimination kinetics, metabolic conversion factors, and concluded that the metabolites can be used in human biomonitoring studies to assess occupational and environmental exposure to NEP. However, 5-HNEP alone may underestimate exposure compared to11.2 Fustinoni
11.2 FustinoniKate Jones
╠²
This study compared the use of hair and urine samples to biomonitor exposure to the herbicide terbutylazine (TBA) in agricultural workers and rural residents. The researchers found that (1) desethylterbutylazine (DET) in urine samples collected after exposure and before the next shift is a biomarker for short-term TBA exposure, (2) TBA can be detected in human hair and levels increase with repeated exposure, and (3) hair TBA detected exposure in rural residents not seen in urine, suggesting hair may be a better indicator of long-term low-level exposure. The study demonstrates the potential for hair and urine samples to biomonitor both short and long-term pesticideRecently uploaded (20)
Science Holiday Homework (interesting slide )
Science Holiday Homework (interesting slide )aryanxkohli88
╠²
science holiday homework
good for childrenDeath in Sleep Apnea: Who and How It Kills
Death in Sleep Apnea: Who and How It KillsRichard Castriotta
╠²
Evaluation of mortality in obstructive sleep apnea.What is Skeleton system.pptx by aahil sir
What is Skeleton system.pptx by aahil sirbhatbashir421
╠²
science, any system of knowledge that is concerned with the physical world and its phenomena and that entails unbiased observations and systematic experimentation. In general, a science involves a pursuit of knowledge covering general truths or the operations of fundamental laws.
Science can be divided into different branches based on the subject of study. The physical sciences study the inorganic world and comprise the fields of astronomy, physics, chemistry, and the Earth sciences. The biological sciences such as biology and medicine study the organic world of life and its processes. Social sciences like anthropology and economics study the social and cultural aspects of human behaviour.
Science is further treated in a number of articles. For the history of Western and Eastern science, see science, history of. For the conceptualization of science and its interrelationships with culture, see science, philosophy of. For the basic aspects of the scientific approach, see physical science, principles of; and scientific method.
Model of a molecule. Atom, Biology, Molecular Structure, Science, Science and Technology. Homepage 2010 arts and entertainment, history and society
Britannica Quiz
Science Quiz
The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica
This article was most recently revised and updated by Encyclopaedia Britannica.
physics
Table of Contents
Introduction & Top Questions
The scope of physics
The methodology of physics
Relations between physics and other disciplines and society
References & Edit History
Related Topics
Images & Videos
Bernoulli model of gas pressureillustration of Robert Hooke's law of elasticity of materialsLaser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA)curved space-timetemperature scalesBrownian particleElectromagnetic radiationDiffraction gratingMillikan oil-drop experiment
Robert Millikan's method for measuring the charge of an electron
For Students
Diffraction grating
physics summary
Quizzes
Michael Faraday (L) English physicist and chemist (electromagnetism) and John Frederic Daniell (R) British chemist and meteorologist who invented the Daniell cell.
Faces of Science
Italian-born physicist Dr. Enrico Fermi draws a diagram at a blackboard with mathematical equations. circa 1950.
Physics and Natural Law
Italian physicist Guglielmo Marconi at work in the wireless room of his yacht Electra, c. 1920.
All About Physics Quiz
atom. Orange and green illustration of protons and neutrons creating the nucleus of an atom.
Another Physics Quiz
Encyclopaedia Britannica thistle graphic to be used with a Mendel/Consumer quiz in place of a photograph.
How Much Do You Know About Physics?
Related Questions
Why does physics work in SI units?
Read Next
Highway Night Traffic Portland, drive, driving, car, automobile.
What's the Difference Between Speed and Velocity?
Galaxy clusters like Abell 2744 can act as a natural cosmic lens, magnifying light from more distant, background objects through gravity. Pneumonia Presentation for CPG Review and Mastery
Pneumonia Presentation for CPG Review and MasteryJayricDepalobos
╠²
Pneumonia Presentation for Internal Medicine DepartmentHow Psychology Can Power Product Decisions: A Human-Centered Blueprint- Shray...
How Psychology Can Power Product Decisions: A Human-Centered Blueprint- Shray...ShrayasiRoy2
╠²
In an era where users are bombarded with endless choices, capturing attention and driving meaningful engagement isn't just about building features ŌĆö it's about understanding what drives human behavior at its core. This presentation offers a deep dive into how psychological principles can inform smarter, more intuitive product decisions. ItŌĆÖs not just theory ŌĆö itŌĆÖs a hands-on blueprint for applying human-centered thinking at every stage of product development.
Grounded in behavioral science, consumer psychology, and cognitive design, this deck unpacks the key psychological drivers behind user motivation, decision-making, emotional engagement, and habit formation. From attention economics and dopamine-driven interactions to trust cues, loss aversion, and the paradox of choice ŌĆö you'll see how to harness what the mind naturally does to build digital products people donŌĆÖt just useŌĆ” they return to, talk about, and even advocate for.
WeŌĆÖll explore:
Cognitive biases that shape user perception and choices ŌĆö and how to use them to your advantage without crossing ethical lines.
Emotional design principles that build trust, trigger desire, and turn features into feelings.
User behavior loops that build stickiness, deepen retention, and create emotional investments.
Psychological friction ŌĆö when to reduce it for conversion, and when to add it for intentionality.
Dark patterns vs. ethical persuasion ŌĆö the thin line between influence and manipulation.
A/B testing with a psychological lens ŌĆö learning not just what works, but why it works.
This is more than UX research or product marketing fluff. ItŌĆÖs a call to build with empathy, backed by science, and sharpened by real-world product thinking. Whether youŌĆÖre shaping onboarding flows, gamifying engagement, designing pricing models, or rethinking retention strategies ŌĆö this deck will arm you with a new lens: the human mind.
Perfect for product managers, growth strategists, UX designers, behavioral scientists, and anyone serious about building products that resonate, retain, and inspire action.
Because at the heart of every great productŌĆ” is a human.
LetŌĆÖs start building for the brain ŌĆö not just the screen.Impact of Network Topologies on Blockchain Performance
Impact of Network Topologies on Blockchain Performancevschiavoni
╠²
Best Student Paper Award at ACM DEBS 2025.
Paper here:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3701717.3730540
Since blockchains are increasingly adopted in real-world applications, it is of paramount importance to evaluate their performance across diverse scenarios. Although the network infrastructure plays a fundamental role, its impact on performance remains largely unexplored. Some studies evaluate blockchain in cloud environments, but this approach is costly and difficult to reproduce. We propose a cost-effective and reproducible environment that supports both cluster-based setups and emulation capabilities and allows the underlying network topology to be easily modified. We evaluate five industry-grade blockchains ŌĆō Algorand, Diem, Ethereum, Quorum, and Solana ŌĆō across five network topologies ŌĆō fat-tree, full mesh, hypercube, scale-free, and torus ŌĆō and different realistic workloads ŌĆō smart contract requests and transfer transactions. Our benchmark framework, Lilith, shows that full mesh, hypercube, and torus topologies improve blockchain performance under heavy workloads. Algorand and Diem perform consistently across the considered topologies, while Ethereum remains robust but slower.Cloud Collaboration Market Challenges, Drivers, Trends, and Forecast by 2031
Cloud Collaboration Market Challenges, Drivers, Trends, and Forecast by 2031moresonali406
╠²
The report is segmented by Component (Solution, Service); Deployment (Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Hybrid Cloud); Organization Size (Large Enterprises, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)); Vertical (BFSI, Consumer Goods And Retail, Education, Government and Public Sector, Healthcare and Life Sciences, Manufacturing, Media and Entertainment, Telecommunication and ITES, Others). The global analysis is further broken-down at regional level and major countries. The report offers the value in USD for the above analysis and segmentsGas Exchange in Insects and structures 01
Gas Exchange in Insects and structures 01PhoebeAkinyi1
╠²
Description of structures involved in gaseous exchangeRelazione di laboratorio Idrolisi dell'amido (in inglese)
Relazione di laboratorio Idrolisi dell'amido (in inglese)paolofvesco
╠²
relazione di laboratorio sull'idrolisi dell'amido Science 8 Quarter 4 first quiz digestive system.docx
Science 8 Quarter 4 first quiz digestive system.docxjunefermunez
╠²
Quiz for the topic Digestive System. 4th QaurterSynthesis and characterization of Thiazole derivatives of N-substituted lsatin
Synthesis and characterization of Thiazole derivatives of N-substituted lsatinProfessional Content Writing's
╠²
Thiazole derivatives of N-substituted isatin have attracted significant interest due to their wide-ranging applications in medicinal chemistry, pharmaceuticals, and materials science. These compounds exhibit diverse biological activities, making them promising drug candidates, while their unique chemical structures offer potential in designing advanced functional materials. This presentation focuses on the synthesis and characterization of these derivatives through targeted chemical reactions involving various substituents on the isatin and thiazole cores, enabling the fine-tuning of their biological and physical properties. Characterization techniques such as NMR, FT-IR, Mass Spectrometry, and X-ray crystallography are employed to confirm molecular structures and analyze solid-state properties. These methods provide critical insights into the structureŌĆōactivity relationships of the synthesized compounds. Our presentation highlights the synthetic pathways, structural elucidation, and potential applications of thiazole-based N-substituted isatin derivatives, aiming to support ongoing advancements in drug discovery and material development.
About Author:
Noor Zulfiqar is an award-winning chemist, Premium member of American Chemical Society (ACS), certified publisher & peer reviewer, and an experienced academic lecturer. As a professional content creator, she offers top-tier presentation design, research writing, and scientific content development services. Her multidisciplinary expertise spans computational science, chemistry, nanotechnology, environmental studies, socio-economics, human resource management, life sciences, engineering management, medical and pharmaceutical sciences, and business, her work ensures clarity, creativity, and academic excellence. Her services are ideal for those seeking impactful, visually compelling content tailored to diverse academic and research needs.
For collaborations or custom-designed academic content, feel free to reach out!
Contact:
Email: professionalwriter94@outlook.com
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/share/1LgwpoyLDg/
Website: https://professional-content-writings.jimdosite.comMatt Ridley: Economic Evolution and Ideas that have Sex
Matt Ridley: Economic Evolution and Ideas that have SexConservative Institute / Konzervat├Łvny in┼Ītit├║t M. R. ┼Ātef├Īnika
╠²
Matt Ridley is a British independent science popularizer, journalist, entrepreneur, and author of several bestselling books, for which he has received numerous awards. He focuses primarily on the economic, biological, and environmental dimensions of the spontaneous functioning and advancement of human society. Synthesis and characterization of Thiazole derivatives of N-substituted lsatin
Synthesis and characterization of Thiazole derivatives of N-substituted lsatinProfessional Content Writing's
╠²
Matt Ridley: Economic Evolution and Ideas that have Sex
Matt Ridley: Economic Evolution and Ideas that have SexConservative Institute / Konzervat├Łvny in┼Ītit├║t M. R. ┼Ātef├Īnika
╠²
Ad