Deptdefinitions
- 1. English Evaluate– comes after analysis. Judging how effective the text is Analyse – pick out words, phrases, prose etc Details of language Explain– clarify. You need to analyse before you can explain Description – senses, simile, metaphor, adjective adverb Varied sentence structures
- 2. Science Analyse– State what data is telling me Use data to identify relationships When you then come up with a conclusion you are evaluating Evaluate – quantify errors in an experiment Look how to improve the experiment Describe – state a fact
- 3. History Evaluate – informed judgement based on evidence. Weigh up importance of different factors Describe– say what something is like Explain – To say why something happens Analysis – break something into its parts
- 4. Change and Continuity Words (and definitions) for different rates of change Words (and definitions) for the extent of change Words (and definitions) for the nature of change When you are describing or explaining change, you need to think about: • the rate of the change (how quick or slow it was) • the extent of change (was it big, small or none at all-continuity) • the nature of the change(is it to do with people, or money etc) Words Examples Fast (Rapid, quick, swift) e.g. a lightening strike Slow (gradual, measured, steady) e.g. a person growing in height Uneven (Undulating, patchy, erratic) e.g. waves in the sea going up and down Word Definition Economic Change to do with money and jobs Political Change to do with laws and leaders Social Change to do with people and how they live Cultural Change to religion and customs Strategic Change to tactics, plans and relationships between countries Structural Change to how people’s lives are organised Physical Change to buildings and the environment Words Examples Big (Massive, dramatic, striking) e.g. Winning the entire lottery Small (Minor, lesser, slight) e.g Winning £100 on the lottery Big but slow (evolutionary) e.g A cliff wearing away Big and fast (seismic, explosive, cataclysmic, revolutionary) e.g. a building being blown up and destroyed Widespread (Macro, pervasive) e.g. the weather gets colder all across the UK in Winter Isolated (Micro, limited, restricted) e.g. it starts raining in Hitchin but nowhere else Unstable (bumpy) e.g. A football team are at the top of the table but might not be next week Continuity This means when something stays the same and does not change e.g. the monarchy is an example of British history in British history
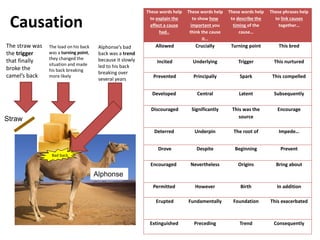
- 5. Causation These words help to explain the effect a cause had.. These words help to show how important you think the cause it… These words help to describe the timing of the cause… These phrases help to link causes together… Allowed Crucially Turning point This bred Incited Underlying Trigger This nurtured Prevented Principally Spark This compelled Developed Central Latent Subsequently Discouraged Significantly This was the source Encourage Deterred Underpin The root of Impede… Drove Despite Beginning Prevent Encouraged Nevertheless Origins Bring about Permitted However Birth In addition Erupted Fundamentally Foundation This exacerbated Extinguished Preceding Trend Consequently Alphonse Bad back Straw The straw was the trigger that finally broke the camel’s back The load on his back was a turning point, they changed the situation and made his back breaking more likely Alphonse’s bad back was a trend because it slowly led to his back breaking over several years
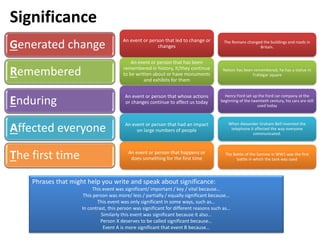
- 6. Significance Generated change Remembered Enduring Affected everyone The first time An event or person that led to change or changes An event or person that has been remembered in history, it/they continue to be written about or have monuments and exhibits for them An event or person that whose actions or changes continue to affect us today An event or person that had an impact on large numbers of people An event or person that happens or does something for the first time The Romans changed the buildings and roads in Britain. Nelson has been remembered, he has a statue in Trafalgar square Henry Ford set up the Ford car company at the beginning of the twentieth century, his cars are still used today When Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone it affected the way everyone communicated. The Battle of the Somme in WW1 was the first battle in which the tank was used Phrases that might help you write and speak about significance: This event was significant/ important / key / vital because… This person was more/ less / partially / equally significant because… This event was only significant in some ways, such as… In contrast, this person was significant for different reasons such as… Similarly this event was significant because it also… Person X deserves to be called significant because… Event A is more significant that event B because…
- 7. Listing Points/Examples Giving Examples (evidence) Linking to the Point (explaining) Changing Point/topic Contrasting firstly, secondly, finally for example which shows that… turning to… however in the first place for instance which proves that… as regards… on the other hand… to begin with such as this demonstrates… with regard to… …although… on top of this …as can be seen this reveals… concerning… despite this… in addition to this …as is shown by this indicates… as far as...is concerned on the contrary… more importantly take the case of… this evidence makes clear… moving on to… instead… in addition this can be proven by… which led to… because… now to consider… as for… …and… by contrast… …whereas… …also alternatively… …while… …as well Then again… …alternatively… furthermore another not only…but also what is more / moreover Emphasising Comparison Persuade Concession Summing up/Concluding mainly compared with… it is clear that… although… in conclusion… usually …in comparison with… …undoubtedly shows that… while it is true that… in summary… mostly similarly… opponents say… but… despite the fact that… to sum up… unfortunately in the same way… by far the most… in spite of… overall… most often likewise… it is certain that… despite this… on the whole… chiefly equally… undeniable however…yet… in short… primarily as with… definitely still… in brief… …are similar in that… it is irrefutable that… nevertheless… to conclude… correspondingly categorically It is fair that… so, to round off… deserves to be… It is reasonable… I want to describe… To describe is when you go into detail, painting a picture with words. You need to use lots of key words and lots of examples. In History you describe an event, a person, or something about people and society in the past. A Point + Example structure is good, and you may use contrasting, comparing and emphasising words to develop your description. I want to persuade or argue… To persuade or argue is to convince someone that your point is correct. You must use Point + Evidence + Explanation. But you must always respect other Points / ideas by explaining them too (PEE). You should contrast them with your opinion, and you might make some concessions, but you will emphasize your point over others.