Etiology of pulp diseases
- 3. The dental pulp loose connective tissue occupying a cavity lying in center of dentin.
- 4. Morphology
- 5. FUNCTIONS OF DENTAL PULP ? Nutrition : blood supply ? Sensation : temp ¨C vibration ¨C chemicals ? Formative : maintain of dentin ? Protective : formation of tertiary dentin ? Defensive : inflammatory response
- 6. Dentin Pulp corePredentin Odontoblasts layer Cell free zone Cell rich zone Histology
- 8. The nerve of pulp consist of : ? Afferent nerves : conduct impulses to be received as a pain ? Sympathetic fibers : regulation of micro circulation in pulp
- 9. Sensory fibers Large myelinated A-fibers A-alpha Touch pressure A-beta vibration A-gamma Mechano- receptor A-delta Pain temp Intermediate efferent B-fibers Small unmyelinated C-fibers Pain temp
- 10. C fibersA-delta fibers UnmylinatedMylinatedMylenation 2 m/s20 m/sConduction velocity DeepSuperficialLocation of terminals Throbbing dull But less bearable Sharp - fast But bearable Pain character High by tissue damageLow by hydrodynamicStimulation threshold
- 12. Normal pulp ?Free of spontaneous pain ?Moderate response to stimulus ?Response disappear when removal
- 13. Diagnosis Objective Subjective ? Visual and tactile ? Thermal testes ? Electrical testes ? Recent ? pain
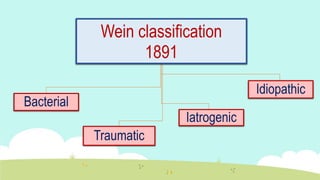
- 16. 1. Bacterial A- coronal ingress ? Caries: the most common cause of ingress of bacteria to pulp ? Fractured crown ? Anomalous tract: as dens invaginatus , dens evaginatus and radicular lingual groove
- 17. B- radicular ingress ? Caries: less common than coronal caries ? Retrogenic infection: periodontal pocket ? Hematogenic infection: anachoresis
- 18. 2. Traumatic A- acute ? Coronal fracture ? Radicular fracture ? Luxation ? Avulsion
- 19. B- chronic ? Attrition: physiological wear ? Abrasion: mechanical loss of tooth structure ? Erosion: chemical loss of tooth structure
- 20. 3. Iatrogenic ? Cavity preparation Heat Depth Desiccation Vibration Acid etching
- 21. ? Restoration Fractured restoration Leaky restoration Acid containing restorations
- 22. ? Periodontal curettage ? Periradicular curettage ? Rhinoplasty ? Osteotomy
- 23. ? local anesthesia ? Orthodontic movement ? Intubation for general anesthesia
- 24. 4. Idiopathic ? Aging ? Internal resorption ? Hereditary hypophosphatemia
- 26. Physical ? Thermal : . Large metallic restorations without base . . cavity preparation . . setting of some cements e.g. Acrylic resin .
- 27. ? Pressure ? Speed ? Depth of cutting ? presence or absence of insulating base
- 28. ? Electrical : presence of two dissimilar metals ( galvanism ) . ? Radiation : -Direct effect -Indirect effect
- 29. Mechanical ? Trauma ? cracked tooth syndrome ? Abrasion ? Lack of temporary coverage after crown- bridge preparation
- 30. ? operative procedures : operative procedures must taken during cavity preparation, ???? cavity depth ???? pulp exposure ???? pin insertion
- 31. ? Orthodontic movements : orthodontic movement , can lead to devitalization of the pulp and pulpal hemorrhage .
- 32. ? Deep periodontal curettage Deep periodontal curettage, leads to damaging the pulpal vessels, so it should be done after R.C.T
- 33. Chemical ? Dental materials ? Antibacterial agents
- 34. ? Dental materials * monomer in composite restorations . * Amalgam, has cytotoxic effect . *cements, some has potential irritation to pulp e.g. Free phosphoric acid in phosphate cements . * Etching agents , if placed over 15 seconds in dentin can cause chronic inflammation of the pulp .
- 35. ? Antibacterial agents * Antibacterial agents as silver nitrate, phenol and eugenol which was used to sterilize the cavity preparation have shown cytotoxic effects and causes inflammatory changes
- 36. Barodontalgia / Aerodontalgia symptom rather than a pathological pain caused by a change in barometric pressure