Formation aimaf-android-part1
- 1. Android Android Training Part 1 RGUIG Saad - AIMAF lundi 21 janvier 13 1
- 2. Android Morning Program : 1.General Introduction 2.Environment Setup 3.HelloWorl Application 4.Android Application Anatomy lundi 21 janvier 13 2
- 3. General Introduction : Android lundi 21 janvier 13 3
- 4. General Introduction : Android Android has more than 48 percent of the smartphone market, versus 32 percent for iOS. Google indicates there are 850,000 Android device activations per day and total Google Play app downloads have reached more than┬Ā15 billion.┬ĀApp search ’¼ürm Xyologic reports that in March 2012 there were 617 million app downloads on Android versus 393 million app downloads on iPhone in the U.S. lundi 21 janvier 13 4
- 5. General Introduction : Android lundi 21 janvier 13 5
- 6. General Introduction : Android 1.0 ASTRO lundi 21 janvier 13 6
- 7. General Introduction : Android 1.5 Cupcake lundi 21 janvier 13 7
- 8. General Introduction : Android 1.6 Donut lundi 21 janvier 13 8
- 9. General Introduction : Android 2.1 Eclair lundi 21 janvier 13 9
- 10. General Introduction : Android 2.2 Froyo lundi 21 janvier 13 10
- 11. General Introduction : Android 2.3 Gingerbread lundi 21 janvier 13 11
- 12. General Introduction : Android 3 Honycomb lundi 21 janvier 13 12
- 13. General Introduction : Android 2.4 Ice Cream Sandwich lundi 21 janvier 13 13
- 14. General Introduction : Android 4.1 Jellybean lundi 21 janvier 13 14
- 15. Environment Setup Android Environment Setup Steps lundi 21 janvier 13 15
- 16. Hello World Application Android Create a new Application lundi 21 janvier 13 16
- 17. Hello World Application Android Eclipse Android Perspective lundi 21 janvier 13 17
- 18. Hello World Application Android Application Installation on device lundi 21 janvier 13 18
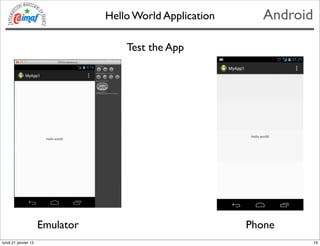
- 19. Hello World Application Android Test the App Emulator Phone lundi 21 janvier 13 19
- 20. Hello World Application Android Android project anatomy src/ ŌĆō Source folder contains all your Java source code gen/ ŌĆō Generated folder contains source code generated by Android/Eclipse. It contains R.java ŌĆō one of AndroidŌĆÖs most important ’¼üle to perform name lookup/resolution and referencing. R.java is automatically generated by the build system and references your resources. assets/ ŌĆō Assets folder contains static ’¼üles such as html which can be included in your program. res/ ŌĆō Resource folder contains your program resource ’¼üles. res/drawables/ ŌĆō Contains image ’¼üles eg. PNG, JPG etc but also drawables which are speci’¼üed in XML format res/layouts/ ŌĆō Contains XML ’¼üles to specify your application View layouts res/values/ ŌĆō Contains XML ’¼üles where you can specify static string,text, numeric and other constant values. libs/ ŌĆō A folder containing third-party/downloaded JAR libraries which can be used in your Android App. AndroidManifest.xml ŌĆō A manifest ’¼üle where you can specify all you Activities, Permissions, and other con’¼ügurations. lundi 21 janvier 13 20
- 21. Hello World Application Android Android project anatomy <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="fr.aimaf" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0" > <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" android:targetSdkVersion="17" /> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <activity android:name="fr.aimaf.MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest> lundi 21 janvier 13 21
- 22. Hello World Application Android Android project anatomy <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:text="@string/hello_world" /> </RelativeLayout> lundi 21 janvier 13 22
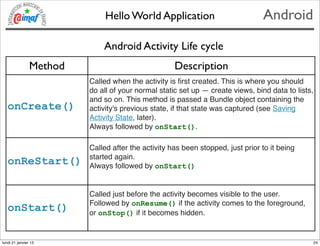
- 23. Hello World Application Android Android Activity Life cycle lundi 21 janvier 13 23
- 24. Hello World Application Android Android Activity Life cycle Method Description Called when the activity is ’¼ürst created. This is where you should do all of your normal static set up ŌĆö create views, bind data to lists, and so on. This method is passed a Bundle object containing the onCreate() activity's previous state, if that state was captured (see Saving Activity State, later). Always followed by onStart(). Called after the activity has been stopped, just prior to it being started again. onReStart() Always followed by onStart() Called just before the activity becomes visible to the user. Followed by onResume() if the activity comes to the foreground, onStart() or onStop() if it becomes hidden. lundi 21 janvier 13 24
- 25. Hello World Application Android Android Activity Life cycle Called just before the activity starts interacting with the user. At this point the activity is at onResume() the top of the activity stack, with user input going to it. Always followed by onPause(). Called when the system is about to start resuming another activity. This method is typically used to commit unsaved changes to persistent data, stop animations and other things that may be consuming CPU, and so on. It should do whatever it does very quickly, onPause() because the next activity will not be resumed until it returns. Followed either by onResume() if the activity returns back to the front, or by onStop() if it becomes invisible to the user. Called when the system is about to start resuming another activity. This method is typically used to commit unsaved changes to persistent data, stop animations and other things that may be consuming CPU, and so on. It should do whatever it does very quickly, onStop() because the next activity will not be resumed until it returns. Followed either by onResume() if the activity returns back to the front, or by onStop() if it becomes invisible to the user. Called before the activity is destroyed. This is the ’¼ünal call that the activity will receive. It could be called either because the activity is ’¼ünishing (someone called finish() on it), onDestroy() or because the system is temporarily destroying this instance of the activity to save space. You can distinguish between these two scenarios with theisFinishing() method. lundi 21 janvier 13 25
- 26. Hello World Application Android Android Activity Life cycle public class MainActivity extends Activity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } } lundi 21 janvier 13 26
- 27. Android lundi 21 janvier 13 27