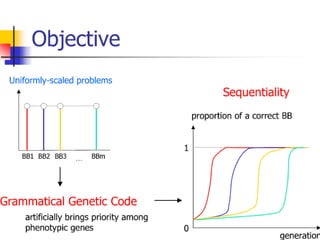
Inducing Sequentiality Using Grammatical Genetic Codes
ŌĆó
0 likesŌĆó400 views
This paper studies the inducement of sequentiality in genetic algorithms (GAs) for uniformly-scaled problems. Sequentiality is a phenomenon in which sub-solutions converge sequentially in time in contrast to uniform convergence observed for uniformly-scaled problems. This study uses three different grammatical genetic codes to induce sequentiality. Genotypic genes in the grammatical codes are interpreted as phenotypes according to the grammar, and the grammar induces sequential interactions among phenotypic genes. The experimental results show that the grammatical codes can indeed induce sequentiality, but the GAs using them need exponential population sizes for a reliable search.
1 of 26