Intra lenticular foreign body
- 1. Intralenticular Foreign Body : a case series DR BIKRAM BAHADUR THAPA DR SWETA SINGH DR GYANENDRA LAMICHHANE DR SAURAV PIYA DR RAKSHYA BASNET DEPARTMENT OF VITREO-RETINA , LUMBINI EYE INSTITUTE, BHAIRAHAWA, NEPAL AT OCULAR TRAUMA SYMPOSIUM 15-12 - 2019
- 4. Financial Disclosure ’üĄ We have no financial disclosure or conflicts of interest with the presented material
- 5. Introduction ’üĄ Open globe injuries(OGI) constitute 28% of all ocular trauma. ’üĄ Intraocular foreign body (IOFB) accounts 17- 41% of OGIs. ’üĄ Intralenticular Foreign body(ILFB) constitutes only 5-11% of all IOFB(0.05-0.1% of all ocular trauma). ’üĄ Entry wound and iris hole with or without cataract suggest the possibility of retained ILFB. ’üĄ Complications like cataract, uveitis, glaucoma, endophthalmitis and intraocular metallosis have been reported. Xie H et al. Eye science.2013;28:108-112 Arora et al. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2000; 48:119ŌĆō22. Coleman et al.Ophthalmol 1987;94:1647-53. Lee W et al J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007;33:550ŌĆō2
- 6. ’üĄ Cataract occurs due to alteration in the capsular integrity in most cases so it is necessary to remove the intralenticular foreign body and cataract ’üĄ ILFBs can be detected through slit-lamp examination. ’üĄ ILFB must be confirmed with imaging including X ray orbit, ultrasound B scan immersion technique, CT scan orbit , Scheimpflug imaging and UBM. ’üĄ MRI is contraindicated unless IOFB is proven to be non magnetic. Lin YC et al Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2019;9(1):53ŌĆō59 Loporchio D et al. Surv Ophthalmol. 2016;61:582ŌĆō96 Singh et al. Nepal J Ophthalmol 2015; 7(13):82-84.
- 7. Management Before 1930 ŌĆó Intracapsular cataract extractions (ICCE) 1930-1985 ŌĆó ILFB removal by manipulating into anterior chamber followed by removing through the entry site or via surgical incision. After 1985 ŌĆó ILFBs expressed with the nucleus by ECCE or SICS ŌĆó 2015: ILFB removed by forcep after capsulorrhexis followed by Phacoemulsification and 3 piece FIOL ŌĆó In our series: ILFB removed by forcep after capsulorrhexis followed by Phacoemulsification /lens aspiration and single piece FIOL ’üĄ Lin YC et al Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2019;9(1):53ŌĆō 59 ’üĄ Loporchio D et al. Surv Ophthalmol. 2016;61:582ŌĆō96 ’üĄ Singh et al. Nepal J Ophthalmol 2015; 7(13):82- 84.
- 8. Materials and Methods Ethical clearance was taken from IRC of LEIRC. ŌĆó Study design: Prospective, observational, case series ŌĆó Sampling Type: consecutive case ŌĆó Study period: JUNE 2019 to December 2019. Inclusion Criteria: 1. Retained IOFB with in the lens. 2. VA of Ōēź PL or better at presentation 3. Completing 45 day follow up after IOFB removal 4. Operated with phacoemulsification or lens aspiration with single piece acrylic foldable IOL implantation in bag. Exclusion criteria: ŌĆóInitial VA of NPLt) ŌĆóPatients not completing 45 day follow up
- 9. Materials and Methods contŌĆ”. ’üĄ Demographic feature, complaints and examination findings were noted in all cases. ’üĄ Open globe injury was classified as per BETT. ’üĄ Ultrasonography A&B-scan, X-ray orbit, AS-OCT finding were collected. ’üĄ Cataract extraction with IOFB removal with single piece hydrophobic acrylic IOL was implanted in all cases. ’üĄ Intraoperative findings, complications and details of IOFB were noted. ’üĄ The post operative VA, IOP, slit lamp finding and complications were noted on the subsequent follow up. Kuhn F et al. (BETT). J Fr. Ophtalmol.2004; 27: 206-210. Loporchio D et al. surv ophthalmol2016;6 1: 582-596.
- 10. Results Case 1 ’üĄ 42 year/M presented with the complaints of slowly progressive defective vision in RE for 1 month. ’üĄ H/o trauma to RE 6 month back while hammering on stone during construction work. ’üĄ Examination: Finding OD OS VA 6/36 6/6 IOP(mmHg) 16 14 cornea Leucoma, pigment deposition on endothelium clear iris Iris defect NAD Lens Cataract, pigment on ALS NAD Fundus Media gr III, disc just visible NAD
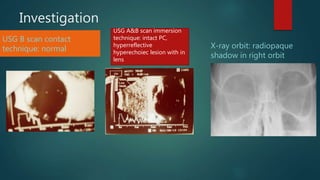
- 11. Investigation USG B scan contact technique: normal X-ray orbit: radiopaque shadow in right orbit USG A&B scan immersion technique: intact PC, hyperreflective hyperechoiec lesion with in lens
- 12. Provisional Diagnosis RE self sealed OGI Zone I type B+C Grade III without RAPD with Cataract and Intralenticular Foreign Body ’üĄ Plan : RE Phacoemulsification + Intralenticular Foreign body removal + Foldable Intraocular lens implantation under Local Anesthesia
- 13. Post operative days VA 6/18 BCVA (-1 DS ) 6/9 A.C. Quiet, iris hole IOL in bag Sign of siderosis Present ( brown pigment on stroma and endothelium, circumciliary congestion, dark brown iris, mild dilated pupil and cataract
- 14. CASE 2 ’üĄ A 20 year male presented with loss of vision in RE with history of injury to right eye while hammering a nail 3 months ago ’üĄ EXAMINATION Finding OD OS VA HM, PR accurate 6/6 IOP 16 18 cornea Leucoma clear iris Iris hole NAD Lens Total cataract NAD Fundus No view NAD
- 15. Investigations Contact B scan : Normal X ray orbit : radiopaque tiny shadow in right orbit Immersion A- B scan : hyper-refletive hyper- echoiec lesion on lens
- 16. Provisional Diagnosis RE self sealed Open globe injury Zone I type B+C Grade IV without RAPD with Cataract and Intralenticular Foreign Body ’üĄ Plan : RE Lens Aspiration + Intralenticular Foreign body removal + Foldable Intraocular lens implantation under Local Anesthesia Surgical video
- 17. Post op Photo Post op findings ’üĄ VA :6/9 (UCVA), 6/6 (-0.25DS) ’üĄ IOP: 14 mm of Hg ’üĄ Cornea : Leucoma ’üĄ AC : quiet ’üĄ Iris : hole ’üĄ Lens : IOL in capsular Bag ’üĄ Fundus : WNL
- 18. Case 3 History ’üĄ A 27-year-old male electrician presented with gradual painless loss of vision in left eye over 10 days. ’üĄ He had trauma to his left eye 2 month back while grinding the wall before placing electric wire. ’üĄ He consulted nearby eye clinic and received an antibiotic eye drop and ointment for 7 day and continued his work Examination OD OS VA 6/6 HM IOP 16 16 Cornea clear Small leucoma Pupil NSNR NSNR iris normal Iris hole Lens clear Total cataract with brown particle inferiorly Fundus normal No view
- 19. Case 3 Anterior segment photo Ultrasound ( contact and immersion technique)
- 20. Provisional Diagnosis LE self sealed Open globe injury Zone I type B+C Grade IV without RAPD with Cataract and Intralenticular Foreign Body ’üĄ Plan : LE Lens Aspiration + Intralenticular Foreign body removal + Foldable Intraocular lens implantation under Local Anesthesia Post operative outcome VA 6/6 A.C. Quiet, inferior iris hole, IOL in the bag Fundus NAD
- 21. Case 4 History ’üĄ A 30-year-old male carpenter presented with gradual painless loss of vision in right eye over 10 days. ’üĄ He had trauma to his right eye 1 month back while hammering on nail while making a desk at Dubai. He had not used protective goggle at the time of trauma. Examination OD OS VA 1/60 6/6 IOP 18 16 Cornea Small sealed laceration clear Pupil NSNR NSNR iris Sphincter tear normal Lens Total cataract, with visible blackish FB clear Fundus No view normal
- 22. Case 4
- 23. Summary of the cases of ILFB and USG Case no Age Sex Eye Occupation Time betwn injury & presentation Use of protective goggles Initial VA cataract siderosi FB Posterior capsule Surgical procedure Final VA 1 20 M R Carpenter 3 month no HM Total No iron intact LA+ILFB rem+ FIOL 6/6 2 27 M L electrician 2 month no HM Total No iron intact LA+ILFB rem +FIOL 6/6 3 42 M R Constructio n worker 6 month no 6/36 Localize d Yes iron intact Phoco + ILFB removal+ FIOL 6/9 4. 30 M R carpenter 1 month no 3/60 total no iron intact Phaco+IL FB R+ FIOL 6/9 5. 23 M R carpenter 2 month no 1/60 total no iron intact
- 24. Our Results: ’üĄ All of our patient were working male ’üĄ Ocupation:1. Electrician ’üĄ 2. Skilled construction laborer ’üĄ 3. carpenter ’üĄ Mechanism : hammering with iron instrument in all case ’üĄ Duration of presentation from trauma: 2, 3 and 6 month ( avg. 3.667 month)( once vision is affected) ’üĄ Presenting visual acuity: HM in two eye and 6/36 in 1 eye.
- 25. ’üĄ Entry wound= cornea(zone I) and self sealed in all eyes. ’üĄ Iris hole = in all eye ’üĄ Lens= total cataract in two eye and localized cataract around IOFB impacted site in one eye ’üĄ Pupil= normal in size and reaction in two eye, mild dilated and sluggishly reacting in one eye ’üĄ Feature of siderosis bulbi : remarkable in one eye ( iron rust on corneal endothelium, heterochromia iridis, deposition of iron on lens epithelium, pigmentary retinopathy and mid dilated pupil)
- 26. Investigations ’üĄ USG B+A scan( contact Technique) is of no value in ILFB localization but provide information regarding posterior segment. ’üĄ USG B+A scan(Immersion technique) detect IOFB in lens and provide information regarding status of posterior capsule. ’üĄ X-ray orbit: showed radiopaque shadow with in orbit in metallic FB ’üĄ We did not perform CT scan orbit, Scheimpflug imaging and UBM due to unavailability of these service, high cost as well as previous investigations already confirmed its location and guided definitive treatment to us.
- 27. Treatment ’üĄ Early removal of ILFB prevents siderosis as well as provides better visual outcome. ’üĄ Use of small(2.8mm) incision is sufficient as ILFB are usually small (Ōēż 2mm). ’üĄ Following Capsulorrhexis, capsulorrhexis forcep can be used to recover ILFB from the lens matter before phacoemulsification.
- 28. Conclusion ’üĄ Siderosis develops if ILFB remains for longer duration. ’üĄ USG B+A scan(Immersion technique) detect IOFB in lens and provide information regarding status of posterior capsule. So It is a very important and recommended investigation for ILFB in developing countries. ’üĄ ILFB removal followed by phacoemulsification or lens aspiration and in the bag implantation of foldable IOL has encouraging refractive and visual outcomes. ’üĄ Removal of ILFB following capsulorrhexis before cataract extraction prevent accidental IOFB drop into the posterior segment. So we recommend ILFB removal before hydro-dissection.
- 29. Preventive measures ’üĄ Educating people working at high risk job ( including welder, construction site worker, electrician ) regarding use of protective spectacle. ’üĄ Discouraging use of fire crackers during festivals and celebration and mandating use of protective spectacles. ’üĄ Use of helmet while travelling in two wheeler.
- 31. Why utrataŌĆÖs forcep ’üĄ No need of other instrument. Usual phaco set iis sufficient ’üĄ Better grip than mcpherson, no need of magnet ’üĄ Staining anterior capsule before capsulorhexis provide better visualization of it. However due to healing process anterior capsule becomes fibrosed and non elastic making capsulorrhexis more difficult. Use of cohesive viscoelastic might help.
- 32. ’üĄ Why siderosis in uvea embedded ’üĄ Type of IOL ’üĄ Why and which forcep? ’üĄ Why not magnet? Any treatment for siderosis?
- 33. ’üĄ Arora [6] suggested that use of McPherson forceps (intraocular lens holding forceps) rather than magnet is sufficient for removal of metallic foreign bodies. Majority of the patients with retained intralenticular foreign body develop cataract formation which causes diminution of vision requiring surgery. However, progressive cataract formation is not inevitable. ’üĄ Lens epithelium makes the small breach in the anterior lens capsule heal quickly by rapid epithelial proliferation restoring its continuity, and limiting the free passage of ions and fluid that may progress to the development of cataract formation [15]
- 34. 1. Observation and close follow up after control of inflammation: Small metallic foreign bodies , not affecting the visual axis, with clear lens and no other intraocular damage. 2. The lens/cataract extraction with removal of foreign body: all the Small metallic foreign bodies with complication and all Medium to large metallic foreign bodies in the lens
- 35. ’üĄ These two steps were performed either as a single-staged procedure or as two separate surgeries.[4] ’üĄ The combined procedure to give good results in 14 eyes, three of which had suture-fixated IOL because of posterior capsular tear.[14]
Editor's Notes
- Demography, complaint, examination findings were noted.































![’üĄ Arora [6] suggested that use of McPherson forceps (intraocular lens
holding forceps) rather than magnet is sufficient for removal of metallic
foreign bodies. Majority of the patients with retained intralenticular
foreign body develop cataract formation which causes diminution of vision
requiring surgery. However, progressive cataract formation is not
inevitable.
’üĄ Lens epithelium makes the small breach in the anterior lens capsule heal
quickly by rapid epithelial proliferation restoring its continuity, and limiting
the free passage of ions and fluid that may progress to the development of
cataract formation [15]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ilfbcaseseries-220521021734-cdc4c8b0/85/Intra-lenticular-foreign-body-33-320.jpg)

![’üĄ These two steps were performed either as a single-staged procedure or as two
separate surgeries.[4]
’üĄ The combined procedure to give good results in 14 eyes, three of which had
suture-fixated IOL because of posterior capsular tear.[14]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ilfbcaseseries-220521021734-cdc4c8b0/85/Intra-lenticular-foreign-body-35-320.jpg)
