L3 Big Data and Application.pptx
- 1. Amity Institute of Information Technology Introduction to Data Science BSc.IT/BCA/ DUAL VI Semester Faculty: Dr. Shambhu Kumar Jha 1
- 2. Amity Institute of Information Technology Module I Introduction to Big Data Difference between Big Data and Data Science, 2
- 3. Amity Institute of Information Technology Introduction to Big Data let’s start by understanding what is Big Data? ? Big Data: It is large or voluminous data, information, or the relevant statistics acquired by large organizations and ventures from various sources. ? Many software and data storages is created and prepared as it is difficult to compute the big data manually. ? It is used to discover patterns and trends and make decisions related to human behavior and interaction technology 3
- 4. Amity Institute of Information Technology Introduction to Big Data Big data encompasses following wide variety of data types: ? Structured data, such as transactions and financial records; ? Unstructured data, such as email, text, documents and multimedia files; ? Semi structured data, such as web server logs and streaming data from sensors. Big data is often characterized by the three V's: ? Large volume of data in many environments; ? Variety of data types frequently stored in big data systems; and ? Velocity at which much of the data is generated, collected and processed. 4
- 5. Amity Institute of Information Technology Why Big Data is Important Companies use big data to : ? Improve operations, ? Provide better customer service, ? Create personalized marketing campaigns and take other actions to increase revenue and profits. ? Competitive advantage over those that don't because they're able to make faster and more informed business decisions. ? Example: Big data provides valuable insights into customers that companies can use to refine their marketing, advertising and promotions in order to increase customer engagement and conversion rates. ? Both historical and real-time data can be analyzed to assess the evolving preferences of consumers or corporate buyers, enabling businesses to become more responsive to customer wants and needs.5
- 6. Amity Institute of Information Technology Is big data part of data science? ? Big Data is essentially a special application of data science, in which the data sets are enormous and require overcoming logistical challenges to deal with them. ? The primary concern is efficiently capturing, storing, extracting, processing, and analyzing information from these enormous data sets. ? Big data is a combination of structured, semi structured and unstructured data collected by organizations that can be mined for information and used in machine learning projects, predictive modeling and other advanced analytics applications. 6
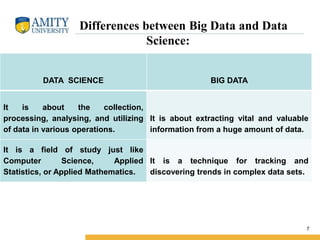
- 7. Amity Institute of Information Technology Differences between Big Data and Data Science: DATA SCIENCE BIG DATA It is about the collection, processing, analysing, and utilizing of data in various operations. It is about extracting vital and valuable information from a huge amount of data. It is a field of study just like Computer Science, Applied Statistics, or Applied Mathematics. It is a technique for tracking and discovering trends in complex data sets. 7
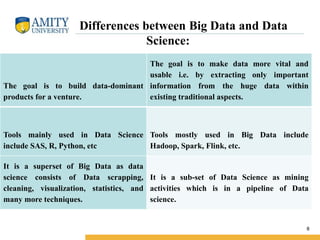
- 8. Amity Institute of Information Technology Differences between Big Data and Data Science: The goal is to build data-dominant products for a venture. The goal is to make data more vital and usable i.e. by extracting only important information from the huge data within existing traditional aspects. Tools mainly used in Data Science include SAS, R, Python, etc Tools mostly used in Big Data include Hadoop, Spark, Flink, etc. It is a superset of Big Data as data science consists of Data scrapping, cleaning, visualization, statistics, and many more techniques. It is a sub-set of Data Science as mining activities which is in a pipeline of Data science. 8
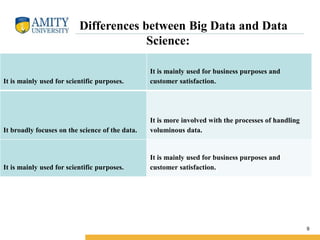
- 9. Amity Institute of Information Technology Differences between Big Data and Data Science: It is mainly used for scientific purposes. It is mainly used for business purposes and customer satisfaction. It broadly focuses on the science of the data. It is more involved with the processes of handling voluminous data. It is mainly used for scientific purposes. It is mainly used for business purposes and customer satisfaction. 9
- 10. AMITY INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Applications Of Big Data Finance o o o o
- 11. AMITY INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Applications of Big Data: Social Network ?Social media in the current scenario is considered as the largest data generator. ?The stats have shown that around 500+ terabytes of new data get generated into the databases of social media every day, particularly in the case of Facebook.
- 12. AMITY INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Applications of Big Data: Healthcare ?Nowadays, doctors rely mostly on patients’ clinical records, which means that a lot of data needs to be gathered, that too for different patients. ?Since there is a large amount of data coming from different sources, in various formats, the need to handle this large amount of data is increased
- 13. AMITY INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Applications of Big Data E-Commerce ?Maintaining customer relationships is the most important in the e- commerce industry. ?E-commerce websites have different marketing ideas to retail their merchandise to their customers, to manage transactions, and to implement better tactics of using innovative ideas with Big Data to improve businesses.
- 14. AMITY INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Applications of Big Data: Education The education sector holds a lot of information with regard to curriculum, students, and faculty. The information is analyzed to get insights that can enhance the operational adequacy of the educational organization. Collecting and analyzing information of a student such as attendance, test scores, grades, and other issues take up a lot of data. So, big data makes an approach for a progressive framework wherein this data can be stored and analyzed making it easier for the institutes to work with.
- 15. Amity Institute of Information Technology Application of Big data Big Data in Communications ?Gaining new subscribers, retaining customers, and expanding within current subscriber bases are top priorities for telecommunication service providers. ?The solutions to these challenges lie in the ability to combine and analyze the masses of customer-generated data and machine-generated data that is being created every day. 15
- 16. Amity Institute of Information Technology Skills Required Becoming a Data Scientist ? In-depth knowledge of SAS or R. For data science, R is generally preferred. ? Python coding: Python is the most common coding language that is used in data science, along with Java, Perl, and C/C++. ? Hadoop platform: Although not always a requirement, knowing the Hadoop platform is still preferred for the field. Having some experience in Hive or Pig is also beneficial. ? SQL database/coding: Although NoSQL and Hadoop have become a significant part of data science, it is still preferred if you can write and execute complex queries in SQL. ? Working with unstructured data: It is essential that a data scientist can work with unstructured data, whether on social media, video feeds, or audio. 16
- 17. Amity Institute of Information Technology Skills Required Becoming a Big Data Specialist ? Analytical skills: These skills are essential for making sense of data, and determining which data is relevant when creating reports and looking for solutions. ? Creativity: You need to have the ability to create new methods to gather, interpret, and analyze a data strategy. Mathematics and statistical skills: Good, old-fashioned “number crunching” is also necessary, be it in data science, data analytics, or big data. ? Computer science: Computers are the backbone of every data strategy. Programmers will have a constant need to come up with algorithms to process data into insights. ? Business skills: Big data professionals will need to have an understanding of the business objectives that are in place, as well as the underlying processes that drive the growth of the business and its profits. 17
Editor's Notes
- 1
- The data generated mainly consist of videos, photos, message exchanges, etc. A single activity on any social media site generates a lot of data which is again stored and gets processed whenever required. Since the data stored is in terabytes, it would take a lot of time for processing if it is done by our legacy systems. Big Data is a solution to this problem.