Modals verbs
- 1. MODALS VERBS
- 2. What is Modals Verbs? ? The modal verbs are type of auxiliary verbs. ? Some word of modal verbs are include in auxiliary verbs. ? Can/could ? May/might ? Will/would ? Shall/should ? Ought to ? Must
- 3. Auxiliary verbs ? Is ? Am ? Are ? Was ? Were ? Do ? Does ? Did
- 4. Auxiliary verbs ? Have ? Has ? Had ? Can ? Could ? May ? Might ? Will
- 5. Auxiliary verbs ? Would ? Shall ? Should ? Must ? Need ? Dare ? Ought ? Used to
- 6. How Modals Verb are difference from normal verbs? ? 1: They don't use an 's' for the third person singular. ? 2: They make questions by inversion ('she can go' becomes 'can she go?'). ? 3: They are followed directly by the infinitive of another verb (without 'to').
- 7. What are Modals Verbs? ?Can/could ?May/might ? Will/would ? Shall/should ?Ought to ? Must
- 8. Can/Could can to be able to ability I can swim to be allowed to permission Can I use your phone please? it is possible possibility Smoking can cause cancer ! could to be able to ability in the past When I was younger I could stay up all night and not get tired.. to be allowed to more polite permission Excuse me, could I just say something? it is possible possibility It could rain tomorrow!
- 9. Structure ? Can – Subject + Can + Main Verb ? Could – Subject + Could + Main Verb ? Be able to – Subject + Be + Able + Infinitive Subjec t auxiliay verb main verb + I can play tennis. - He cannot play tennis. can't ? Can you play tennis ? subject auxiliary verb main verb + My grandmot her could swim. - She could not walk. couldn't ? Could your grandmot her swim?
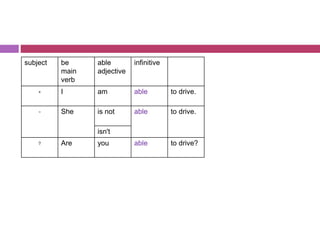
- 10. subject be main verb able adjective infinitive + I am able to drive. - She is not able to drive. isn't ? Are you able to drive?
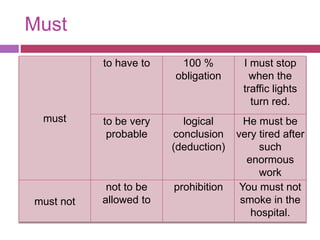
- 11. Must must to have to 100 % obligation I must stop when the traffic lights turn red. to be very probable logical conclusion (deduction) He must be very tired after such enormous work must not not to be allowed to prohibition You must not smoke in the hospital.
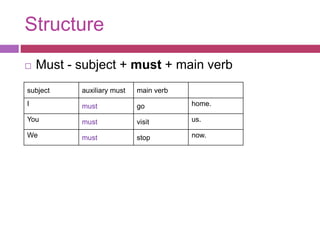
- 12. Structure ? Must - subject + must + main verb subject auxiliary must main verb I must go home. You must visit us. We must stop now.
- 13. May/Might may to be allowed to permission May I use your phone please? it is possible, probable possibility, probability It may rain tomorrow! might to be allowed to more polite permission Might I use your phone please? it is possible, probable weak possibility, probability I might come and visit you in America next year, if I can save enough money.
- 14. Structure ? May - Subject + May + Infinitive without to ? Might - Subject + Might + Infinitive without to
- 15. Should/Ought to should/ought to used to say or ask what is the correct or best thing to do 50 % obligation I should / ought to see a doctor. I have a terrible headache. to suggest an action or to show that it is necessary advice You should / ought to revise your lessons to be very probable logical conclusion (deduction) He should / ought to be very tired after such enormous work
- 16. Structure ? Subject + Should + main verb ? Subject + Ought to + main verb
- 17. Will/Would Will I can’t see any taxis so I’ll walk.I'll do that for you if you like. I’ll get back to you first thing on Monday. Profits will increase next year. Instant decisionsOffer Promise Certain prediction Would Would you mind if I brought a colleague with me?Would you pass the salt please? Would you mind waiting a moment? "Would three o`clock suit you?" - "That’d be fine." Would you like to play golf this Friday? "Would you prefer tea or coffee?" - "I’d like tea please." Asking for permissionReques t Request Making arrangements Invitation Preferences
- 18. Structure ? Will – Subject + will + main verb ? Would – Subject + would + main verb
- 19. Reference ? http://www.myenglishpages.com/site_php_files/grammar-lesson- modals.php#.VAxfacKSwrU ? http://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/modal-verbs.html ? http://esl.fis.edu/grammar/rules/modal.htm ? https://www.englishclub.com/grammar/verbs-modals.html ? http://www.gingersoftware.com/content/grammar-rules/ verbs/modal-verbs/ ? http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Modal_verb ? http://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/modal-verbs.html ? http://www.learnenglish.de/grammar/verbmodal.html ? http://eazyclass.com/2012/02/29/modal-verbs/ ? http://speakspeak.com/resources/english-grammar-rules/ modal-verbs
Editor's Notes
- Can - Present, Future Could – Past Be able to – Past, Present, Future