1 of 7
Downloaded 414 times





Ad
Recommended
Padeye design calculation
Padeye design calculationadiq1901
╠²
The document provides guidelines for padeye design and calculations for lifting attachments. It states that padeyes shall be designed for at least 5% of the design load applied laterally and that permissible stresses shall follow AISC standards with additional requirements limiting through-thickness stresses to 0.2 times the yield strength if the material does not have through-thickness properties. It then provides examples of calculations for padeye design including shear stress, tension stress, weld shear stress, and dimensional requirements.Padeye calculation example
Padeye calculation exampleJhon Keliat
╠²
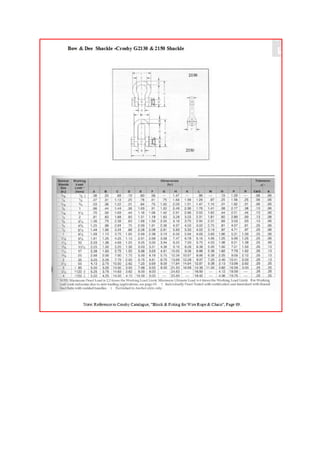
This document provides design details and checks for a lifting shackle, sling, and padeye assembly. Key points include:
1. The sling and shackle are selected to have sufficient minimum breaking load capacity to safely lift the design load of 8417 kN, with safety factors applied according to standards.
2. The padeye dimensions are checked against criteria for the pin hole diameter, thickness, radii, and plate sizes. Stress checks are performed at critical locations like the pin hole.
3. Forces acting on the assembly are calculated based on the design load and orientation. Stresses are analyzed at points on the padeye to ensure values are below allowable limits.135613248 lifting-lug
135613248 lifting-lugMohmmad Hussain Hussain
╠²
The document describes a spreadsheet program called "LIFTING_LUG" that analyzes lifting lugs used in rigging operations. The program allows the user to input parameters of a lifting lug and determines its ultimate strength based on several checks. It then applies a desired factor of safety to calculate allowable loads for the lifting lug. The program consists of two worksheets - one for documentation and one for performing the lifting lug analysis calculations according to industry standards.Plumbness & Roundness of storage tanks
Plumbness & Roundness of storage tanksWeld Maniac
╠²
The document discusses methods for measuring the plumbness and roundness of storage tank shells during construction and maintenance. Plumbness is measured using a total station to determine the verticality of each shell course, while roundness is measured to check how circular each course is. Measurements are taken at regular intervals and positions around the tank circumference and shell height. The document provides acceptance criteria from API standards, specifying maximum allowable deviations for plumbness and roundness based on tank size.Design by Analysis - A general guideline for pressure vessel
Design by Analysis - A general guideline for pressure vesselAnalyzeForSafety
╠²
The document outlines the design procedure for pressure vessels according to ASME Section VIII Division 1 and Division 2, detailing the necessary input data, shell and head design under both external and internal pressures, and various calculations for components like nozzles and stiffening rings. It also introduces the concept of 'design by analysis' to prevent different failure modes of pressure vessels through comprehensive stress analysis. Furthermore, the document specifies load conditions, design parameters, and criteria for safety and functionality in pressure vessel construction.is 1367 2
is 1367 2sixramesh23
╠²
This document provides standards and tolerances for threaded steel fasteners including bolts, screws, studs, and nuts. It specifies tolerances for dimensions, threads, driving features, and other characteristics. Tolerances are defined for product grades A, B, and C, with grade A being the most precise and grade C being the least precise. The tolerances are selected from international standards for limits, fits, threads, and geometric specifications. The document provides detailed tables and figures outlining the tolerances for various features of threaded steel fasteners.Asme sec viii div 1 icb
Asme sec viii div 1 icbPraj Industries Ltd.
╠²
This document provides an agenda and overview of a training program on the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Codes. It discusses the objectives of codes and standards, highlights of the ASME Code system including sections I through XI, and introduces Section VIII Division 1 which governs pressure vessels. Key points covered include material requirements, design thickness calculation, weld joint categories, non-destructive testing requirements, and post-weld heat treatment stipulations. The training aims to help participants understand the application and requirements of the ASME pressure vessel codes.Api 570 01_api_570
Api 570 01_api_570natarajan murugesan
╠²
API 570 covers inspection, repair, alteration and re-rating procedures for metallic piping systems that have been in-service. It was developed for the petroleum refining and chemical process industries and applies to piping systems for flammable and toxic fluids. The document contains 53 practice questions related to API 570 covering topics like corrosion mechanisms, inspection techniques, qualifications of inspectors and more. Respondents are asked to pick the correct option from the given choices for each question.Api 650 & 653 questions closed book with answers
Api 650 & 653 questions closed book with answersJasminder singh
╠²
This document contains 100 multiple choice practice questions related to API standards 650 and 653 for aboveground storage tanks. The questions cover topics such as welding procedures, inspections, repairs, alterations, testing and qualifications. Correct answers are provided for each question. The purpose of the document is to test knowledge of the requirements and recommendations in API 650 and 653 for ensuring the integrity and safety of aboveground storage tanks.Anchor bolt design
Anchor bolt designVaradaraj Ck
╠²
This document provides details of the design of a headed concrete anchor and end plate connection supporting a reinforced concrete beam. Key details include:
- Supported member is a hopper applying 5000kg vertical force
- Anchor bolt diameter is 20mm
- There are 4 anchors in a 2x2 configuration spaced 50mm apart
- Concrete strength is 40MPa
- Checks are performed to ensure the connection has sufficient capacity for the applied tension and shear loads considering factors like concrete breakout strength, steel strength, pryout strength, etc. with all checks indicating the design is safe.Aramco inspection handbook
Aramco inspection handbookram111eg
╠²
This document provides guidance for inspectors on paints and coatings. It outlines approved coating systems for various applications and services, including internal and external pipe coatings for buried, insulated, and atmospheric exposure conditions. It also provides standards on surface preparation, coating application, thickness measurement, and repair. Inspectors are instructed to follow the coating manufacturer's recommendations and use properly calibrated equipment to ensure coatings meet thickness and cure requirements.QC Welding Inspector Interview Question & Answers.pdf
QC Welding Inspector Interview Question & Answers.pdfUniversity of Sarajevo, Manufacturing Technology:
╠²
This document provides concise summaries of key terms and concepts for a QC welding inspector interview. It defines common quality control terms like QA, QC, QAP, ITP, and explains the differences between them. It also summarizes welding concepts such as the four main welding types, the purpose of welding procedures like WPS and PQR, essential versus non-essential variables, and what organizations like ASME and AWS stand for.Guidelines for Pressure Boundary Bolted Flange Joint Assembly
Guidelines for Pressure Boundary Bolted Flange Joint AssemblyPGE India - PILOT Gaskets
╠²
The document establishes guidelines for the assembly of pressure boundary bolted flange joints as defined in ASME PCC-1ŌĆō2010. It outlines various processes such as training, cleaning, installation, alignment, tightening, and disassembly of joints, emphasizing good practices and responsibilities for users. The standard was developed following accredited procedures and includes references for further guidance in pressure equipment maintenance and integrity management.Peaking & Banding
Peaking & BandingWeld Maniac
╠²
Peaking and banding refer to the roundness and straightness of shell plates around vertical and horizontal joints in storage tanks. Peaking is measured using a horizontal sweep board along vertical joints, while banding is measured using a vertical sweep board along horizontal joints. Acceptance criteria per API standards allow for peaking deviations of up to 13 mm and banding deviations of up to 13 or 25 mm depending on the standard. Proper measurement procedures involve visually inspecting the tank, positioning the sweep board accurately, and taking measurements at a minimum of 8 locations around the tank circumference.Process piping b31.3 detailed
Process piping b31.3 detailedAdeel Mazhar
╠²
This document provides standards and specifications for piping components used in process piping systems. It lists dimensional standards for piping components in Table 326.1 and specifies that components must meet pressure design and mechanical strength requirements. It also states that pressure-temperature ratings of listed components are accepted for design, while unlisted components must meet provisions for rating. Dimensional requirements in appendices must also be considered.Saes q-005
Saes q-005ahmedhashem483214
╠²
This document provides standards for the design and construction of concrete foundations at Saudi Aramco. It outlines requirements for soils analysis, foundation stability, concrete specifications, and the use of precast foundations. The standards are intended to ensure foundations are adequately designed for their intended use based on accepted engineering practices and industry codes. The document provides mandatory rules for soil bearing pressures, reinforcement, construction methods, and addressing potential underground interferences.Presentation on SECVIII
Presentation on SECVIIIStatic Equipment Design
╠²
This document provides an overview and contents of an online course about ASME Section I and Section VIII fundamentals. It includes:
- An introduction to the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code which contains 12 sections covering various topics like power boilers, materials, pressure vessels, welding qualifications, and piping codes.
- Summaries of the scopes and requirements of key sections like Section I (power boilers), Section VIII (pressure vessels), and the B31 piping codes.
- Information on ASME certification and inspection procedures for pressure equipment.
- A note on converting between imperial and metric units in the ASME codes.
- An introduction to the fundamentals and design requirementsSteel Warehouse Project
Steel Warehouse ProjectJawad Shaukat
╠²
This document contains calculations for wind loads and structural design of a steel warehouse. The wind calculations determine the basic wind velocity as 32 m/s. Mean wind velocity and turbulence intensity are also calculated. Using these values, peak velocity pressure is found to be 1521 Pa. Plastic analysis is performed to determine critical load combinations and failure mechanisms. The maximum plastic moment is found to be 829.89 kNm. Connection design calculations are provided for the primary beam to column connection including bolt shear, bearing, block tearing, and plate and web bearing capacities. Design is checked against Eurocodes.API 1104 ES.pdfDanielAlexanderRiaoR
╠²
Este documento establece los est├Īndares para soldaduras de tuber├Łas utilizadas en la industria petrolera. Describe los diferentes procesos de soldadura, materiales, equipos y cualificaciones requeridas. Tambi├®n especifica los procedimientos para inspecci├│n y aceptaci├│n de soldaduras, as├Ł como referencias a otras normas relacionadas. El objetivo es asegurar que las soldaduras cumplen con los requerimientos mec├Īnicos y son seguras para su uso en sistemas de transporte y almacenamiento de petr├│leo y gas.Cmaa specification-70
Cmaa specification-70tecnidibujos
╠²
This document is C.M.A.A. Specification No. 70-1983 which provides specifications for electric overhead traveling cranes. It was developed by the Crane Manufacturers Association of America to promote standardization and provide guidelines for equipment selection. The specification contains eight sections covering general specifications, crane service classification, structural design, mechanical design, electrical equipment, inquiry data sheets and speeds, glossary, and index. It is intended to provide technical guidelines but not limit manufacturer ingenuity.Design Guide 01- Base Plate and Anchor Rod Design (2nd Edition).pdf
Design Guide 01- Base Plate and Anchor Rod Design (2nd Edition).pdfRichard Villon
╠²
This document provides guidance on designing column base plate and anchor rod connections. It discusses material selection, fabrication, installation, and repairs. The document recommends ASTM A36 as the preferred material for base plates up to 4 inches thick, and ASTM A572 Gr 42 or 50 for thicker plates. It recommends ASTM F1554 Gr 36 or 55 for anchor rods. The document provides design procedures for column base plates subjected to axial compression and tension, with and without moments. It includes examples calculating strength limits for various limit states. The document aims to provide guidelines to avoid common fabrication and erection problems and design economical but adequate column base plate details.Piping inspector questions 1
Piping inspector questions 1 MOHAMMAD ATIF ALI
╠²
The document contains questions and answers related to the duties and responsibilities of a piping inspector. Some key points include:
1. A piping inspector is responsible for material receiving inspection, visual inspection of welds and joints, pressure testing, database reporting, and verifying that piping meets codes and standards.
2. They must understand gasket types, flange designs, how to read isometric drawings, and which codes and standards apply to piping inspection.
3. Inspectors check for proper material, dimensions, supports, and cleanliness and oversee hydrostatic testing and valve installation.Steel warehouse design report
Steel warehouse design reportHavit Steel Structure Co.,ltd
╠²
This document describes the design of a single-floor steel warehouse with specifications including an 18m clear span, 6m eave height, and various loading calculations for dead, live, and wind loads based on structural guidelines. It details the materials used, structural configurations, load combinations, and internal force analysis required to ensure safety and compliance with building codes. The document concludes with a consideration of the frame design and section checking for structural integrity.Asme sec viii div 2
Asme sec viii div 2Jithu John
╠²
This document summarizes ASME Section VIII Division 2 requirements for welding and non-destructive testing of welds. It outlines weld categories, fabrication requirements including repair of defects, welding identification markings, and acceptance standards for radiographic, penetrant, and ultrasonic testing of welds. Impact testing of welds is also addressed including testing of vessel test plates to qualify welding procedures for different weld categories.[Point] pipe stress analysis by computer-caesar ii
[Point] pipe stress analysis by computer-caesar iiLuis Luis
╠²
A mathematical model of a piping system was built using Caesar II software to perform pipe stress analysis. Caesar II allows engineers to create complete digital models of piping systems and have the software analyze them and calculate stresses, displacements, and loads. It can model both static and dynamic load cases. Caesar II is commonly used for designing new piping systems and troubleshooting existing systems by determining causes of failures or evaluating unanticipated operating conditions.What does cold stretching mean
What does cold stretching meanJiun Fa ,Lai
╠²
The document outlines ASME Section VIII Division 1 rules for constructing pressure vessels with a focus on cold stretching, which enhances the yield limit of austenitic stainless steel through post-forming deformation. It details procedures, stress variations, and requirements for cold-stretching practices, including allowable stress increases and design considerations. Additional guidance on certification and stamping for vessels constructed using these methods is also provided.Stressed Induced in Supports of Horizontal Pressure vessel (Zick Analysis)
Stressed Induced in Supports of Horizontal Pressure vessel (Zick Analysis)Mahendra Prabhu S
╠²
The document summarizes Zick's analysis for stresses induced in large horizontal cylindrical pressure vessels supported on two saddles. It outlines the longitudinal bending stress, tangential shear stress, and circumferential stress at the saddle horn that Zick analyzed. It also discusses the additional stress in vessel heads used as stiffeners. The document provides equations to calculate these stresses and outlines design procedures for locating saddles, including selecting saddle angles and distances. It lists typical saddle part designs including webs, base plates, ribs, and wear plates.Afes foundation design
Afes foundation designHengkimhab
╠²
1. The document provides guidelines for designing vertical vessel foundations using AFES software. It outlines the steps in the design process, including setting soil and pile parameters, creating the structure, assigning foundation groups, editing footing sizes, and defining reinforcement.
2. Key steps include setting bearing capacities and pile properties, creating the structure model, assigning foundations to groups, editing footing dimensions for each group, and specifying pier and footing reinforcement sizes and spacing.
3. The document includes examples of foundation types, design data, and load calculations to illustrate the design process.Wrs rigging practice
Wrs rigging practiceLuis Manuel Rodr├Łguez
╠²
Use multiple single leg slings to wrap around off-center loads for better stability. Secure all loose equipment before lifting. When using eye bolts or slings, be aware that their capacity decreases significantly at angled loads. Use proper padding and hitches to control loads and prevent damage.Sacs otc 2012
Sacs otc 2012HSD Luu
╠²
Bentley Systems is a global leader in engineering software for infrastructure modeling and analysis. It offers SACS, a software for designing and analyzing offshore structures from conceptual design through installation, operation, and decommissioning. SACS can model various offshore structure types and perform analyses like structural analysis, fatigue analysis, earthquake analysis, and dropped object analysis.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Api 650 & 653 questions closed book with answers
Api 650 & 653 questions closed book with answersJasminder singh
╠²
This document contains 100 multiple choice practice questions related to API standards 650 and 653 for aboveground storage tanks. The questions cover topics such as welding procedures, inspections, repairs, alterations, testing and qualifications. Correct answers are provided for each question. The purpose of the document is to test knowledge of the requirements and recommendations in API 650 and 653 for ensuring the integrity and safety of aboveground storage tanks.Anchor bolt design
Anchor bolt designVaradaraj Ck
╠²
This document provides details of the design of a headed concrete anchor and end plate connection supporting a reinforced concrete beam. Key details include:
- Supported member is a hopper applying 5000kg vertical force
- Anchor bolt diameter is 20mm
- There are 4 anchors in a 2x2 configuration spaced 50mm apart
- Concrete strength is 40MPa
- Checks are performed to ensure the connection has sufficient capacity for the applied tension and shear loads considering factors like concrete breakout strength, steel strength, pryout strength, etc. with all checks indicating the design is safe.Aramco inspection handbook
Aramco inspection handbookram111eg
╠²
This document provides guidance for inspectors on paints and coatings. It outlines approved coating systems for various applications and services, including internal and external pipe coatings for buried, insulated, and atmospheric exposure conditions. It also provides standards on surface preparation, coating application, thickness measurement, and repair. Inspectors are instructed to follow the coating manufacturer's recommendations and use properly calibrated equipment to ensure coatings meet thickness and cure requirements.QC Welding Inspector Interview Question & Answers.pdf
QC Welding Inspector Interview Question & Answers.pdfUniversity of Sarajevo, Manufacturing Technology:
╠²
This document provides concise summaries of key terms and concepts for a QC welding inspector interview. It defines common quality control terms like QA, QC, QAP, ITP, and explains the differences between them. It also summarizes welding concepts such as the four main welding types, the purpose of welding procedures like WPS and PQR, essential versus non-essential variables, and what organizations like ASME and AWS stand for.Guidelines for Pressure Boundary Bolted Flange Joint Assembly
Guidelines for Pressure Boundary Bolted Flange Joint AssemblyPGE India - PILOT Gaskets
╠²
The document establishes guidelines for the assembly of pressure boundary bolted flange joints as defined in ASME PCC-1ŌĆō2010. It outlines various processes such as training, cleaning, installation, alignment, tightening, and disassembly of joints, emphasizing good practices and responsibilities for users. The standard was developed following accredited procedures and includes references for further guidance in pressure equipment maintenance and integrity management.Peaking & Banding
Peaking & BandingWeld Maniac
╠²
Peaking and banding refer to the roundness and straightness of shell plates around vertical and horizontal joints in storage tanks. Peaking is measured using a horizontal sweep board along vertical joints, while banding is measured using a vertical sweep board along horizontal joints. Acceptance criteria per API standards allow for peaking deviations of up to 13 mm and banding deviations of up to 13 or 25 mm depending on the standard. Proper measurement procedures involve visually inspecting the tank, positioning the sweep board accurately, and taking measurements at a minimum of 8 locations around the tank circumference.Process piping b31.3 detailed
Process piping b31.3 detailedAdeel Mazhar
╠²
This document provides standards and specifications for piping components used in process piping systems. It lists dimensional standards for piping components in Table 326.1 and specifies that components must meet pressure design and mechanical strength requirements. It also states that pressure-temperature ratings of listed components are accepted for design, while unlisted components must meet provisions for rating. Dimensional requirements in appendices must also be considered.Saes q-005
Saes q-005ahmedhashem483214
╠²
This document provides standards for the design and construction of concrete foundations at Saudi Aramco. It outlines requirements for soils analysis, foundation stability, concrete specifications, and the use of precast foundations. The standards are intended to ensure foundations are adequately designed for their intended use based on accepted engineering practices and industry codes. The document provides mandatory rules for soil bearing pressures, reinforcement, construction methods, and addressing potential underground interferences.Presentation on SECVIII
Presentation on SECVIIIStatic Equipment Design
╠²
This document provides an overview and contents of an online course about ASME Section I and Section VIII fundamentals. It includes:
- An introduction to the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code which contains 12 sections covering various topics like power boilers, materials, pressure vessels, welding qualifications, and piping codes.
- Summaries of the scopes and requirements of key sections like Section I (power boilers), Section VIII (pressure vessels), and the B31 piping codes.
- Information on ASME certification and inspection procedures for pressure equipment.
- A note on converting between imperial and metric units in the ASME codes.
- An introduction to the fundamentals and design requirementsSteel Warehouse Project
Steel Warehouse ProjectJawad Shaukat
╠²
This document contains calculations for wind loads and structural design of a steel warehouse. The wind calculations determine the basic wind velocity as 32 m/s. Mean wind velocity and turbulence intensity are also calculated. Using these values, peak velocity pressure is found to be 1521 Pa. Plastic analysis is performed to determine critical load combinations and failure mechanisms. The maximum plastic moment is found to be 829.89 kNm. Connection design calculations are provided for the primary beam to column connection including bolt shear, bearing, block tearing, and plate and web bearing capacities. Design is checked against Eurocodes.API 1104 ES.pdfDanielAlexanderRiaoR
╠²
Este documento establece los est├Īndares para soldaduras de tuber├Łas utilizadas en la industria petrolera. Describe los diferentes procesos de soldadura, materiales, equipos y cualificaciones requeridas. Tambi├®n especifica los procedimientos para inspecci├│n y aceptaci├│n de soldaduras, as├Ł como referencias a otras normas relacionadas. El objetivo es asegurar que las soldaduras cumplen con los requerimientos mec├Īnicos y son seguras para su uso en sistemas de transporte y almacenamiento de petr├│leo y gas.Cmaa specification-70
Cmaa specification-70tecnidibujos
╠²
This document is C.M.A.A. Specification No. 70-1983 which provides specifications for electric overhead traveling cranes. It was developed by the Crane Manufacturers Association of America to promote standardization and provide guidelines for equipment selection. The specification contains eight sections covering general specifications, crane service classification, structural design, mechanical design, electrical equipment, inquiry data sheets and speeds, glossary, and index. It is intended to provide technical guidelines but not limit manufacturer ingenuity.Design Guide 01- Base Plate and Anchor Rod Design (2nd Edition).pdf
Design Guide 01- Base Plate and Anchor Rod Design (2nd Edition).pdfRichard Villon
╠²
This document provides guidance on designing column base plate and anchor rod connections. It discusses material selection, fabrication, installation, and repairs. The document recommends ASTM A36 as the preferred material for base plates up to 4 inches thick, and ASTM A572 Gr 42 or 50 for thicker plates. It recommends ASTM F1554 Gr 36 or 55 for anchor rods. The document provides design procedures for column base plates subjected to axial compression and tension, with and without moments. It includes examples calculating strength limits for various limit states. The document aims to provide guidelines to avoid common fabrication and erection problems and design economical but adequate column base plate details.Piping inspector questions 1
Piping inspector questions 1 MOHAMMAD ATIF ALI
╠²
The document contains questions and answers related to the duties and responsibilities of a piping inspector. Some key points include:
1. A piping inspector is responsible for material receiving inspection, visual inspection of welds and joints, pressure testing, database reporting, and verifying that piping meets codes and standards.
2. They must understand gasket types, flange designs, how to read isometric drawings, and which codes and standards apply to piping inspection.
3. Inspectors check for proper material, dimensions, supports, and cleanliness and oversee hydrostatic testing and valve installation.Steel warehouse design report
Steel warehouse design reportHavit Steel Structure Co.,ltd
╠²
This document describes the design of a single-floor steel warehouse with specifications including an 18m clear span, 6m eave height, and various loading calculations for dead, live, and wind loads based on structural guidelines. It details the materials used, structural configurations, load combinations, and internal force analysis required to ensure safety and compliance with building codes. The document concludes with a consideration of the frame design and section checking for structural integrity.Asme sec viii div 2
Asme sec viii div 2Jithu John
╠²
This document summarizes ASME Section VIII Division 2 requirements for welding and non-destructive testing of welds. It outlines weld categories, fabrication requirements including repair of defects, welding identification markings, and acceptance standards for radiographic, penetrant, and ultrasonic testing of welds. Impact testing of welds is also addressed including testing of vessel test plates to qualify welding procedures for different weld categories.[Point] pipe stress analysis by computer-caesar ii
[Point] pipe stress analysis by computer-caesar iiLuis Luis
╠²
A mathematical model of a piping system was built using Caesar II software to perform pipe stress analysis. Caesar II allows engineers to create complete digital models of piping systems and have the software analyze them and calculate stresses, displacements, and loads. It can model both static and dynamic load cases. Caesar II is commonly used for designing new piping systems and troubleshooting existing systems by determining causes of failures or evaluating unanticipated operating conditions.What does cold stretching mean
What does cold stretching meanJiun Fa ,Lai
╠²
The document outlines ASME Section VIII Division 1 rules for constructing pressure vessels with a focus on cold stretching, which enhances the yield limit of austenitic stainless steel through post-forming deformation. It details procedures, stress variations, and requirements for cold-stretching practices, including allowable stress increases and design considerations. Additional guidance on certification and stamping for vessels constructed using these methods is also provided.Stressed Induced in Supports of Horizontal Pressure vessel (Zick Analysis)
Stressed Induced in Supports of Horizontal Pressure vessel (Zick Analysis)Mahendra Prabhu S
╠²
The document summarizes Zick's analysis for stresses induced in large horizontal cylindrical pressure vessels supported on two saddles. It outlines the longitudinal bending stress, tangential shear stress, and circumferential stress at the saddle horn that Zick analyzed. It also discusses the additional stress in vessel heads used as stiffeners. The document provides equations to calculate these stresses and outlines design procedures for locating saddles, including selecting saddle angles and distances. It lists typical saddle part designs including webs, base plates, ribs, and wear plates.Afes foundation design
Afes foundation designHengkimhab
╠²
1. The document provides guidelines for designing vertical vessel foundations using AFES software. It outlines the steps in the design process, including setting soil and pile parameters, creating the structure, assigning foundation groups, editing footing sizes, and defining reinforcement.
2. Key steps include setting bearing capacities and pile properties, creating the structure model, assigning foundations to groups, editing footing dimensions for each group, and specifying pier and footing reinforcement sizes and spacing.
3. The document includes examples of foundation types, design data, and load calculations to illustrate the design process.QC Welding Inspector Interview Question & Answers.pdf
QC Welding Inspector Interview Question & Answers.pdfUniversity of Sarajevo, Manufacturing Technology:
╠²
Viewers also liked (18)
Wrs rigging practice
Wrs rigging practiceLuis Manuel Rodr├Łguez
╠²
Use multiple single leg slings to wrap around off-center loads for better stability. Secure all loose equipment before lifting. When using eye bolts or slings, be aware that their capacity decreases significantly at angled loads. Use proper padding and hitches to control loads and prevent damage.Sacs otc 2012
Sacs otc 2012HSD Luu
╠²
Bentley Systems is a global leader in engineering software for infrastructure modeling and analysis. It offers SACS, a software for designing and analyzing offshore structures from conceptual design through installation, operation, and decommissioning. SACS can model various offshore structure types and perform analyses like structural analysis, fatigue analysis, earthquake analysis, and dropped object analysis.DESIGN OF A MODEL HAULAGE TECHNIQUE FOR WATER FLOODING CAISSON ASSEMBLY.
DESIGN OF A MODEL HAULAGE TECHNIQUE FOR WATER FLOODING CAISSON ASSEMBLY.Emeka Ngwobia
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of offshore construction, emphasizing the installation of structures and facilities in marine environments, particularly for oil and gas production. It outlines various construction strategies, safety considerations, and engineering challenges associated with the lifting and transportation of a 63m caisson, as well as identifying key components and procedures involved in the process. The study aims to improve reliability in water flooding systems through effective lifting techniques and precise transportation analysis to meet relevant engineering standards.Tutorial #5 - SACS Basic
Tutorial #5 - SACS BasicFaisal Purnawarman
╠²
This document summarizes the steps for performing an offshore platform analysis using analysis generator software. It reviews loading and parameters, covers the options available for analysis type, load combination factors, and allowable stresses. The document also highlights important points for configuring the analysis, including specifying the working directory, input and output files, and solution options. Students are then instructed to run an analysis on their model, ensuring the load combination is included, and upload the results to an FTP site using a specified naming convention.Baseplate
Baseplatepeerfn88
╠²
(1) The document provides calculations to determine the required base plate thickness for a column base connection according to Eurocode standards. It includes input parameters such as column forces, material properties, bolt sizes and locations.
(2) Three equations are solved simultaneously to determine the maximum pressure under the base plate, tension in the hold down bolts, and active concrete area.
(3) The calculated pressure and bolt tension exceed design values, requiring a redesign of the base plate length/width or use of higher strength concrete.
(4) The minimum required base plate thickness is then calculated based on the design bending moment and material yield strength.Tutorial #4 - SACS Basic
Tutorial #4 - SACS BasicFaisal Purnawarman
╠²
This document provides an overview of load modeling for an offshore platform, including self-weight, live loads, equipment loads, crane loads, wave loads, current loads, wind loads, and environmental load factors and combinations. It discusses determining member properties, offsets, load details, and references for weight, dimensions, and assumptions. Load inputs from a previous model are also addressed.Tutorial #1 - SACS Basic
Tutorial #1 - SACS BasicFaisal Purnawarman
╠²
This document provides an overview of the SACS software, which is used for analyzing offshore structures. It discusses the history and capabilities of SACS, including that it can perform various types of analyses like pre-service, service, and incident analyses. It also outlines the process for setting up and performing an analysis in SACS, including defining the structure, running the analysis, and checking the results. The final section provides instructions for an assignment to build a jacket structure in SACS based on specific criteria.Tutorial #2 - SACS Basic
Tutorial #2 - SACS BasicFaisal Purnawarman
╠²
This document summarizes the topics that will be covered in Tutorial #2 on modeling an offshore platform. It includes reviewing structure definition, adding and modifying joints and members, creating member groups and properties, and laying out the deck design. The instructor asks if there are any questions and provides example member group types. Students will be guided to add member properties to their jacket model from Assignment #1 and lay out the deck beams by using example drawings available on an online FTP site.Presentacion asme seccion viii division 2 2013
Presentacion asme seccion viii division 2 2013leo040490
╠²
This document outlines steps for developing a quality control system manual (QCSM) to meet ASME Section VIII Division 2 regulations for pressure vessel certification. The key steps include:
1. Applying to ASME and the National Board for certification.
2. Developing detailed design calculations, drawings, materials specifications, and fabrication and inspection procedures meeting code requirements.
3. Implementing the QCSM in the shop and warehouses, and distributing it to all relevant personnel, to ensure all code requirements are met during construction.
4. Scheduling audits by the Authorized Inspector to confirm readiness for joint review and certification.Design of column base plates anchor bolt
Design of column base plates anchor boltKhaled Eid
╠²
This document discusses the design of column base plates and steel anchorage to concrete. It covers base plate materials and design for different load cases including axial, moment, and shear loads. It also discusses anchor rod types, materials, and design for tension and shear loading based on calculations of the steel and concrete breakout strengths according to building codes.design and analysis of pressure vessel
design and analysis of pressure vesselAkshay Chinchamalatpure
╠²
This document summarizes a student project on designing and analyzing pressure vessels using conventional and ASME standards methods. It includes:
- Design and analysis of pressure vessels using conventional design, 3D modeling, ANSYS analysis, and ASME code design using PV-Elite software.
- Comparison of designs from conventional versus ASME code methods to determine the safest and most economical approach.
- The project aims to avoid pressure vessel failures and accidents through optimized design and increased safety factors.Guidebook for the design of Asme Section VIII Pressure Vessel
Guidebook for the design of Asme Section VIII Pressure Vesselmarco garofanello
╠²
Map of ASME VIII rules. Easy guide to use of ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code. Lifting plan
Lifting plantnsv22
╠²
This document provides a crane lifting plan and risk assessment for a lifting operation. It details the crane and lift information, including load details, lifting tackle, and crane setup procedures. Safety procedures are outlined, such as conducting a site inspection, briefing personnel, establishing communication methods, and following weather restrictions. Personnel qualifications and roles are defined. The plan is intended to ensure the lifting operation is carried out safely in compliance with relevant standards and regulations.Eugene f. megyesy-pressure_vessel_handbook_12th edition
Eugene f. megyesy-pressure_vessel_handbook_12th editionGowtham M
╠²
The document is an introduction to the Pressure Vessel Handbook, which provides concise summaries and essential information for designing and constructing pressure vessels. It compares the scope and purpose of the Pressure Vessel Handbook to the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code. The Handbook covers carbon steel pressure vessels made by welding, utilizing the most economical and practical construction methods according to Code rules. It aims to make information easily accessible, while the Code establishes broader rules and does not serve as a design handbook. The Handbook is updated every three years to reflect changes to the Code and industry developments.Megyesy pressure vessel hand book [11th ed.]
Megyesy pressure vessel hand book [11th ed.]Gowtham M
╠²
The document discusses the history and importance of chocolate in human civilization. It notes that chocolate originated in Mesoamerica over 3000 years ago and was prized by the Aztecs and Mayans for its taste. Cocoa beans were used as currency and their cultivation was tightly regulated. The document highlights how chocolate spread around the world following the age of exploration and is now one of the most popular flavors globally.Daily mobile crane inspection checklist
Daily mobile crane inspection checklist Rahmat Mohamed
╠²
This document outlines a daily inspection checklist for a mobile crane. It contains 39 items across various crane systems that are to be checked for issues and documented. Any deficiencies must be reported to supervisors and rectified before crane use. The checklist is to be completed by the crane operator and approved by the lifting supervisor, who must also complete a separate safety inspection checklist.Mobile crane
Mobile craneANA ISABEL R.R.
╠²
This document provides an overview of mobile crane regulations around the world. It discusses the parts of mobile cranes including the chassis/base, upperworks, swing mechanism, and parameters considered for safe operation. Load charts and duty charts are described which specify the rated capacity of cranes under different configurations. Factors that influence safe working like ground conditions, wind, electricity hazards and multi-crane lifts are also covered.Basic rigging training manual
Basic rigging training manualSyam Tawakkal
╠²
The document provides information on basic rigging training based on national occupational health and safety standards. It discusses the key objectives and duties outlined in the relevant Act, including employer and employee responsibilities to maintain a safe working environment. The document also provides definitions of key terms, and outlines the scope of work covered under a basic rigging certificate, as well as guidelines for proper use and maintenance of common rigging appliances like chain blocks.Ad