1 of 20










Ad
Recommended
Pecha Kucha - David Hutchins
Pecha Kucha - David Hutchinsintensivecaresociety
╠²
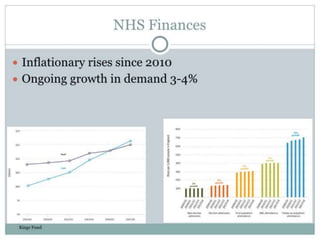
1) Critical care units can do without information technology failures, communication failures, and unevidenced practices.
2) Early pioneers like Florence Nightingale were able to significantly reduce mortality rates in the Crimean War through simple measures like improved hygiene, nutrition, and staffing levels.
3) Modern ICUs should embrace technologies but address challenges, improve communication across units through multidisciplinary teams, and generate more evidence through research to continually improve patient care.Pecha Kucha - Liam Scott
Pecha Kucha - Liam Scottintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document discusses the advantages of videolaryngoscopy over traditional Macintosh laryngoscopy for intubating critically ill patients in the ICU. It notes that videolaryngoscopy allows for faster intubation, higher first-pass success rates, better views for the whole team, and less neck manipulation. The document argues that for sick ICU patients where time is critical, a videolaryngoscope should be the first-line device used rather than the older and lower-tech Macintosh laryngoscope, in order to maximize first-attempt success.Come on baby light my fire! - Forrest
Come on baby light my fire! - Forrestintensivecaresociety
╠²
The document discusses traditional PowerPoint presentations and more effective presentation techniques. Traditional presentations often included too many text-heavy slides with small fonts, long sentences, and repetitive bullet points. More effective presentations focus one major message per slide using large fonts, minimal text, good color contrast, and include images, videos, and data to engage the audience rather than distract them from the speaker. The presentation encourages the use of more dynamic techniques to inspire and engage audiences.Pecha Kucha - Diane Murray
Pecha Kucha - Diane Murrayintensivecaresociety
╠²
The document discusses the abolition of the post ward round tea and toast break tradition in intensive care units. It notes that eating white bread and butter increases the risk of overweight and obesity due to the refined flour being rapidly absorbed as sugar and transformed into fat. Replacing butter with margarine can remove 3 kg of saturated fat from one's diet in a year, since butter is around 50% saturated fat and 4% trans fat, which are unhealthy fats that raise cholesterol levels.Petcha Kucha - Alexander Scott
Petcha Kucha - Alexander Scottintensivecaresociety
╠²
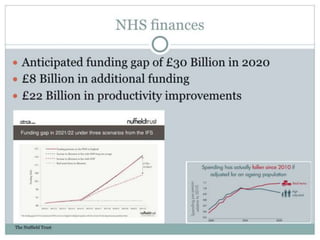
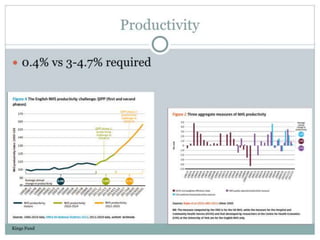
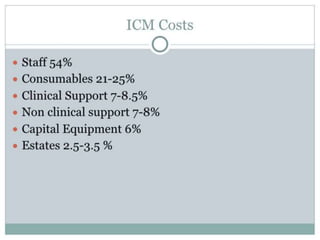
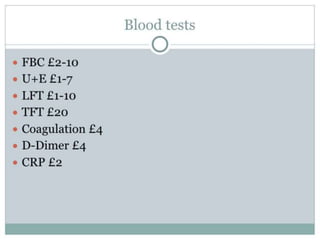
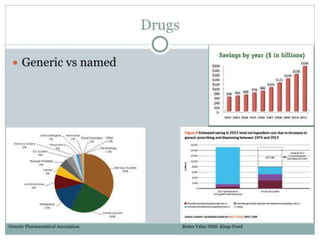
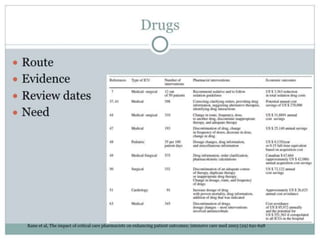
The document discusses clinical trials and research in intensive care. It notes the inadequate staffing and resources for ICUs. It then lists various interventions that have been tested in clinical trials for conditions like ARDS, sepsis and cardiac arrest, including tight glycemic control, nitric oxide, early goal directed therapy and therapeutic hypothermia. It emphasizes conducting primary research to better understand disease mechanisms and targeting interventions to patients that may benefit based on evidence.What makes a successful ICU? - Knighton
What makes a successful ICU? - Knightonintensivecaresociety
╠²
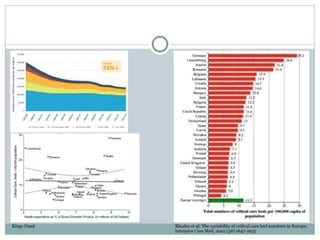
The document discusses what makes a successful ICU based on John Knighton's experience as Clinical Director of Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust Critical Care Department. It provides details on factors that contributed to the department being rated "Outstanding" by the CQC such as outcomes data, safety culture, education/training programs, and innovative use of technology. The document also discusses challenges faced by the department such as high occupancy rates and staffing shortages.Integrating Palliative Care in Rapid Response (MET) Critical Care - Nelson
Integrating Palliative Care in Rapid Response (MET) Critical Care - Nelsonintensivecaresociety
╠²
1) Rapid response teams (RRTs) are often called for patients at the end of life, presenting opportunities for palliative care integration.
2) When RRTs assess deteriorating patients, goals of care discussions and palliative care interventions like DNR orders are frequently initiated.
3) However, providing palliative care during acute RRT assessments can be challenging due to issues like lack of advance care planning, surrogate unavailability, and time pressures of crisis situations.Super refractory status epilepticus. How long should we persevere? - Hirsch
Super refractory status epilepticus. How long should we persevere? - Hirschintensivecaresociety
╠²
Super refractory status epilepticus is a rare but serious condition seen in neurointensive care units where seizures continue despite treatment with general anesthesia. The aetiology and prognosis varies, with conditions like autoimmune encephalitis from anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antibodies having a better outlook if treated early with immunotherapy and tumor removal. Intensive care management aims to control seizures, support ventilation, and treat the underlying cause like removing ovarian teratomas in anti-NMDAR encephalitis patients. While morbidity and mortality is high, complete recovery is possible even after months of status epilepticus depending on the specific cause.Learning from the iceman - Pickkers
Learning from the iceman - Pickkers intensivecaresociety
╠²
The document summarizes a study investigating whether voluntary modulation of the autonomic nervous system and immune response is possible using methods taught by "iceman" Wim Hof. The study found that subjects trained in Wim Hof's breathing techniques and meditation methods had reduced inflammatory cytokine responses and increased anti-inflammatory cytokine responses after experimental endotoxemia compared to untrained controls. Adrenaline levels were also higher in the trained group. This suggests that voluntary influence of the autonomic nervous system and immune response is possible through non-pharmacological means like Wim Hof's training techniques.Intensivist-delivered echo: dangerous in the wrong hands? - Price
Intensivist-delivered echo: dangerous in the wrong hands? - Priceintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document discusses the debate around intensivists performing echocardiography on critically ill patients. While some argue it should only be done by cardiologists due to the risk of misinterpretation, others believe intensivists can be trained to properly use focused cardiac ultrasound. The document notes repeated studies showing intensivists identify life-threatening issues in a timely manner. Ultimately, the goal on both sides should be providing optimal patient care safely, and finding a way to work together on this issue.Echo Directed Therapy Saves Lives in ICU - Vieillard-Baron
Echo Directed Therapy Saves Lives in ICU - Vieillard-Baron intensivecaresociety
╠²
This document discusses how echocardiography can be used as both a diagnostic and hemodynamic tool in intensive care units (ICUs) to help save lives. A 1-day study observed echocardiography being used in 140 ICUs to assess 36% of patients. A prospective study of 540 ICU patients found that changes in echocardiography dynamic parameters such as delta pulse pressure and delta superior vena cava collapsibility had high sensitivity and specificity for predicting fluid responsiveness. Echocardiography can accurately record hemodynamic data relevant for improving patient prognosis and guiding treatment in the ICU.Big Data: Learning from MIMIC- Celi
Big Data: Learning from MIMIC- Celiintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document discusses lessons learned from analyzing data from the MIMIC database. It makes the following key points:
1) While causality cannot be proven with observational data, large datasets like MIMIC can still provide useful insights, especially when multiple studies find consistent results.
2) Single-center databases are limited; collaborating and sharing data across centers expands what can be learned.
3) Reliable research requires transparent and continuous peer review as well as open sharing of data, methods, and findings.
4) Bringing together different experts in data-driven "datathons" can help ensure robust and impactful analyses.ARDS VILI Pro-Con Debate - Mac Sweeney
ARDS VILI Pro-Con Debate - Mac Sweeneyintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document summarizes the key debates from the SOA 2015 conference on ventilator-induced lung injury (VALI). It discusses the evidence from experimental, physiological, and interventional studies comparing higher (12 ml/kg) and lower (6 ml/kg) tidal volume ventilation strategies. Studies show that higher tidal volumes are associated with worse outcomes like increased ARDS development, mortality, and decreased lung harvest rates compared to lower tidal volumes. The evidence is analogous to the Charge of the Light Brigade military disaster where miscommunication led to heavy losses, similar to how misunderstandings of lung physiology formerly led to harmful ventilation practices.ARDS Pro-Con Debate - Mac Sweeney
ARDS Pro-Con Debate - Mac Sweeneyintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document appears to be notes from a presentation on acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and acute lung injury (ALI). It discusses the history and definitions of ARDS/ALI, including the 1988 Murray Lung Injury Score and subsequent definitions from 1994, 2005, and 2012. It also summarizes initial successes in understanding the epidemiology and pathology, but then notes hundreds of failed clinical trials trying various treatments. It suggests reasons trials may have failed and ideas for improving future trials such as using tissue biomarkers and focusing on specific ARDS phenotypes. The presentation was given by Rob Mac Sweeney in London on December 8, 2015.Blood and plasma: learning from the pre-hospital setting
Blood and plasma: learning from the pre-hospital settingintensivecaresociety
╠²
The document summarizes the current evidence regarding the use of pre-hospital blood products. It finds that while 28 studies have evaluated this intervention, the evidence is of very low quality as the studies are mostly retrospective case series and none are randomized controlled trials. Some studies found benefits to outcomes like mortality and vital signs, but others found no clear benefits or potential harms. Ongoing randomized trials are still needed to provide higher quality evidence on the risks and benefits of pre-hospital blood products.Bleeding in liver disease - Wendon
Bleeding in liver disease - Wendonintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document summarizes key findings from a study on coagulation abnormalities in patients with acute or chronic liver disease. It finds that while routine coagulation tests often indicate a bleeding tendency, the situation is complex as both pro-coagulant and anti-coagulant factors are affected. Patients can be in a balanced state but are at risk of tipping into a hypo- or hyper-coagulable condition. Tests such as thromboelastography and thrombin generation testing provide a more comprehensive assessment than standard coagulation tests. The balance of factors in liver disease patients may shift with conditions like sepsis or renal failure, increasing bleeding or thrombosis risk.ECMO: You're doing it all wrong! Or are we? - Fan
ECMO: You're doing it all wrong! Or are we? - Fanintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document summarizes a presentation by Dr. Eddy Fan on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) and lung protective ventilation strategies for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). The presentation discusses how ECMO can be used to facilitate lung rest and prevent ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) in ARDS patients who cannot be safely ventilated with conventional lung protective strategies. It reviews evidence that ECMO combined with lower tidal volumes and plateau pressures may improve lung inflammation outcomes. However, optimal ventilation settings for ARDS patients on ECMO are still unknown. The presentation then describes the SOLVE ARDS study which aims to determine best practices for lung ventilation during ECMO through an international survey, systematic review,ECMO: You're doing it all wrong - Gattinoni
ECMO: You're doing it all wrong - Gattinoniintensivecaresociety
╠²
1) Luciano Gattinoni, MD discusses extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) and strategies for ventilating patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
2) Gattinoni's research in the 1970s established the "lung rest concept" which uses ECMO to reduce ventilator pressures and volumes to prevent ventilator-induced lung injury.
3) Gattinoni presents graphs showing how adjusting positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) and driving pressures can optimize lung ventilation and avoid pressures that are too high or too low for different ARDS severity levels.The ARDS Definition is Killing Advances in the Field - Fan
The ARDS Definition is Killing Advances in the Field - Fanintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document summarizes a presentation by Dr. Eddy Fan on the limitations and concerns with the current ARDS definition. The presentation discusses how syndromes in critical care like ARDS require reliable definitions to conduct research and interpret clinical trials. However, the current AECC/Berlin definitions have limitations. Specifically, the criteria like chest x-rays and PAOP measurements have poor reliability. Additionally, factors like mechanical ventilation settings are not standardized when assessing oxygenation. The definitions also do not capture other important variables for clinicians. Overall, while the Berlin definition made improvements, its criteria need further validation and refinement.The Complex Surgical Abdomen in ICU: When do you reopen? - Warusavitarne
The Complex Surgical Abdomen in ICU: When do you reopen? - Warusavitarneintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document discusses the complex surgical abdomen in the intensive care unit and considerations around reopening a patient. It notes that reoperation is associated with high mortality rates of 40-72% and should generally be avoided, especially in the first 10 days to 3 months post-operatively. Instead, the goals should be to control sepsis through drainage and an open abdomen approach rather than trying to immediately repair leaks or close the abdominal wall. Reoperation should only be undertaken when the patient is in the best possible condition to optimize outcomes.UK Joint Specialist Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Menin...
UK Joint Specialist Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Menin...intensivecaresociety
╠²
This document provides a summary of guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute meningitis and meningococcal sepsis in immunocompetent adults in the UK. It was created by a collaboration of medical societies. Key points include:
- Meningitis has a high mortality rate and guidelines may improve outcomes.
- Patients should receive rapid initial assessment, antibiotics, and lumbar puncture if safe.
- Not all patients require neuroimaging first; it can delay treatment.
- Treatment includes empirical antibiotics, dexamethasone adjunct therapy, and supportive critical care as needed.
- Guidelines aim to standardize best practices and improve outcomes through a multifaceted implementation strategy engaging clinicians.Rethinking DNACPR orders: ethical issues and a proposal for change - Fritz
Rethinking DNACPR orders: ethical issues and a proposal for change - Fritzintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document summarizes the key issues regarding DNACPR (Do Not Attempt Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) orders and proposes an alternative approach called the Universal Form of Treatment Options (UFTO). The summary includes:
1. There are several ethical issues with the current use of DNACPR orders, including that they are not routinely completed for patients, sometimes result in inappropriate resuscitation attempts, and often lack discussions with patients and families.
2. The document proposes the UFTO as an alternative, which aims to remove the ad hoc nature of consideration, improve discussions, and shift the focus to goals of care rather than a "resus/no resus" decision.
3. A studyDecision-making for Intensive Care: Deciding who to admit - Bassford
Decision-making for Intensive Care: Deciding who to admit - Bassfordintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document discusses decision-making for intensive care unit admissions. It notes that intensive care clinicians are generally best suited to make admission decisions, but that they could benefit from better methods of predicting patient outcomes, more training in decision-making, and ensuring decisions are made in an ethically justifiable manner. Several factors can influence admission decisions, including patient characteristics, clinician factors, and organizational constraints like bed availability. The document calls for further research to improve understanding and transparency around ICU admission decision-making processes.Sepsis - Process and Scale - Daniels
Sepsis - Process and Scale - Danielsintensivecaresociety
╠²
1) Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. Left untreated, sepsis can lead to septic shock, multiple organ failure, and death.
2) Early recognition and treatment of sepsis is key to reducing mortality. The "Sepsis Six" bundle of interventions should be completed within one hour for patients with sepsis, including administering oxygen, antibiotics, fluids, and monitoring lactate levels and urine output.
3) Sepsis can cause long-term cognitive and physical impairment in survivors. A study found that 16.8% of severe sepsis survivors had moderate to severe cognitive impairment after recovering.RSS Feeds - Forrest
RSS Feeds - Forrestintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document discusses RSS feeds and how to use them to build your own personal journal of online content through feed readers like Feedly and Pocket. It recommends using RSS feeds to get more relevant information with less extraneous content and describes how feed readers allow you to save articles and build a collection of content to read later.Periscope - Wong
Periscope - Wong intensivecaresociety
╠²
Periscope allows one host with video replays available for 24 hours after a live stream, while Blab allows 2-4 hosts and video replays available after live streaming. Both are live video streaming platforms accessible via Twitter accounts with interactive commenting features.Keeping a record for your appraisal - Mathieu
Keeping a record for your appraisal - Mathieuintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document provides guidance on keeping records for an appraisal. It recommends documenting all continuing professional development activities from January 1st to December 31st, including recording details of activities, reflections on learning, and how the learning will be applied. The records should then be submitted for the annual appraisal process.Digital Media Episodic Downoadable (Podcasts) - Downham
Digital Media Episodic Downoadable (Podcasts) - Downhamintensivecaresociety
╠²
ICS State of the Art Meeting 2015Unlocking the Potential of Long-Acting PrEP to Halt HIV Transmissions
Unlocking the Potential of Long-Acting PrEP to Halt HIV TransmissionsPVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Chair, Allison Agwu, MD, ScM, FAAP, FIDSA, discusses HIV in this CME/MOC/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE activity titled ŌĆ£Unlocking the Potential of Long-Acting PrEP to Halt HIV Transmissions.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/MOC/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/40Mr2AC. CME/MOC/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE credit will be available until June 12, 2026.Coarse Dispersion, Physical Pharmaceutics
Coarse Dispersion, Physical Pharmaceuticsnishiprakashj
╠²
Its a compilation of unit 3 as per PCI syllabus of B.Pharm IV sem, Subject Physical Pharmaceutics.More Related Content
More from intensivecaresociety (20)
Learning from the iceman - Pickkers
Learning from the iceman - Pickkers intensivecaresociety
╠²
The document summarizes a study investigating whether voluntary modulation of the autonomic nervous system and immune response is possible using methods taught by "iceman" Wim Hof. The study found that subjects trained in Wim Hof's breathing techniques and meditation methods had reduced inflammatory cytokine responses and increased anti-inflammatory cytokine responses after experimental endotoxemia compared to untrained controls. Adrenaline levels were also higher in the trained group. This suggests that voluntary influence of the autonomic nervous system and immune response is possible through non-pharmacological means like Wim Hof's training techniques.Intensivist-delivered echo: dangerous in the wrong hands? - Price
Intensivist-delivered echo: dangerous in the wrong hands? - Priceintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document discusses the debate around intensivists performing echocardiography on critically ill patients. While some argue it should only be done by cardiologists due to the risk of misinterpretation, others believe intensivists can be trained to properly use focused cardiac ultrasound. The document notes repeated studies showing intensivists identify life-threatening issues in a timely manner. Ultimately, the goal on both sides should be providing optimal patient care safely, and finding a way to work together on this issue.Echo Directed Therapy Saves Lives in ICU - Vieillard-Baron
Echo Directed Therapy Saves Lives in ICU - Vieillard-Baron intensivecaresociety
╠²
This document discusses how echocardiography can be used as both a diagnostic and hemodynamic tool in intensive care units (ICUs) to help save lives. A 1-day study observed echocardiography being used in 140 ICUs to assess 36% of patients. A prospective study of 540 ICU patients found that changes in echocardiography dynamic parameters such as delta pulse pressure and delta superior vena cava collapsibility had high sensitivity and specificity for predicting fluid responsiveness. Echocardiography can accurately record hemodynamic data relevant for improving patient prognosis and guiding treatment in the ICU.Big Data: Learning from MIMIC- Celi
Big Data: Learning from MIMIC- Celiintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document discusses lessons learned from analyzing data from the MIMIC database. It makes the following key points:
1) While causality cannot be proven with observational data, large datasets like MIMIC can still provide useful insights, especially when multiple studies find consistent results.
2) Single-center databases are limited; collaborating and sharing data across centers expands what can be learned.
3) Reliable research requires transparent and continuous peer review as well as open sharing of data, methods, and findings.
4) Bringing together different experts in data-driven "datathons" can help ensure robust and impactful analyses.ARDS VILI Pro-Con Debate - Mac Sweeney
ARDS VILI Pro-Con Debate - Mac Sweeneyintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document summarizes the key debates from the SOA 2015 conference on ventilator-induced lung injury (VALI). It discusses the evidence from experimental, physiological, and interventional studies comparing higher (12 ml/kg) and lower (6 ml/kg) tidal volume ventilation strategies. Studies show that higher tidal volumes are associated with worse outcomes like increased ARDS development, mortality, and decreased lung harvest rates compared to lower tidal volumes. The evidence is analogous to the Charge of the Light Brigade military disaster where miscommunication led to heavy losses, similar to how misunderstandings of lung physiology formerly led to harmful ventilation practices.ARDS Pro-Con Debate - Mac Sweeney
ARDS Pro-Con Debate - Mac Sweeneyintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document appears to be notes from a presentation on acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and acute lung injury (ALI). It discusses the history and definitions of ARDS/ALI, including the 1988 Murray Lung Injury Score and subsequent definitions from 1994, 2005, and 2012. It also summarizes initial successes in understanding the epidemiology and pathology, but then notes hundreds of failed clinical trials trying various treatments. It suggests reasons trials may have failed and ideas for improving future trials such as using tissue biomarkers and focusing on specific ARDS phenotypes. The presentation was given by Rob Mac Sweeney in London on December 8, 2015.Blood and plasma: learning from the pre-hospital setting
Blood and plasma: learning from the pre-hospital settingintensivecaresociety
╠²
The document summarizes the current evidence regarding the use of pre-hospital blood products. It finds that while 28 studies have evaluated this intervention, the evidence is of very low quality as the studies are mostly retrospective case series and none are randomized controlled trials. Some studies found benefits to outcomes like mortality and vital signs, but others found no clear benefits or potential harms. Ongoing randomized trials are still needed to provide higher quality evidence on the risks and benefits of pre-hospital blood products.Bleeding in liver disease - Wendon
Bleeding in liver disease - Wendonintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document summarizes key findings from a study on coagulation abnormalities in patients with acute or chronic liver disease. It finds that while routine coagulation tests often indicate a bleeding tendency, the situation is complex as both pro-coagulant and anti-coagulant factors are affected. Patients can be in a balanced state but are at risk of tipping into a hypo- or hyper-coagulable condition. Tests such as thromboelastography and thrombin generation testing provide a more comprehensive assessment than standard coagulation tests. The balance of factors in liver disease patients may shift with conditions like sepsis or renal failure, increasing bleeding or thrombosis risk.ECMO: You're doing it all wrong! Or are we? - Fan
ECMO: You're doing it all wrong! Or are we? - Fanintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document summarizes a presentation by Dr. Eddy Fan on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) and lung protective ventilation strategies for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). The presentation discusses how ECMO can be used to facilitate lung rest and prevent ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) in ARDS patients who cannot be safely ventilated with conventional lung protective strategies. It reviews evidence that ECMO combined with lower tidal volumes and plateau pressures may improve lung inflammation outcomes. However, optimal ventilation settings for ARDS patients on ECMO are still unknown. The presentation then describes the SOLVE ARDS study which aims to determine best practices for lung ventilation during ECMO through an international survey, systematic review,ECMO: You're doing it all wrong - Gattinoni
ECMO: You're doing it all wrong - Gattinoniintensivecaresociety
╠²
1) Luciano Gattinoni, MD discusses extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) and strategies for ventilating patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
2) Gattinoni's research in the 1970s established the "lung rest concept" which uses ECMO to reduce ventilator pressures and volumes to prevent ventilator-induced lung injury.
3) Gattinoni presents graphs showing how adjusting positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) and driving pressures can optimize lung ventilation and avoid pressures that are too high or too low for different ARDS severity levels.The ARDS Definition is Killing Advances in the Field - Fan
The ARDS Definition is Killing Advances in the Field - Fanintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document summarizes a presentation by Dr. Eddy Fan on the limitations and concerns with the current ARDS definition. The presentation discusses how syndromes in critical care like ARDS require reliable definitions to conduct research and interpret clinical trials. However, the current AECC/Berlin definitions have limitations. Specifically, the criteria like chest x-rays and PAOP measurements have poor reliability. Additionally, factors like mechanical ventilation settings are not standardized when assessing oxygenation. The definitions also do not capture other important variables for clinicians. Overall, while the Berlin definition made improvements, its criteria need further validation and refinement.The Complex Surgical Abdomen in ICU: When do you reopen? - Warusavitarne
The Complex Surgical Abdomen in ICU: When do you reopen? - Warusavitarneintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document discusses the complex surgical abdomen in the intensive care unit and considerations around reopening a patient. It notes that reoperation is associated with high mortality rates of 40-72% and should generally be avoided, especially in the first 10 days to 3 months post-operatively. Instead, the goals should be to control sepsis through drainage and an open abdomen approach rather than trying to immediately repair leaks or close the abdominal wall. Reoperation should only be undertaken when the patient is in the best possible condition to optimize outcomes.UK Joint Specialist Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Menin...
UK Joint Specialist Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Menin...intensivecaresociety
╠²
This document provides a summary of guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute meningitis and meningococcal sepsis in immunocompetent adults in the UK. It was created by a collaboration of medical societies. Key points include:
- Meningitis has a high mortality rate and guidelines may improve outcomes.
- Patients should receive rapid initial assessment, antibiotics, and lumbar puncture if safe.
- Not all patients require neuroimaging first; it can delay treatment.
- Treatment includes empirical antibiotics, dexamethasone adjunct therapy, and supportive critical care as needed.
- Guidelines aim to standardize best practices and improve outcomes through a multifaceted implementation strategy engaging clinicians.Rethinking DNACPR orders: ethical issues and a proposal for change - Fritz
Rethinking DNACPR orders: ethical issues and a proposal for change - Fritzintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document summarizes the key issues regarding DNACPR (Do Not Attempt Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) orders and proposes an alternative approach called the Universal Form of Treatment Options (UFTO). The summary includes:
1. There are several ethical issues with the current use of DNACPR orders, including that they are not routinely completed for patients, sometimes result in inappropriate resuscitation attempts, and often lack discussions with patients and families.
2. The document proposes the UFTO as an alternative, which aims to remove the ad hoc nature of consideration, improve discussions, and shift the focus to goals of care rather than a "resus/no resus" decision.
3. A studyDecision-making for Intensive Care: Deciding who to admit - Bassford
Decision-making for Intensive Care: Deciding who to admit - Bassfordintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document discusses decision-making for intensive care unit admissions. It notes that intensive care clinicians are generally best suited to make admission decisions, but that they could benefit from better methods of predicting patient outcomes, more training in decision-making, and ensuring decisions are made in an ethically justifiable manner. Several factors can influence admission decisions, including patient characteristics, clinician factors, and organizational constraints like bed availability. The document calls for further research to improve understanding and transparency around ICU admission decision-making processes.Sepsis - Process and Scale - Daniels
Sepsis - Process and Scale - Danielsintensivecaresociety
╠²
1) Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. Left untreated, sepsis can lead to septic shock, multiple organ failure, and death.
2) Early recognition and treatment of sepsis is key to reducing mortality. The "Sepsis Six" bundle of interventions should be completed within one hour for patients with sepsis, including administering oxygen, antibiotics, fluids, and monitoring lactate levels and urine output.
3) Sepsis can cause long-term cognitive and physical impairment in survivors. A study found that 16.8% of severe sepsis survivors had moderate to severe cognitive impairment after recovering.RSS Feeds - Forrest
RSS Feeds - Forrestintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document discusses RSS feeds and how to use them to build your own personal journal of online content through feed readers like Feedly and Pocket. It recommends using RSS feeds to get more relevant information with less extraneous content and describes how feed readers allow you to save articles and build a collection of content to read later.Periscope - Wong
Periscope - Wong intensivecaresociety
╠²
Periscope allows one host with video replays available for 24 hours after a live stream, while Blab allows 2-4 hosts and video replays available after live streaming. Both are live video streaming platforms accessible via Twitter accounts with interactive commenting features.Keeping a record for your appraisal - Mathieu
Keeping a record for your appraisal - Mathieuintensivecaresociety
╠²
This document provides guidance on keeping records for an appraisal. It recommends documenting all continuing professional development activities from January 1st to December 31st, including recording details of activities, reflections on learning, and how the learning will be applied. The records should then be submitted for the annual appraisal process.Digital Media Episodic Downoadable (Podcasts) - Downham
Digital Media Episodic Downoadable (Podcasts) - Downhamintensivecaresociety
╠²
ICS State of the Art Meeting 2015UK Joint Specialist Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Menin...
UK Joint Specialist Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Menin...intensivecaresociety
╠²
Recently uploaded (20)
Unlocking the Potential of Long-Acting PrEP to Halt HIV Transmissions
Unlocking the Potential of Long-Acting PrEP to Halt HIV TransmissionsPVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Chair, Allison Agwu, MD, ScM, FAAP, FIDSA, discusses HIV in this CME/MOC/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE activity titled ŌĆ£Unlocking the Potential of Long-Acting PrEP to Halt HIV Transmissions.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/MOC/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/40Mr2AC. CME/MOC/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE credit will be available until June 12, 2026.Coarse Dispersion, Physical Pharmaceutics
Coarse Dispersion, Physical Pharmaceuticsnishiprakashj
╠²
Its a compilation of unit 3 as per PCI syllabus of B.Pharm IV sem, Subject Physical Pharmaceutics.AD-SAFE: An Initiative to Build Understanding of ARIA and Skills Needed to Gu...
AD-SAFE: An Initiative to Build Understanding of ARIA and Skills Needed to Gu...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Chair and Presenter, Ana M. Franceschi, MD, PhD, and Petrice M. Cogswell, MD, PhD, discuss AlzheimerŌĆÖs disease in this CME/MOC/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE activity titled ŌĆ£AD-SAFE: An Initiative to Build Understanding of ARIA and Skills Needed to Guide Treatment Decisions and Support Rapid Recognition and Response in Radiology.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/MOC/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/42nd09H. CME/MOC/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE credit will be available until May 26, 2026.whooping cough community health nursing.
whooping cough community health nursing.ASWIN S
╠²
Whooping cough for BSC 5th sem community health nursing..
This includes
Introduction
Definition
Incidence
Incubation period
Causes
Clinical manifestations
Diagnostic evaluation
Treatment
Prevention
Complications
Of whooping cough....Aspirin powder or Acetyl salicylic acid powder.docx
Aspirin powder or Acetyl salicylic acid powder.docxkopalsharma85
╠²
pharmacy exercise on aspirin powderRatricharya according to ayurveda along with day and night pattern in various...
Ratricharya according to ayurveda along with day and night pattern in various...DR DHARMENDRA BINJHWAR
╠²
This slide are more importents for ayurveda students and teachers because i have mentioned in this slide night time routine in ayurveda the ancient science of India along with day and night pattern in various counteries within in one ppt. thanks for watching i will be greatful for your suggestion and feedback... please like share and suppourtInferential statistics-part 2Chi-Square Test
Inferential statistics-part 2Chi-Square TestBabitha Devu
╠²
Inferential Statistics Part - 2 deals with Nonparametric test.
Only Chi-square is discussed here. HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA - thalassemia, AIHA, and NACP
HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA - thalassemia, AIHA, and NACPSSIMS & RC
╠²
Competency based classes for MBBS students.. GAIT in Biomechanics along with abnormal gait
GAIT in Biomechanics along with abnormal gaitNerusu sai priyanka
╠²
Gait , ab normal gait,normal biomechanics,pathomechanics of gait,unilateral stance,factors affectoing gait Self-Awareness and Self-Care How Professionals Can Avoid Burnout
Self-Awareness and Self-Care How Professionals Can Avoid BurnoutOlaf Kraus de Camargo
╠²
Closing Keynote at the IV OG├ōLNOPOLSKA KONFERENCJA & WARSZTATY
KomunikAACja, Samoswiadomosc, Seksualnosc
June 13th ŌĆō 14th, 2025
An overview of the definition and presentation of burnout in healthcare workers, strategies to prevent it and to build resilience. The presentation also explores the barriers and enablers to introducing wellness strategies in organizations.nanoparticle and liposomes ppt .(NTDS)pdf
nanoparticle and liposomes ppt .(NTDS)pdfsiddhikalbande
╠²
Nanoparticles and liposomes are advanced carriers used for targeted drug delivery.
Nanoparticles enhance drug effectiveness by directing treatment to specific sites.
Liposomes are biocompatible vesicles that enable controlled and sustained drug release.Anti-Infective Agents: Classification, Uses & Formulations Detailed Guide to...
Anti-Infective Agents: Classification, Uses & Formulations Detailed Guide to...Sajini
╠²
This presentation covers various classes of anti-infective agents including antifungal, antiviral, antitubercular, antimalarial, urinary tract anti-infectives, and sulphonamides. It provides classification, properties, storage conditions, uses, brand names, and pharmaceutical formulations of each drug. Ideal for pharmacy, nursing, and medical students preparing for pharmacology and mediciUpdates_in Head__Neck TNM staging- 9th edition.pptx
Updates_in Head__Neck TNM staging- 9th edition.pptxDr. Maroti Wadewale
╠²
The Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) and the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) collaborate closely to produce the globally recognized TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. Therefore, when discussing the "9th edition of UICC head and neck staging," it's largely in alignment with the updates introduced by the AJCC's Version 9. The UICC's TNM Core Committee finalized the 9th edition of the TNM Classification, with publication anticipated in August 2025.
The key updates for head and neck cancers in the 9th edition (or Version 9) reflect an ongoing effort to improve prognostic accuracy and align staging with contemporary clinical understanding and treatment outcomes. Here are the significant changes, particularly those relevant to head and neck:
* Emphasis on Personalized Care and Prognostic Refinements: The 9th edition reflects a greater focus on personalized care, incorporating refinements that aim to better predict patient outcomes.
* Revised Criteria for Specific Head and Neck Cancers:
* Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma (NPC): This site has seen substantial revisions, as highlighted in the previous response on AJCC updates. Key changes include:
* More precise definition of T3 disease (unequivocal evidence of bone involvement).
* Introduction of advanced radiologic extranodal extension (ENE) as an N3 criterion. This acknowledges the prognostic impact of ENE seen on imaging.
* Subclassification of M1 disease into M1a (3 or fewer metastatic lesions) and M1b (more than 3 lesions) to better stratify prognosis in metastatic settings.
* Redefined Stage Groups for NPC, with T1-2N0-1 now often falling into Stage I, and Stage IV being exclusively for metastatic disease, further subdivided by the M1a/M1b categories.
* Salivary Gland Cancers: Revised criteria based on updated imaging and anatomical features are being incorporated.
* HPV-Related Oropharyngeal Cancers: New staging is introduced for HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancers to better reflect their distinct biological behavior and prognosis, which is generally more favorable than HPV-negative oropharyngeal cancers. This often involves specific considerations for nodal burden.
* Integration of Imaging and Anatomical Features: The updates are grounded in recent evidence, incorporating insights from advanced imaging techniques and a deeper understanding of anatomical spread.
* International Collaboration: These updates are the result of collaborative efforts between the AJCC and UICC, involving input from cancer registries, clinical outcomes data, and disease-specific experts worldwide. The goal is to provide a unified and globally applicable staging system.
* Dynamic Update Process: Similar to the AJCC's shift from "Editions" to "Versions" for specific sites, the UICC is also exploring more flexible ways to share future TNM updates.
In essence, the 9th edition of the UICC staging system for head and neck cancers, particularly in areas like NPC and HPVTheories of Learning and Teaching.......
Theories of Learning and Teaching.......Avantika Gupta
╠²
Definition of Teaching:
ŌĆ£Teaching is a form of interpersonal influence aim at changing the behavior potential of another personŌĆØ.
Nature and Characteristics of Teaching:
’āś Teaching is giving information.
’āś Teaching is causing to learn.
’āś Teaching is a matter of helping the child to respond to his environment in an effective manner.
’āś Teaching is helping a child to adjust himself to his environment.
’āś Teaching is stimulation and encouragement.
’āś Teaching is guidance.
’āś Teaching is Training the emotions of the child.
’āś Teaching is a mean of preparation.
’āś Teaching is an art and science.
General Theory of Teaching:
The General Theory of Teaching, also known as the "Theory of Teaching" or "General Theory of Instruction," is a comprehensive framework that outlines the fundamental principles and processes of teaching.
Benefits of the General Theory of Teaching:
ŌĆó Improved Student Learning
ŌĆó Increased Teacher Efficacy
ŌĆó Enhanced Teacher Professional Development
ŌĆó Better Student Engagement
CONCLUSION
ŌĆó Teaching theory is prescriptive.
ŌĆó Teachers and pupils are the major variables of teaching theory.
ŌĆó It is narrow and specific.
ŌĆó It is based upon learning theory, learning conditions and learning components.
ŌĆó While learning theory are formulated by conducting experiments on animals teaching theory is developed by dealing with human subjects in normal situations.
ŌĆó It is concerned with effective learning and development of pupils.
Learning is a complex and multifaceted process that involves the acquisition, processing, and retention of knowledge, skills, and attitudes.
The relatively permanent change in a person's knowledge or behavior due to experience.
Characteristics of Learning:
ŌĆó Learning is Growth.
ŌĆó Learning is adjustment.
ŌĆó Learning is purposeful.
ŌĆó Learning is intelligent.
ŌĆó Learning is active.
ŌĆó Learning is both individual and social.
ŌĆó Learning is the product of the environment.
ŌĆó Learning is experience.
Learning Theory: Learning theory refers to the body of knowledge that explains how people learn and acquire new knowledge, skills, and attitudes.
Types of Teaching Theory:
1.Formal Theory of Teaching
ŌĆó Meutic Theory of teaching.
ŌĆó Communication theory of teaching.
ŌĆó Moulding theory of teaching.
ŌĆó The mutual enquiry theory.
2.Descriptive theory of teaching
ŌĆó Theories of instruction
ŌĆó Prescriptive theory of teaching
3.Normative theory of teaching
ŌĆó Cognitive theory of teaching
ŌĆó Theory of teacher behaviour
ŌĆó Psychological theory of teaching
ŌĆó General theory of teaching
FORMAL THEORY OF TEACHING
Formal theory of teaching is also known as philosophical theory. The theory which is based upon certain logic, certain metaphysical, epistemological assumptions and propositions is known as formal theory of teaching.
1.Meutic Theory of Teaching:
ŌĆó This theory conceives that teaching process helps to recollect or unfold that knowledge with questioning techniques.
ŌĆó The SocraticŌĆÖs method is an essential for this theory.
ŌĆó The heredity plays an importA Day in the Life of an Immunologist.pptx
A Day in the Life of an Immunologist.pptxClinical Immunology Laboratory, HMRUO, Oran.
╠²
My day usually begins with a short team meeting.
Then I move into the labŌĆ”ŌĆØ
To study how the immune system reactsŌĆ”...
Then I move into the clinicŌĆ”ŌĆØ
After the lab, the clinicŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”
I return to my office
Another part of my job is teachingŌĆ”ŌĆ”. Inside the hospital and outside
Communication is also part of my job.
Another wonderful aspect of my lifeŌĆ”..
clinical studies
In the afternoons or evenings,
I often work on academic writing.
Special Research Contribution:
Special Research Contribution:
Pharmaceutical Agents Acting on the Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT)
Pharmaceutical Agents Acting on the Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT)Sajini
╠²
This presentation provides a detailed overview of gastrointestinal (GIT) agents used in pharmaceutical practice, including antacids, acidifying agents, cathartics, protectives, and adsorbents. It covers classification, mechanisms, properties, uses, and common brand names. Ideal for pharmacy students and healthcare professionals.When is the Right Time to Refer to (Advanced) Heart Failure?
When is the Right Time to Refer to (Advanced) Heart Failure?Duke Heart
╠²
Adam DeVore, MD, MHS
Duke University Filtration Factories : Anatomy and Physiology of Renal system
Filtration Factories : Anatomy and Physiology of Renal systemViresh Mahajani
╠²
This in-depth PowerPoint presentation provides a comprehensive and essential guide to the human urinary system, specifically tailored for nursing students. Designed to simplify complex concepts and enhance learning, this PPT covers all critical aspects of urinary anatomy and physiology.
Key topics meticulously explored include:
Gross and Microscopic Anatomy of the Urinary System: Detailed examination of the kidneys (cortex, medulla, nephrons, renal pyramids, calyces, renal pelvis), ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. High-quality anatomical diagrams and histological images are integrated to facilitate visual learning.
Physiology of Urine Formation: A step-by-step breakdown of glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption (proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule, collecting duct), and tubular secretion. Emphasis is placed on the roles of various hormones (ADH, aldosterone, ANP, parathyroid hormone) and their impact on fluid and electrolyte balance. Understanding the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) and its role in blood pressure regulation is also a key focus.
Regulation of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance: Exploration of the body's mechanisms for maintaining homeostasis, including the roles of the kidneys in regulating water balance, sodium, potassium, calcium, phosphate, and acid-base balance (bicarbonate buffer system).
Unlocking the Potential of Long-Acting PrEP to Halt HIV Transmissions
Unlocking the Potential of Long-Acting PrEP to Halt HIV TransmissionsPVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
AD-SAFE: An Initiative to Build Understanding of ARIA and Skills Needed to Gu...
AD-SAFE: An Initiative to Build Understanding of ARIA and Skills Needed to Gu...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Ratricharya according to ayurveda along with day and night pattern in various...
Ratricharya according to ayurveda along with day and night pattern in various...DR DHARMENDRA BINJHWAR
╠²
Ad
