Pmp session 6
- 1. PMP & CAPM Exam Preparation March 5, 2013
- 2. Sessions 1. About the exam 2. Integration & Scope Management 3. Time & Cost Management 4. Quality & HR Management 5. Communication & Risk Management 6. Procurement Management
- 3. Last Session Key point âĒ Process groups: IPEMCC âĒ 9 Knowledge Area: ISTiCoQuHurCoRiP âĒ Project Integration Management â DevPC.PMP.DirManPex.MoConPW.PerICC.CloPP âĒ Project Scope Management â CoDeWoBVCon
- 4. Last Session Key point â contâd âĒ Project Time Management (DeSeReDDevCon) âĒ Project Cost Management (EsCDeBCon) âĒ Project Quality Management (PlanQAQC) âĒ Project Human Resources (Plan ADM) âĒ Project Communication Management (IdS Plan DisInt ManSEx RepPer) âĒ Project Risk Management (PlanR IdR QQ Rp MC)
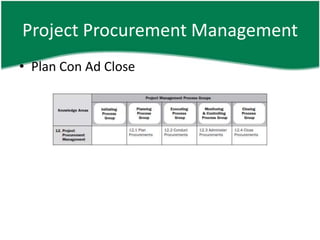
- 5. Project Procurement Management âĒ Plan Con Ad Close
- 6. Project Procurement Management âĒ To acquire / purchase products, services, or results needed from outside the project team âĒ Includes contract management âĒ Contracts: legal document between buyer and seller, represents a legally binding agreement which obligates the seller to provide the specified products, services, or results and obligates the buyer to provide monetary or other valuable consideration
- 8. Project Procurement Management âĒ A complex project may involve managing multiple contracts or subcontracts simultaneously or in sequence âĒ Seller = contractor, subcontractor, vendor, supplier, service provider âĒ Buyer = client, customer, prime contractor, acquiring organization, purchaser, requestor
- 9. Project Procurement Management âĒ This chapter assumes as buyer and seller is external provider
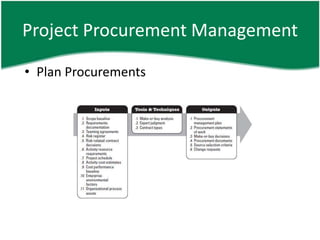
- 10. Project Procurement Management âĒ Plan Procurements âĒ Documenting project purchasing decisions âĒ Specify purchasing approach âĒ Identifying potential sellers âĒ Answers, âShould we acquire it externally?, What to require, How to require, How much and When to acquireâ
- 11. Project Procurement Management âĒ Plan Procurements
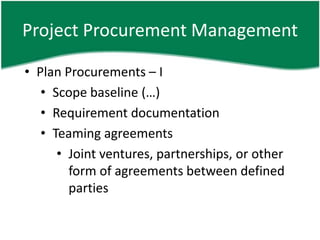
- 12. Project Procurement Management âĒ Plan Procurements â I âĒ Scope baseline (âĶ) âĒ Requirement documentation âĒ Teaming agreements âĒ Joint ventures, partnerships, or other form of agreements between defined parties
- 13. Project Procurement Management âĒ Plan Procurements â I (contâd) âĒ Risk register âĒ Risk related contract decisions âĒ Activity resource requirements âĒ Project schedule âĒ Activity cost estimates âĒ Cost performance basline âĒ EEF
- 14. Project Procurement Management âĒ Plan Procurements â TT âĒ Make-or-buy analysis âĒ Expert judgment âĒ Contract types ïFixed-price contract ïCost-reimbursable contract ïTime and material
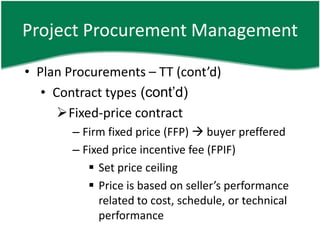
- 15. Project Procurement Management âĒ Plan Procurements â TT (contâd) âĒ Contract types (contâd) ïFixed-price contract â Firm fixed price (FFP) ï buyer preffered â Fixed price incentive fee (FPIF) ï§ Set price ceiling ï§ Price is based on sellerâs performance related to cost, schedule, or technical performance
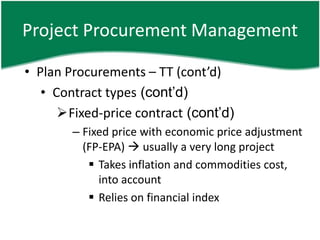
- 16. Project Procurement Management âĒ Plan Procurements â TT (contâd) âĒ Contract types (contâd) ïFixed-price contract (contâd) â Fixed price with economic price adjustment (FP-EPA) ï usually a very long project ï§ Takes inflation and commodities cost, into account ï§ Relies on financial index
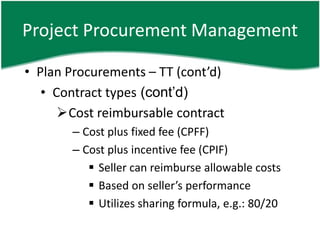
- 17. Project Procurement Management âĒ Plan Procurements â TT (contâd) âĒ Contract types (contâd) ïCost reimbursable contract â Cost plus fixed fee (CPFF) â Cost plus incentive fee (CPIF) ï§ Seller can reimburse allowable costs ï§ Based on sellerâs performance ï§ Utilizes sharing formula, e.g.: 80/20
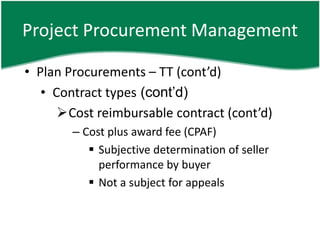
- 18. Project Procurement Management âĒ Plan Procurements â TT (contâd) âĒ Contract types (contâd) ïCost reimbursable contract (contâd) â Cost plus award fee (CPAF) ï§ Subjective determination of seller performance by buyer ï§ Not a subject for appeals
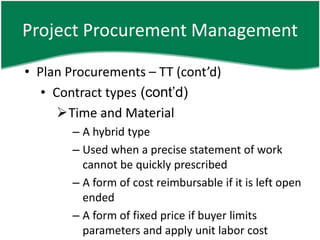
- 19. Project Procurement Management âĒ Plan Procurements â TT (contâd) âĒ Contract types (contâd) ïTime and Material â A hybrid type â Used when a precise statement of work cannot be quickly prescribed â A form of cost reimbursable if it is left open ended â A form of fixed price if buyer limits parameters and apply unit labor cost
- 20. Project Procurement Management âĒ Plan Procurements â O âĒ Procurement management plan ï§ Contract type, risk management issue ï§ Evaluation criteria, multiple contracts criteria ï§ Constraints and assumptions, etc
- 21. Project Procurement Management âĒ Plan Procurements â O (contâd) âĒ Procurement statement of work ï§ Developed from project scope baseline and defines only a portion of project scope to be included in related contract ï§ Must be in sufficient detail so that prospective sellers can determine their capability to provide such product, service, or results
- 22. Project Procurement Management âĒ Plan Procurements â O (contâd) âĒ Procurement statement of work (contâd) ï§ Includes specifications, quantity, quality levels, performance data, performance period, work location, etc ï§ Must be clear, complete, and concise ï§ Multiple products / services can be grouped into single SOW ï§ Is subject to change until a contract is awarded
- 23. Project Procurement Management âĒ Plan Procurements â O (contâd) âĒ Make-or-buy decisions ï§ May include decision to require insurance policies or performance bonds to address some identified risks âĒ Procurement documents ï§ Quotation, bidding document, tender, RFP, RFQ, RFI, etc
- 24. Project Procurement Management âĒ Plan Procurements â O (contâd) âĒ Source selection criteria
- 25. Project Procurement Management âĒ Plan Procurements â O (contâd) âĒ Source selection criteria (contâd)
- 26. Project Procurement Management âĒ Plan Procurements â O (contâd) âĒ CR
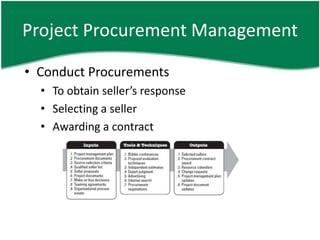
- 27. Project Procurement Management âĒ Conduct Procurements âĒ To obtain sellerâs response âĒ Selecting a seller âĒ Awarding a contract
- 28. Project Procurement Management âĒ Conduct Procurements â I âĒ PMP âĒ Procurement document âĒ Source selection criteria âĒ Qualified seller list âĒ Seller proposals âĒ Project documents âĒ Make-or-buy decisions
- 29. Project Procurement Management âĒ Conduct Procurements â I (contâd) âĒ Teaming agreement âĒ OPA
- 30. Project Procurement Management âĒ Conduct Procurements â TT âĒ Bidder conferences ï§ To ensure buyer and seller have a clear and common understanding of the procurement ï§ No sellers received preferential treatment ï§ Every prospective sellers hear individual questions and the answers from buyers âĒ Proposal evaluation techniques
- 31. Project Procurement Management âĒ Conduct Procurements â TT (contâd) âĒ Independent estimates âĒ Expert judgment âĒ Advertising âĒ Internet search âĒ Procurement negotiations
- 32. Project Procurement Management âĒ Conduct Procurements â O âĒ Selected sellers âĒ Procurement contract award
- 33. Project Procurement Management âĒ Conduct Procurements â O (contâd) âĒ Resource calendars âĒ CR âĒ PMP U âĒ PD U
- 34. Project Procurement Management âĒ Administer Procurements âĒ Process of managing procurement relationships, monitoring contract performance, making changes / corrections âĒ To ensure both parties meet their contractual agreements and their own legal rights are protected âĒ Might be carried out by separate function of the organization
- 35. Project Procurement Management âĒ Administer Procurements âĒ Applied project management processes (but not limited to): ïž Direct and manage project execution ïž Report performance ïž Perform quality control ïž Perform integrated change control ïž Monitor and control risk
- 36. Project Procurement Management âĒ Administer Procurements âĒ Also includes monitoring payments to sellers âĒ Document sellerâs performance / evaluation âĒ Contracts can be amended at any time prior to contract closure by mutual consent
- 37. Project Procurement Management âĒ Administer Procurements
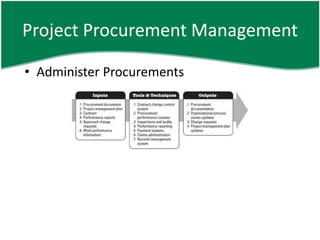
- 38. Project Procurement Management âĒ Administer Procurements â I âĒ Procurement documents âĒ PMP âĒ Contract âĒ Performance report âĒ Approved CR âĒ WPI
- 39. Project Procurement Management âĒ Administer Procurements â TT âĒ Contract change control system âĒ Procurement performance review âĒ Inspection and audit âĒ Performance reporting âĒ Payment system âĒ Claims administration âĒ Records management system
- 40. Project Procurement Management âĒ Administer Procurements â O âĒ Procurement documentations âĒ OPA U âĒ CR âĒ PMP U
- 41. Project Procurement Management âĒ Close Procurements âĒ Completion of project procurement âĒ Includes administrative activities âĒ Finalizing open claims, update information to project records âĒ In multi phase project, close procurement only applicable to given phase of the project
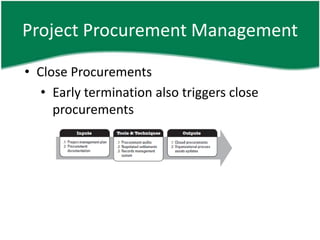
- 42. Project Procurement Management âĒ Close Procurements âĒ Early termination also triggers close procurements
- 43. Project Procurement Management âĒ Close Procurements â I âĒ PMP âĒ Procurement documentation
- 44. Project Procurement Management âĒ Close Procurements â TT âĒ Procurement audit âĒ Negotiated settlement âĒ Record management system
- 45. Project Procurement Management âĒ Close Procurements â O âĒ Closed procurements âĒ OPA U
- 47. Sample Questions 1. Which of the following is a false statement about project risks? A. A risk arises out of uncertainty. B. A risk can only have a negative effect on a project. C. Identified risks are usually listed in a document called the risk register. D. Risks can be categorized by developing a risk breakdown structure (RBS).