Sensors, actuators and the Raspberry PI using Python
- 1. Sensors, actuators and the Raspberry PI Programming GPIO using Python
- 2. Raspberry PI vs Desktop PC ? Smaller footprint ? Slower processor ? Less memory ? Non-standard peripherals
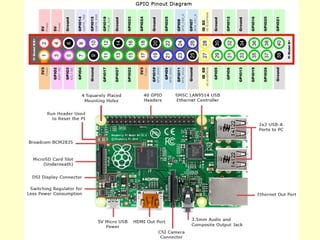
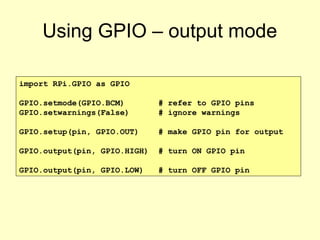
- 6. Using GPIO ¨C output mode import RPi.GPIO as GPIO GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) # refer to GPIO pins GPIO.setwarnings(False) # ignore warnings GPIO.setup(pin, GPIO.OUT) # make GPIO pin for output GPIO.output(pin, GPIO.HIGH) # turn ON GPIO pin GPIO.output(pin, GPIO.LOW) # turn OFF GPIO pin
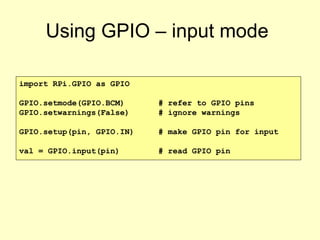
- 7. Using GPIO ¨C input mode import RPi.GPIO as GPIO GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) # refer to GPIO pins GPIO.setwarnings(False) # ignore warnings GPIO.setup(pin, GPIO.IN) # make GPIO pin for input val = GPIO.input(pin) # read GPIO pin
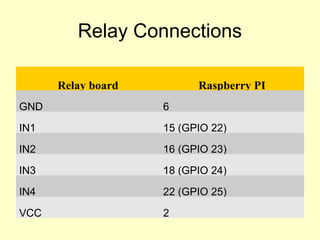
- 11. Relay Connections Relay board Raspberry PI GND 6 IN1 15 (GPIO 22) IN2 16 (GPIO 23) IN3 18 (GPIO 24) IN4 22 (GPIO 25) VCC 2
- 13. Relay controller sample code import RPi.GPIO as GPIO import time pins = [22,23,24,25] for p in pins: GPIO.setup(p, GPIO.OUT) while True: for q in pins: GPIO.output(q, GPIO.HIGH) time.sleep(5) for q in pins: GPIO.output(q, GPIO.LOW) time.sleep(5)
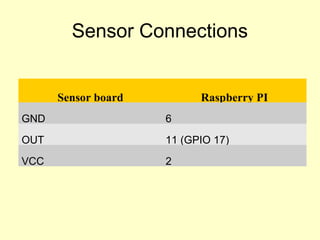
- 17. Sensor Connections Sensor board Raspberry PI GND 6 OUT 11 (GPIO 17) VCC 2
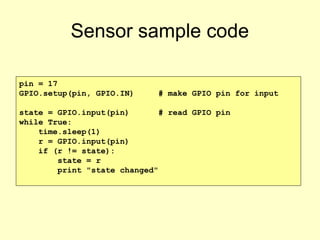
- 18. Sensor sample code pin = 17 GPIO.setup(pin, GPIO.IN) # make GPIO pin for input state = GPIO.input(pin) # read GPIO pin while True: time.sleep(1) r = GPIO.input(pin) if (r != state): state = r print "state changed"
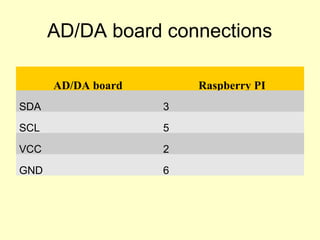
- 21. AD/DA board connections AD/DA board Raspberry PI SDA 3 SCL 5 VCC 2 GND 6
- 22. Convertor sample code import smbus def read(a): bus.read_byte_data(0x48, a) return bus.read_data(0x48) bus = smbus.SMBus(1) control = read(0) light = read(1) temperature = read(2) custom = read(3) bus.write_byte(self.addr, 99)







![Relay controller sample code
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
pins = [22,23,24,25]
for p in pins:
GPIO.setup(p, GPIO.OUT)
while True:
for q in pins:
GPIO.output(q, GPIO.HIGH)
time.sleep(5)
for q in pins:
GPIO.output(q, GPIO.LOW)
time.sleep(5)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workingwitharaspberrypi-151128155857-lva1-app6892/85/Sensors-actuators-and-the-Raspberry-PI-using-Python-13-320.jpg)