Store layout
- 1. Store Layout and Design
- 2. Shopper found dead in Local Store; Cause of Death - Boredom Stanley Marcus, Chairperson â Neimen Marcus In Time Poverty Economy, stores have to make shopping experience exciting
- 3. Store Image & Space Productivity Merchandising Fixture Selection Merchandise Presentation Visual Merchandising Store Design Exterior Design Ambience Lighting Store Planning Space Allocation Layout Circulation Visual Communications Retail Identity Graphics POS, Signage
- 4. Store Image Store Image = Merchandise stocked + Promotional Activities + Customer Service 7 -Eleven â 7-Elevenâ a US retailer having 4000 convenience stores Why not â8-Twelveâ ï 7-Eleven stresses on store hours Rhyme and Rhythm of seven-eleven Orange-Green logo ï Quality â Freshness Price saving signs conveys promotional environment Smell of Cheese +Sight of sausages create certain atmosphere
- 5. Space Productivity The more merchandise the customer are exposed to, that is presented in the orderly manner, the more they tend to buy In-store Advertising and displays let the customer know that what is happening in other shopping areas and thus encourage to visit that area Retailers are spending more on in-store design, merchandise presentation, Visual displays and in-store promotions instead of advertising It is easy to make; that customer buy more who is already in the store than getting new one
- 6. Consumer Behaviour â Supermarket Style Most Customers are not only right handed but also right headed Stock national brand right of store brands so that consumer goes across store brand to get the national brand Display higher gross margin product on right side of the aisles Put bakery product on right so as to make the customer hungary. Supermarkets know hungary customer is the best customer Most customers think neatness counts â Dump Displaysâ are haphazard displays ï they give cheap looks ï Great Bargain Handwritten signs create the impression of recently lowered prices
- 7. Most Customer are likely to focus on large central display Follow 25-25-50 rule Of all endcaps 25% should have advertised sale merchandise (that the customer will seek out) Other 25% should be unadvertised sale items (that causes customer to remain alert when looking at an endcap) Remaining 50% should be regular priced seasonal or impulse merchandise Retailers tend to violate above rule when mfr. offer rent for their displays
- 8. There is little bit greed in every one of us â Limit 3 to a customerâ ï interprets as great deal ï tend to buy 3 Customer are so excited to buy great price on butter that they fail to notice that itemâs complementary product i.e., jelly and breads prices have increased
- 9. Allocating Space Starting point for developing a floorplan is analysing how the available store space measured in square footage, should be allocated for different departments
- 10. Types of space needed Five Types: 1) Back Room 2) Office and other personal space 3)Aisles, Service Areas 4) Wall Merchandise Space 5)Floor Merchandise space Back Room: Back Room is required to receive, process and hold inventory This space varies with the type of retailer (50% in Department store, 10% in Specialty and Convenience store) SCM practices with JIT has brought down back room space Warehouse Clubs have only receiving areas but no back room Cartons of excess inventory is kept at higher levels (84â) Retailer thus pays same rent for the sq. footage but use heights thus using cubic footage This stocking method interestingly creates low-cost image of the store
- 11. Offices and other Functional Spaces This includes break room, training/meeting room, cabin, bathroom facilities This space gets lesser priority Aisles, Service Areas and other Nonselling areas Main aisles should be broad and should lead to smaller aisles like herringbone structure These aisles should be wide enough upto 15 ft. Other non-merchandised area are dressing rooms, layaway areas, service desks Productivity â Merchandised area or non-merchandised area (Trade off ?) Floor Merchandise Space Here, many different types of fixtures are used to display wide variety of merchandise Its just not to cram the largest amount but to place so that consumer can understand and shop
- 12. Wall Merchandise Space They serve as fixtures; holding tremendous amount of merchandise Provide visual backdrop to the floor merchandise Space Allocation Planning 20% of the inventory is not looked by the customer This stresses to know the productivity and profitability of all merchandise Two reasons for the space planning â 1)Revising the space allocation of existing store OR planning a new store One such measure is Space Productivity index % age of total gross margin dollars for a particular merchandise %age of space required by that merchandise =
- 13. If the index is below 1 than category is underperforming For Apparels the index is highest, for furniture- least (lesson?) Underperforming categories sometimes have to be continued Space Allocations for a new Store In the absence of past data, space allocation is based on industry standards Robert Kahn to Sam Walton â Store profitability is not the function of adding more merchandise displays, but Sales per square foot = f (Number of Customers) x (The length of time they spend on the store Wal Mart then built ten 85,000 sq. ft. store and ten 1,15,000 sq. ft. store Larger stores produced higher sales per square foot Parking space was always full, showing shoppers were spending more time
- 14. Comfortable space should be there for the customers to pass through the aisles Myth: If customer is sitting down, he is not shopping. Put at least one bench for the customer to rest Put a water stand in the corner
- 15. Space Planning Considerations High traffic & highly visible areas Entrances, escalators, check-out area, end aisles, feature areas Profitability of merchandise Private brand, higher margin categories Customer buying considerations Impulse products near front Demand/destination areas in back, off the beaten path Physical characteristics of product Bulky vs. small/easily stolen Complementary products should be adjacent Sales rate Display more units of fast-selling merchandise (tonnage merchandising
- 16. Types of Layouts
- 17. Produce Books, magazines, seasonal display Receiving & storage Entrance Checkouts Grid Layout Aesthetics repetitive, limited site lines + Efficiency cost, space productivity , time Fixtures Straight racks Gondolas (island-type self-service counters; tiers of shelves, bins, or pegs) Repetitive pattern Bulk of stock areas + Feature areas End caps Promotional aisles/areas Walls Point-of-sale areas Location of depts. Exit Office & customer service
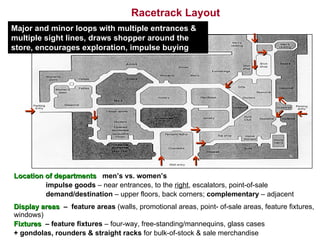
- 18. Racetrack Layout Major and minor loops with multiple entrances & multiple sight lines , draws shopper around the store, encourages exploration, impulse buying Location of departments menâs vs. womenâs impulse goods â near entrances, to the right , escalators, point-of-sale demand/destination â upper floors, back corners; complementary â adjacent Display areas â feature areas (walls, promotional areas, point- of-sale areas, feature fixtures, windows) Fixtures â feature fixtures â four-way, free-standing/mannequins, glass cases + gondolas, rounders & straight racks for bulk-of-stock & sale merchandise ï§ ï§ ï§ ïĻ ïĻ ïĻ ï§ ïĐ ïĐ ïĶ ïŠ ïŽ ïŽ
- 19. Free-Form (Boutique) Layout Storage, Receiving, Marking Underwear Dressing Rooms Checkout Clearance Items Feature Feature Jeans Casual Wear Stockings Accessories Pants Tops Tops Skirts and Dresses Hats and Handbags Display Window Display Window Fixtures Bulk-of-stock - straight racks, gondolas, rounders (very flexible) Feature â glass cases, 4-way, free-standing, custom-built fixtures Feature areas Windows, walls, feature fixtures, point-of-sale + Aesthetically pleasing, relaxing, asymmetrical, invites browsing - Less efficient, more costly, more sales assistance needed, more theft
- 20. Shrinkage Loss of merchandise through theft, loss and damage is called Shrinkage Retailers only know that their inventory in the store has shrunk Stores that make the customer to move through entire store fall victim to high shrinkage Shrinkage ranges from 1 to 4 percent of retail sales Avoid hidden areas of the store Bring down the merchandise movement to avoid damage
- 21. vertical merchandising - eye movement - left to right & down high margin merchandise - 15% below horizontal (51â - 53â & 56â - 58â) not alphabetical, âflankâ new & private label with popular national brands Location of Merchandise â PLANOGRMS (map â photos, drawings, computer generated)
- 22. Merchandise Presentation Techniques Style/Item Presentation â most basic, most common Idea-Oriented Presentation â complementary, unifying theme Color Presentation â blocks or concentrations of color Price Lining â e.g., designer, bridge, better, moderate; under glass, not under glass Vertical Merchandising â uses walls, high gondolas; uses natural eye movement; often combined with color Tonnage Merchandising â large quantities, âstock it high and let it flyâ â equated with value/low price Frontal Presentation â 4-way fixtures, display face-out, often combined with vertical merchandising