Textile Fiber Identification testing method
- 1. IDENTIFICATION AND IMPORTANT PROPERTIES OF FIBERS
- 2. Fibers • Fibers Can be characterized based on comparison of both physical and chemical properties.
- 3. Fabric 1. Fabric is made of Yarn. 2. Yarn are made of twisted filaments or Fibers. 3. Types of fibers : - Natural—animal, vegetable - Artificial—synthesized or created from altered natural sources
- 5. Classification Natural fibers are classified according to their origin: 1.Vegetable or cellulose 2.Animal or protein
- 6. Cellulose Fibers 1. Cotton—vegetable fiber; strong, tough, flexible, moisture-absorbent, not shape-retentive. 2. Rayon—chemically altered cellulose; soft, lustrous, versatile. 3. Cellulose acetate—cellulose that is chemically altered to create an entirely new compound not found in nature.
- 7. Fiber Comparison Describe the difference(s) between the cotton and the rayon.
- 8. Protein Fibers 1. Wool—animal fiber coming most often from sheep, but may be goat (mohair), rabbit (angora), camel. 2. Silk—insect fiber that is spun by a silkworm to make its cocoon; the fiber reflects light.
- 9. Man-made Fibers Fibers derived from either natural or synthetic polymers –Regenerated Fibers –Synthetic Fibers
- 10. Synthetic Fibers • Made from derivatives of petroleum, coal, and natural gas.
- 11. Synthetic Fibers 1.Nylon—most durable of man- made fibers; extremely lightweight 2.Polyester—most widely used man-made fiber 3.Acrylic—provides warmth from a lightweight, soft, and resilient fiber 4.Spandex—extreme elastic properties
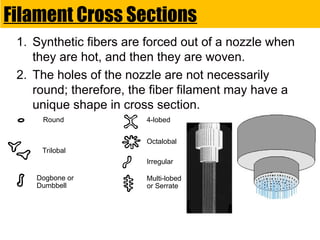
- 12. Filament Cross Sections 1. Synthetic fibers are forced out of a nozzle when they are hot, and then they are woven. 2. The holes of the nozzle are not necessarily round; therefore, the fiber filament may have a unique shape in cross section. Round 4-lobed Octalobal Irregular Multi-lobed or Serrate Trilobal Dogbone or Dumbbell
- 14. Testing for Identification 1. Microscopic observation 2. Burning — observation of how a fiber burns, the odor, color of flame, color of smoke, and the appearance of the residue 3. Thermal decomposition — gently heating to break down the fiber to the basic monomers 4. Chemical tests — solubility and decomposition
- 15. Basic Comparison of Fiber Samples 1. Microscopic comparison of color and diameter 2. Compare lengthwise striations 3. Compare cross-section of fiber (shape) 4. Color separation
- 17. Microscopic View The cotton fiber is a single elongated cell. Under a microscope, it looks like flat, spirally twisted ribbon like tube with rough granular surface.
- 18. • Burning Test • Flame: Orange • Odor: Paper burning like odor After burning it’s converting into ashes gray or black powder • Chemical Test • At 45 °C, 75% zinc chloride solution dissolves cotton that has not been mercerized.
- 19. Viscose (Rayon) Fiber Identification Cross-Section
- 20. Microscopic View Microscopic view Rayon fiber has uniform diameter with glass like shine. If delustered then rayon fiber shows marks similar to pepper, when viewed cross sectionally. Viscose fiber of rayon looks irregular when viewed cross sectionally.
- 21. • Burning Text • Yellow-orange flame, burns evenly, does not smolder, no smoke • The burning smell like a burning leaves or paper Leaves only a slight ash • Chemical test • Rayon Dissolved in 38% solution of hydrochloric acid at the temperature of 24 degree in 5min.
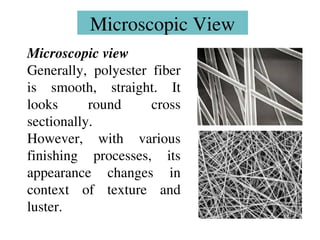
- 23. Microscopic View Microscopic view Generally, polyester fiber is smooth, straight. It looks round cross sectionally. However, with various finishing processes, its appearance changes in context of texture and luster.
- 24. • Burning Test • When polyester burn it’s creating orange, Sweet and fruity odor. • The ash is hard. • Chemical Test • Polyester Dissolved in 100% solution of meta-cresol at the temperature of 139 degree in 5m.
- 26. Microscopic View Microscopic view The basic microscopic appearance is generally fine, round, smooth, and translucent. It is also produced in multilobal cross-sectional types. it will also be dotted under the microscope.
- 27. • Burning Test • When we burn nylon it’s create blue flame. • Plastic Burning like odor After burning it convert round, yellow bead ashes. • Chemical Test • At 20 °C, concentrated Formic acid dissolves nylon.
- 29. Microscopic View Microscopic view Raw silk fiber, composed of two filaments, has elliptical shape under the microscope. The two fine and lustrous filaments are shown clearly looking like transparent rods with triangular shape.
- 30. Burning Test When we burn silk it’s create orange flame. Hair burning like odor After burning it convert black ashes. Chemical Test At 20 °C, 60% sulfuric acid dissolves silk At 100 °C, a 5% solution of sodium hydroxide dissolves silk and reconstituted protein fibers dissolve only partially and very slowly.
- 32. Thank You
- 33. Polyester Yarn Manufacturing Process
- 34. Cotton Yarn Manufacturing Process
- 35. Silk Yarn Manufacturing Process