The Global Carbon Cycle and its Relation to Global Climate
- 1. The Global Carbon Cycle and its Relation to Global Climate David Archer, University of Chicago
- 2. Airborne fraction of fossil fuel CO2 Airborne Fraction of Carbon Released Century timescale peak Millennial timescale tail
- 3. Paleocene/Eocene Thermal Maximum Event 55 Myr Ago A natural release of CO2, comparable to the potential fossil fuel release. Warming, with a recovery that took 100,000 years. Zachos et al. 2001
- 4. Long Tail Model Intercomparison Project LTMIP D. Archer, M.l Eby, V. Brovkin, A. Ridgwell, L. Cao, U. Mikolajewicz, K. Caldeira, K. Matsumoto, G. Munhoven, A. Montenegro, Ann. Rev. Earth Sciences, 2009.
- 5. IPCC 2001 and earlier Summaries for Policymakers IPCC 2001 and earlier reports implied that global warming would last about a century.
- 6. Seawater pH Chemistry CO2 + CO3= + H2O <--> 2 HCO3- 10 100 2000 M Concentration in seawater CO2 uptake capacity is determined by CO3=
- 7. Atmosphere / Ocean Equilibrium 600 Gton C 1800 Gton C as CO3= We expect a partitioning of ~1:3 between air and ocean Gton C = 1015 g
- 8. Atmosphere / Ocean Equilibrium Airborne Fraction of CO2 Slug 1000-2000 4000-5000 Gton Gton Archer 2005 22% 33% Lenton 2006 21-26% 34% CLIMBER 22% 35% Goodwin 2007 24-26% 40% Ridgwell 2007 31%
- 9. Atmosphere / Ocean Equilibrium Affected by: changes in circulation biology ocean temperature saturating the carbonate ion buffer
- 10. Neutralization by CaCO3 CO2 + CaCO3 + H2O ==> Ca2+ + 2 HCO3-
- 11. How long does it take? Neutralization e-folding timescale Archer 2005 5-8kyr Lenton 2006 500 - 1000 yr Ridgwell 2007 1-2 kyr Tyrell 2007 2-3 kyr
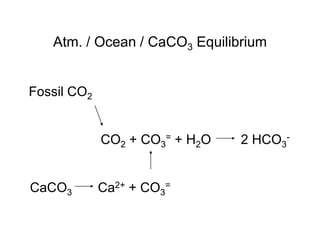
- 12. Atm. / Ocean / CaCO3 Equilibrium Fossil CO2 CO2 + CO3= + H2O 2 HCO3- CaCO3 Ca2+ + CO3=
- 13. Atm. / Ocean / CaCO3 Equilibrium Proportional to pCO2 (Henry’s law). Restored by Goes up ~ 10% of fossil CO2 CaCO3 equilibrium release [CO2] [CO3=] K2 -]2 = [HCO3 K1 Increases by 2x fossil fuel release
- 14. The Silicate Weathering CO2 Thermostat CO2 Weathering = function(climate) CaO CaCO3 Burial Subduction Metamorphosis
- 15. The long tail 1800 1600 1400 pCO2 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 6 5 4 °C 3 2 1 0 0 100 200 300 400 500 kyr
- 16. A Geochemical Joke One gallon of gasoline Usable energy: 2500 kcal Unwanted greenhouse energy over CO2 lifetime:
- 17. A Geochemical Joke One gallon of gasoline Usable energy: 2500 kcal Unwanted greenhouse energy over CO2 lifetime: 100,000,000,000 kcal
- 18. Sea Level Sea Level, m 100 Eocene 40 Myr ago 50 Pliocene 3 Myr ago Global Mean T, °C Today 5 10 15 20 -50 Last Glacial -100 Maximum 20 kyr ago -150
- 19. Sea Level Sea Level, m 100 Eocene 40 Myr ago 50 Pliocene 3 Myr ago Global Mean T, °C Today 5 10 15 IPCC 20 Forecast -50 Year 2100 -100 Last Glacial Eventual change Maximum 20 kyr ago 100x higher than -150 IPCC forecast for 2100
- 20. Conclusions The climate impacts of fossil fuel CO2 release will persist for millennia. Sea level rise could ultimately be 100 times greater than the IPCC forecast for the year 2100. The carbon cycle on century timescales in the past has acted as an amplifier of climate change. So far, the carbon cycle today has been absorbing carbon (stabilizing feedback), but this could change.
- 21. Intended for a “popular”- level audience thaw
- 22. Global carbon cycle Carbon cycle science for climate wonks
- 23. Understanding the forecast Rocks-for-jocks level undergraduate textbook
- 24. Open climate 101 Open access class video lectures on-line models quizzes and labs print out a useless non-certificate
- 25. Climate crisis IPCC 2007 “Unofficial Guide” Working Groups 1 (mostly), plus 2 and 3
- 26. Warming papers Classic scientific papers (1827-2008) with snarky commentary











![Atm. / Ocean / CaCO3 Equilibrium
Proportional to
pCO2 (Henry’s law). Restored by
Goes up ~ 10% of fossil CO2 CaCO3 equilibrium
release
[CO2] [CO3=] K2
-]2
=
[HCO3 K1
Increases by 2x fossil fuel release](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/global-carbon-cycle-its-120509100148-phpapp01/85/The-Global-Carbon-Cycle-and-its-Relation-to-Global-Climate-13-320.jpg)












