using contextual clues in reading passage.pptx
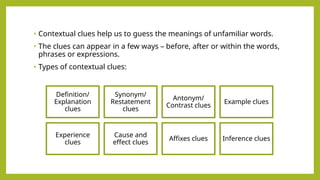
- 2. • Contextual clues help us to guess the meanings of unfamiliar words. • The clues can appear in a few ways – before, after or within the words, phrases or expressions. • Types of contextual clues: Definition/ Explanation clues Synonym/ Restatement clues Antonym/ Contrast clues Example clues Experience clues Cause and effect clues Affixes clues Inference clues
- 3. 1. Definition/ Explanation Clues • The definition or explanation of the unknown word appears in the sentence that precedes it. • Generally, this clue is signalled by the phrase ‘that is’ and punctuations such as the comma [,], dash [-] as well as parentheses [()]. • E.g. Various theories, or ideas, were suggested about how the murder had happened. • Theories = ideas.
- 4. 2. Synonym/ Restatement Clues • Other words with similar meanings are used in the sentence. • E.g. The slender woman is very thin that her clothes look a few sizes bigger on her. • Slender = thin
- 5. 3. Antonym/ Contrast Clues • A word or group of words that carries the opposite meaning of the unknown word is given in the sentence. • Generally, this clue is signalled by the use of ‘even though’, ‘whereas’, ‘unlike’ and ‘as opposed to’. • E.g. The flight departure time from Kuala Lumpur is 9.40 a.m., whereas its arrival time in Alor Star is 10.40 a.m. • Departure = leaving
- 6. 4. Example Clues • Examples are provided to define the unknown word. • E.g. Foods which are nutritious, for instance fruits and vegetables, help human growth. • Nutritious = healthy
- 7. 5. Experience Clues • How people or things act in a given situation can be related to the reader’s own experience. This knowledge provides clues to the meaning of the unknown word. • E.g. Nandini prefers solitude as she lives alone in an isolated cabin on the small island, without any telephone connection. • Solitude = being alone
- 8. 6. Cause and Effect Clues • The reason for or the result of the unknown word is explained in the sentence. • Generally this clue is signalled by the use of ‘so’, ‘since’, ‘because’, ‘thus’ and ‘therefore’. • E.g. She wanted to impress her dinner guests with the food she served, so she bought a culinary art book and studied it the whole week. • Culinary = food preparation
- 9. 7. Affixes Clues • Affixes (prefix and suffix) can provide direct clues to the meaning of the unknown word. • Generally, this clue is signalled by the use of ‘pre-’, ‘re-’, ‘un-’, ‘in-’, ‘dis-’ and ‘mis-’. • E.g. She had to rewrite the report due to too many grammatical errors. • Rewrite = to write again
- 10. 8. Inference Clues • Inference: a conclusion reached based on reasoning and evidence. • The meaning can be inferred based on the context given in the text. • E.g. Nobody wants to be an underachiever, he will never get good grades, never secure a job, and never be successful. • Underachiever = to achieve less success than expected
- 11. In many cases, the usernames, which usually use the users’ e-mail addresses and passwords in unencrypted texts, are among the huge trove of stolen information available in the Internet. Encik Amin further states that his company has not yet provided any information about the attacks to other cyber security firms. However, he intends to alert the involved companies soon so that they can take the necessary precautions on the issue.


![1. Definition/ Explanation Clues
• The definition or explanation of the unknown word appears in the
sentence that precedes it.
• Generally, this clue is signalled by the phrase ‘that is’ and punctuations
such as the comma [,], dash [-] as well as parentheses [()].
• E.g. Various theories, or ideas, were suggested about how the murder
had happened.
• Theories = ideas.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contextualclues-241022082325-57c5dc6a/85/using-contextual-clues-in-reading-passage-pptx-3-320.jpg)







