Where Does Our Electricity Come From
2 likes474 views
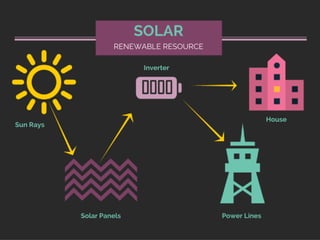
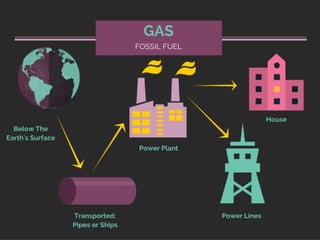
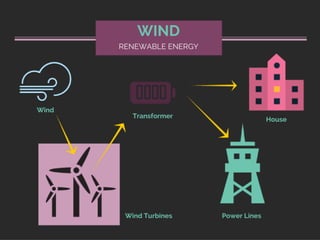
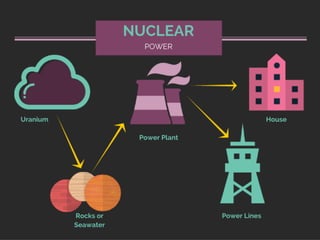
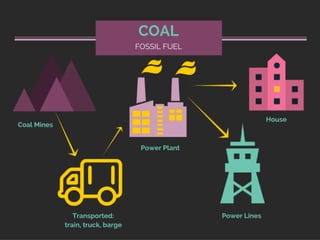
IG Federal Electrical Supply provides this presentation on where our electricity comes from.
1 of 7
Download to read offline


Recommended
5 Facts About LED Lights



5 Facts About LED LightsIG Federal Electrical Supply
?
This document is a slide deck promoting the Haiku Deck presentation tool and contains photos credited to various photographers. It encourages the viewer to create their own Haiku Deck presentation by getting started on 狠狠撸Share and sharing their work.A320 electrical system



A320 electrical systemParas Gangwani
?
The document describes the electrical system configuration of an Airbus A320 aircraft. In normal configuration, external power can supply the AC and DC ground/flight buses directly without powering the entire aircraft network when only ground services are required. The document also outlines failure scenarios for individual engine generators, AC bus 1, and transformer rectifiers TR1 and TR2, as well as flight operations using only battery power on the ground or in flight at speeds under 50 knots.Static Electricity



Static ElectricityShafie Sofian
?
1. Charging by friction is demonstrated using a plastic straw and tissue paper. Rubbing the straw with tissue gives it a static charge, causing small bits of paper to be attracted.
2. There are two types of electrical charges: positive and negative. Charge is measured in coulombs. Unlike charges attract and like charges repel according to Coulomb's law.
3. An electric field is a region where an electric charge would experience force. It is represented by electric field lines originating from positive charges and terminating on negative charges.Current Electricity



Current ElectricityShafie Sofian
?
The document provides information about current, electromotive force, potential difference, and resistance. It defines key terms, provides equations, and examples of calculations. It describes:
- Current is the flow of charge measured in amperes. It is carried by the flow of electrons in a conductor.
- Electromotive force is the work done per unit charge to drive charge around a complete circuit. It is measured in volts.
- Potential difference is the work done per unit charge to move charge through a circuit component. It is also measured in volts.
- Resistance is the opposition to current flow. It is calculated as potential difference divided by current and measured in ohms.Practical Electricity



Practical ElectricityShafie Sofian
?
Electricity can be used for heating, lighting, and powering motors. Heating elements get hot when electricity passes through, lighting works when the filament in a bulb is heated to glow, and motors use magnetic fields to convert electricity into rotational motion. Dangers of electricity include damaged insulation, overheating of cables from overloading or thin wires, and damp conditions allowing electricity to pass through water to a person's body. Proper and safe use of electricity in the home requires awareness of these hazards.Introduction to measuring instruments (ALIV - Bangladesh)



Introduction to measuring instruments (ALIV - Bangladesh)Md Abu Jauad Khan Aliv
?
This document provides an introduction to various types of measuring instruments, including ammeters, voltmeters, multimeters, oscilloscopes, wattmeters, tachometers, signal generators, and LCR meters. Ammeters measure electrical current, voltmeters measure potential difference, and multimeters can measure voltage, current, and resistance. Oscilloscopes observe exact wave shapes, wattmeters measure electrical power, and tachometers measure rotational speed. Signal generators create electronic signals, and LCR meters measure inductance, capacitance, and resistance of components.Basics of electrical engineering



Basics of electrical engineeringNishkam Dhiman
?
This document provides an overview of basics of electrical engineering including wires, cables, types of wires, three core wire, cable structure, cable classification, cable grading, cable termination, cable safety, and electrical joints. It also discusses Ohm's law, electric circuits including series and parallel circuits, and mixed circuits. Key topics covered include that wire thickness must match power needs, common wire types like PVC and their uses, color coding in wiring, cable components, and calculating equivalent resistances in various circuit configurations.AC MOTORS



AC MOTORSJ.T.A.JONES
?
AC motors are commonly used on aircraft and are classified by output power. Large motors have over 3KW output and are three-phase, while medium and small motors range from 3KW to 50W and are mostly single-phase. Miniature motors are under 50W. The document then describes various types of AC motors used on aircraft, including induction motors, which are the most widely used type and operate using a rotating magnetic field to induce current in the rotor. Two-phase induction motors can control rotation direction and speed, while split-phase motors use a capacitive winding to phase split the current. Synchronous motors maintain a constant speed set by the rotating magnetic field frequency.Ac motors



Ac motorsJamilah Abbas
?
The document discusses different types of AC motors, including induction motors and synchronous motors. Induction motors operate slightly slower than the supply frequency, while synchronous motors rotate exactly at the supply frequency. Common types of AC motors include squirrel cage motors and wound rotor motors. Squirrel cage motors have conductors in the rotor that produce torque from induced currents, while wound rotor motors have insulated windings in the rotor that allow external resistance to control starting torque and speed.Measuring instruments



Measuring instrumentsSayyed Raza
?
1. Indicating instruments measure electrical quantities by deflecting a pointer on a calibrated scale. They use a deflection system to produce a force proportional to the measured value, a control system to limit deflection, and a damping system to prevent oscillations.
2. Permanent magnet moving coil (PMMC) instruments have a coil mounted between magnet poles that deflects proportional to current. They are used as ammeters, voltmeters, and galvanometers. As an ammeter, the coil is connected across a low resistance shunt; as a voltmeter, it is connected in series with a high resistance.
3. Moving iron instruments can measure AC using an iron core acted on by a coilIndicating instruments



Indicating instrumentsKausik das
?
This document discusses electrical and electronics measurements. It describes the process of measurement by comparing unknown values to known standards. It then discusses key characteristics of instruments used for measurement, including calibration, accuracy, precision, repeatability, reproducibility, drift, span, sensitivity, resolution, and dead zone. The document also covers types of errors in measurement, including static, mistakes, systematic, and random errors. It lists sources of error and types of instruments, including absolute, secondary, indicating, recording, and integrating instruments. Finally, it provides details on permanent magnet moving coil (PMMC) and moving iron (MI) types of indicating instruments.Induction motor



Induction motorsodanforeva
?
The induction motor operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction. It consists of two main parts - the stator and the rotor. The stator contains windings that generate a rotating magnetic field, acting as the primary. This rotating field induces currents in the rotor windings, which acts as the secondary. The rotor is then pushed to rotate at a slightly lower speed than the rotating field due to "slip."Dc motors and its types



Dc motors and its typesSumeet Patel
?
The document discusses DC motors. It begins with an introduction to DC motors, noting they convert electrical to mechanical energy. It then covers the principles, construction, types, and applications of DC motors. The principles section explains how DC motors work using electromagnetism and the Lorentz force. Construction includes field and armature windings. There are three main types - shunt, series, and compound motors - which vary in how their field windings are connected. Applications include uses for different motor types like fans, tools, and mills.Electrical tools and its function



Electrical tools and its functionFortunato de Guzman
?
The document discusses various electrical tools and their functions. It describes screwdrivers like standard, Philips, and stubby screwdrivers which are used to drive different types of screws. Pliers are also discussed, including combination pliers, side cutting pliers, and long nose pliers which are used for gripping, cutting, and holding wires. Additional tools mentioned are wire strippers, electrician's knives, portable electric drills, and hacksaws, each serving a specific purpose like stripping wire insulation or cutting metal materials. Proper tool use and safety are emphasized.Dc motor



Dc motorSayyed Raza
?
1. A DC motor runs on direct current electricity. It has a field winding that produces a magnetic field when energized, and an armature winding that rotates when placed in this magnetic field.
2. The key parts of a DC motor include the yoke, poles, field winding, armature core, armature winding, commutator, and brushes. The field winding produces flux, and the rotation of the armature winding within this flux induces voltage that is used to power the load.
3. DC motors can be shunt wound, series wound, or compound wound depending on how the field and armature windings are connected. Shunt and series motors have different torque-speed characteristics duetransformer ppt



transformer pptSharukh Ansari
?
A transformer is a static device that changes alternating current (AC) at one voltage level to AC at another voltage level through electromagnetic induction. It consists of two coils, the primary and secondary windings, wrapped around a laminated iron core. When an alternating current is applied to the primary winding, it produces an alternating magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary winding. This allows the transformer to step up or step down voltages without changing the frequency. The transformer transfers power between its two coils through electromagnetic coupling between the coils wound around the iron core.Common Wire splices



Common Wire splicesDeth Guiasilon
?
An extension cord allows for multiple electrical devices to be plugged in when outlets are insufficient. It consists of a flexible electrical cable with a plug on one end and multiple sockets on the other. The document discusses how to make an extension cord by skinning copper wires of different gauges, splicing the wires together, and attaching a plug and socket. Safety tools and materials needed include solid and stranded copper wire in sizes #14, #12, and #10, as well as an outlet, flat cord, connectors, and a male plug.一比一原版(颁颁毕业证)卡莫森学院毕业证如何办理



一比一原版(颁颁毕业证)卡莫森学院毕业证如何办理taqyed
?
在线快速补办加拿大本科毕业证、硕士文凭证书,购买加拿大学位证【q薇1954292140】卡莫森学院Offer,加拿大大学文凭在线购买。高仿真还原加拿大文凭证书和外壳,定制加拿大卡莫森学院成绩单和信封。学位证书的英文CC毕业证【q薇1954292140】办理加拿大卡莫森学院毕业证(CC毕业证书)【q薇1954292140】diploma学位认证卡莫森学院offer/学位证学位证书电子图在线定制服务、留信官方学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作。帮你解决卡莫森学院学历学位认证难题。在线制作假学位证加拿大文凭购买,加拿大文凭定制,加拿大卡莫森学院文凭补办【q薇1954292140】专业在线定制加拿大大学文凭学位证购买,定做加拿大本科文凭,【q薇1954292140】复制加拿大Camosun College completion letter。
如果您在英、加、美、澳、欧洲等留学过程中或回国后:
1、在校期间因各种原因未能顺利毕业《CC成绩单工艺详解》【Q/WeChat:1954292140】《Buy Camosun College Transcript快速办理卡莫森学院教育部学历认证书毕业文凭证书》,拿不到官方毕业证;
2、面对父母的压力,希望尽快拿到;
3、不清楚认证流程以及材料该如何准备;
4、回国时间很长,忘记办理;
5、回国马上就要找工作《正式成绩单卡莫森学院成绩单购买》【q薇1954292140】《毕业证工艺详解CC学位证和毕业证》办给用人单位看;
6、企事业单位必须要求办理的;
7、需要报考公务员、购买免税车、落转户口、申请留学生创业基金。
加拿大文凭卡莫森学院成绩单,CC毕业证【q薇1954292140】办理加拿大卡莫森学院毕业证(CC毕业证书)【q薇1954292140】毕业证办理需要多久拿到?卡莫森学院offer/学位证学历认证制作代办流程、留信官方学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作。帮你解决卡莫森学院学历学位认证难题。
【q薇1954292140】办理卡莫森学院毕业证(CC毕业证书)diploma学位认证【q薇1954292140】卡莫森学院offer/学位证、留信官方学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作加拿大卡莫森学院毕业证(CC毕业证书)假学历认证
特殊原因导致无法毕业,也可以联系我们帮您办理相关材料:
1:在卡莫森学院挂科了,不想读了,成绩不理想怎么办???
2:打算回国了,找工作的时候,需要提供认证《CC成绩单购买办理卡莫森学院毕业证书范本》【Q/WeChat:1954292140】Buy Camosun College Diploma《正式成绩单论文没过》有文凭却得不到认证。又该怎么办???加拿大毕业证购买,加拿大文凭购买,
3:回国了找工作没有卡莫森学院文凭怎么办?有本科却要求硕士又怎么办?
帮您解决在加拿大卡莫森学院未毕业难题(Camosun College)文凭购买、毕业证购买、大学文凭购买、大学毕业证购买、买文凭、日韩文凭、英国大学文凭、美国大学文凭、澳洲大学文凭、加拿大大学文凭(q薇1954292140)新加坡大学文凭、新西兰大学文凭、爱尔兰文凭、西班牙文凭、德国文凭、教育部认证,买毕业证,毕业证购买,买大学文凭,购买日韩毕业证、英国大学毕业证、美国大学毕业证、澳洲大学毕业证、加拿大大学毕业证(q薇1954292140)新加坡大学毕业证、新西兰大学毕业证、爱尔兰毕业证、西班牙毕业证、德国毕业证,回国证明,留信网认证,留信认证办理,学历认证。从而完成就业。
主营项目:
1、真实教育部国外学历学位认证《加拿大毕业文凭证书快速办理卡莫森学院文凭购买》【q薇1954292140】《论文没过卡莫森学院正式成绩单》,教育部存档,教育部留服网站100%可查.
2、办理CC毕业证,改成绩单《CC毕业证明办理卡莫森学院购买毕业证流程》【Q/WeChat:1954292140】Buy Camosun College Certificates《正式成绩单论文没过》,卡莫森学院Offer、在读证明、学生卡、信封、证明信等全套材料,从防伪到印刷,从水印到钢印烫金,高精仿度跟学校原版100%相同.
3、真实使馆认证(即留学人员回国证明),使馆存档可通过大使馆查询确认.
4、留信网认证,国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书,留信网存档可查.
《卡莫森学院录取通知书加拿大毕业证书办理CC成绩单用纸》【q薇1954292140】学位证1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。
挂科处理解决方案加拿大文凭卡莫森学院成绩单【q薇1954292140】复刻成绩单加拿大卡莫森学院毕业证(CC毕业证书)研究生offer在线制作 卡莫森学院毕业证办理,办成绩单加拿大卡莫森学院文凭办理,加拿大卡莫森学院成绩单办理和真实留信认证、留服认证、卡莫森学院学历认证。学院文凭定制,卡莫森学院原版文凭补办,扫描件文凭定做,100%文凭复刻。【q薇1954292140】Buy Camosun College Diploma购买美国毕业证,购买英国毕业证,购买澳洲毕业证,购买加拿大毕业证,以及德国毕业证,购买法国毕业证(q薇1954292140)购买荷兰毕业证、购买瑞士毕业证、购买日本毕业证、购买韩国毕业证、购买新西兰毕业证、购买新加坡毕业证、购买西班牙毕业证、购买马来西亚毕业证等。包括了本科毕业证,硕士毕业证。
留信认证的作用:
1. 身份认证:留信认证可以证明你的留学经历是真实的,且你获得的学历或学位是正规且经过认证的。这对于一些用人单位来说,尤其是对留学经历有高度要求的公司(如跨国公司或国内高端公司),这是非常重要的一个凭证。
专业评定:留信认证不仅认证你的学位证书,还会对你的所学专业进行评定。这有助于展示你的学术背景,特别是对于国内公司而言,能够清楚了解你所学专业的水平和价值。
国家人才库入库:认证后,你的信息将被纳入国家人才库,并且可以在国家人才网等平台上展示,供包括500强公司等大型公司挑选和聘用人才。这对于回国找工作特别是进入大公司,具有非常积极的作用。
2. 留信认证对就业的好处
提高竞争力:通过留信认证,尤其是对你所学专业的认证,可以大大提高你在国内求职时的竞争力。许多公司对留学生背景和所学专业有很高的要求,认证后的信息能够帮助公司快速识别符合条件的候选人。Day 1 Seminar_Environment Workshop presentation_FINAL_web.pptx



Day 1 Seminar_Environment Workshop presentation_FINAL_web.pptxmhutttch
?
Nature and Planning What's Next?Wildlife Day 2025: Celebrating Nature and Conservation Efforts



Wildlife Day 2025: Celebrating Nature and Conservation Effortssun web solutionss
?
Join us as we celebrate Wildlife Day 2025! This 狠狠撸Share presentation explores the fascinating world of wildlife and highlights the importance of conservation efforts. From majestic elephants to endangered species, we delve into the unique behaviors and habitats of various animals and discuss how we can contribute to protecting these incredible creatures. Discover the beauty of biodiversity and learn about the crucial role we all play in preserving our natural world. Let's come together to make every day a Wildlife DayKamil Pyciak, A Name Making Waves in the Digital World



Kamil Pyciak, A Name Making Waves in the Digital Worldkamilpyciakinfo1
?
Kamil Pyciak, based in the USA, is a passionate explorer and nature lover who connects with a Polish audience through an international platform. Surrounded by America’s breathtaking landscapes, he ventures into national parks, capturing the essence of the wilderness through his lens. Despite being miles away from Poland, Kamil’s digital presence transcends borders, uniting a global community of outdoor enthusiasts. Through striking photography and engaging storytelling, he fosters a shared admiration for nature, proving that the love for the great outdoors is a universal language that brings people together across continents.Anisfeld Water Management Chapter 2.pptx



Anisfeld Water Management Chapter 2.pptxShimon Anisfeld
?
狠狠撸show based on Chapter 2 of Water Management: Prioritizing Justice and Sustainability (Island Press, 2024)Multi_Tester_Presentation.pttx. grade 11 electrical installation and maintenance



Multi_Tester_Presentation.pttx. grade 11 electrical installation and maintenanceTyroneSedillo1
?
electrical installation and maintenanceImproving castor (Ricinus communis) productivity through different sowing sch...



Improving castor (Ricinus communis) productivity through different sowing sch...Open Access Research Paper
?
Field experiment was conducted at Tapioca and Castor Research Station during 2014 -15 on evaluation of different sowing schedules (August, September, October and November) and varieties/ hybrids (DCS -107, DCH – 177, GCH – 7 and YRCH – 1) in castor. Among the sowing dates, sowing of castor at 2nd fortnight of August has recorded significantly higher kernel yield (705.8kg/ha) followed by September (497.0kg/ha) over October and November sown plots due to deficit in rainfall. Among the varieties/hybrids tested GCH7 has recorded significantly higher mean kernel yield (597.7kg/ha) in all dates of sowing over other genotypes. GCH7 and DCH 177 have recorded significantly higher kernel yield by taking sowing during 2nd fortnight of August (1046 and 927.6kg/ha).
Sostenibilidad en SEAT - Maria Tarrés #SImposioFunseam



Sostenibilidad en SEAT - Maria Tarrés #SImposioFunseamFunseam - Fundación para la Sostenibilidad Energética y Ambiental
?
Presentación de Maria Tarrés, responsable de Estrategia de Sostenibilidad de SEAT, en el marco del XIII Simposio Empresarial Internacional, organizado por Funseam el pasado 3 de febrero de 2025, en Barcelona.
Más información en: https://funseam.com/xiii-simposio-empresarial-internacional-funseam-2025/VENTILATION SYSTEM IN ANIMAL HOUSES.pptx



VENTILATION SYSTEM IN ANIMAL HOUSES.pptxRishiChaudhary20
?
VENTILATION SYSTEM IN ANIMAL HOUSE
WHY DO WE need VENTILATION?
To keep Air movement
To keep cooling
To keep control relative humidity
To improve air quality for confined animals.
Air distribution
To remove moisture, gases, dust, odors and pathogens
For livestock productivity.
To limit carbon dioxide & methane buildup.
More Related Content
Viewers also liked (9)
Ac motors



Ac motorsJamilah Abbas
?
The document discusses different types of AC motors, including induction motors and synchronous motors. Induction motors operate slightly slower than the supply frequency, while synchronous motors rotate exactly at the supply frequency. Common types of AC motors include squirrel cage motors and wound rotor motors. Squirrel cage motors have conductors in the rotor that produce torque from induced currents, while wound rotor motors have insulated windings in the rotor that allow external resistance to control starting torque and speed.Measuring instruments



Measuring instrumentsSayyed Raza
?
1. Indicating instruments measure electrical quantities by deflecting a pointer on a calibrated scale. They use a deflection system to produce a force proportional to the measured value, a control system to limit deflection, and a damping system to prevent oscillations.
2. Permanent magnet moving coil (PMMC) instruments have a coil mounted between magnet poles that deflects proportional to current. They are used as ammeters, voltmeters, and galvanometers. As an ammeter, the coil is connected across a low resistance shunt; as a voltmeter, it is connected in series with a high resistance.
3. Moving iron instruments can measure AC using an iron core acted on by a coilIndicating instruments



Indicating instrumentsKausik das
?
This document discusses electrical and electronics measurements. It describes the process of measurement by comparing unknown values to known standards. It then discusses key characteristics of instruments used for measurement, including calibration, accuracy, precision, repeatability, reproducibility, drift, span, sensitivity, resolution, and dead zone. The document also covers types of errors in measurement, including static, mistakes, systematic, and random errors. It lists sources of error and types of instruments, including absolute, secondary, indicating, recording, and integrating instruments. Finally, it provides details on permanent magnet moving coil (PMMC) and moving iron (MI) types of indicating instruments.Induction motor



Induction motorsodanforeva
?
The induction motor operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction. It consists of two main parts - the stator and the rotor. The stator contains windings that generate a rotating magnetic field, acting as the primary. This rotating field induces currents in the rotor windings, which acts as the secondary. The rotor is then pushed to rotate at a slightly lower speed than the rotating field due to "slip."Dc motors and its types



Dc motors and its typesSumeet Patel
?
The document discusses DC motors. It begins with an introduction to DC motors, noting they convert electrical to mechanical energy. It then covers the principles, construction, types, and applications of DC motors. The principles section explains how DC motors work using electromagnetism and the Lorentz force. Construction includes field and armature windings. There are three main types - shunt, series, and compound motors - which vary in how their field windings are connected. Applications include uses for different motor types like fans, tools, and mills.Electrical tools and its function



Electrical tools and its functionFortunato de Guzman
?
The document discusses various electrical tools and their functions. It describes screwdrivers like standard, Philips, and stubby screwdrivers which are used to drive different types of screws. Pliers are also discussed, including combination pliers, side cutting pliers, and long nose pliers which are used for gripping, cutting, and holding wires. Additional tools mentioned are wire strippers, electrician's knives, portable electric drills, and hacksaws, each serving a specific purpose like stripping wire insulation or cutting metal materials. Proper tool use and safety are emphasized.Dc motor



Dc motorSayyed Raza
?
1. A DC motor runs on direct current electricity. It has a field winding that produces a magnetic field when energized, and an armature winding that rotates when placed in this magnetic field.
2. The key parts of a DC motor include the yoke, poles, field winding, armature core, armature winding, commutator, and brushes. The field winding produces flux, and the rotation of the armature winding within this flux induces voltage that is used to power the load.
3. DC motors can be shunt wound, series wound, or compound wound depending on how the field and armature windings are connected. Shunt and series motors have different torque-speed characteristics duetransformer ppt



transformer pptSharukh Ansari
?
A transformer is a static device that changes alternating current (AC) at one voltage level to AC at another voltage level through electromagnetic induction. It consists of two coils, the primary and secondary windings, wrapped around a laminated iron core. When an alternating current is applied to the primary winding, it produces an alternating magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary winding. This allows the transformer to step up or step down voltages without changing the frequency. The transformer transfers power between its two coils through electromagnetic coupling between the coils wound around the iron core.Common Wire splices



Common Wire splicesDeth Guiasilon
?
An extension cord allows for multiple electrical devices to be plugged in when outlets are insufficient. It consists of a flexible electrical cable with a plug on one end and multiple sockets on the other. The document discusses how to make an extension cord by skinning copper wires of different gauges, splicing the wires together, and attaching a plug and socket. Safety tools and materials needed include solid and stranded copper wire in sizes #14, #12, and #10, as well as an outlet, flat cord, connectors, and a male plug.Recently uploaded (20)
一比一原版(颁颁毕业证)卡莫森学院毕业证如何办理



一比一原版(颁颁毕业证)卡莫森学院毕业证如何办理taqyed
?
在线快速补办加拿大本科毕业证、硕士文凭证书,购买加拿大学位证【q薇1954292140】卡莫森学院Offer,加拿大大学文凭在线购买。高仿真还原加拿大文凭证书和外壳,定制加拿大卡莫森学院成绩单和信封。学位证书的英文CC毕业证【q薇1954292140】办理加拿大卡莫森学院毕业证(CC毕业证书)【q薇1954292140】diploma学位认证卡莫森学院offer/学位证学位证书电子图在线定制服务、留信官方学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作。帮你解决卡莫森学院学历学位认证难题。在线制作假学位证加拿大文凭购买,加拿大文凭定制,加拿大卡莫森学院文凭补办【q薇1954292140】专业在线定制加拿大大学文凭学位证购买,定做加拿大本科文凭,【q薇1954292140】复制加拿大Camosun College completion letter。
如果您在英、加、美、澳、欧洲等留学过程中或回国后:
1、在校期间因各种原因未能顺利毕业《CC成绩单工艺详解》【Q/WeChat:1954292140】《Buy Camosun College Transcript快速办理卡莫森学院教育部学历认证书毕业文凭证书》,拿不到官方毕业证;
2、面对父母的压力,希望尽快拿到;
3、不清楚认证流程以及材料该如何准备;
4、回国时间很长,忘记办理;
5、回国马上就要找工作《正式成绩单卡莫森学院成绩单购买》【q薇1954292140】《毕业证工艺详解CC学位证和毕业证》办给用人单位看;
6、企事业单位必须要求办理的;
7、需要报考公务员、购买免税车、落转户口、申请留学生创业基金。
加拿大文凭卡莫森学院成绩单,CC毕业证【q薇1954292140】办理加拿大卡莫森学院毕业证(CC毕业证书)【q薇1954292140】毕业证办理需要多久拿到?卡莫森学院offer/学位证学历认证制作代办流程、留信官方学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作。帮你解决卡莫森学院学历学位认证难题。
【q薇1954292140】办理卡莫森学院毕业证(CC毕业证书)diploma学位认证【q薇1954292140】卡莫森学院offer/学位证、留信官方学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作加拿大卡莫森学院毕业证(CC毕业证书)假学历认证
特殊原因导致无法毕业,也可以联系我们帮您办理相关材料:
1:在卡莫森学院挂科了,不想读了,成绩不理想怎么办???
2:打算回国了,找工作的时候,需要提供认证《CC成绩单购买办理卡莫森学院毕业证书范本》【Q/WeChat:1954292140】Buy Camosun College Diploma《正式成绩单论文没过》有文凭却得不到认证。又该怎么办???加拿大毕业证购买,加拿大文凭购买,
3:回国了找工作没有卡莫森学院文凭怎么办?有本科却要求硕士又怎么办?
帮您解决在加拿大卡莫森学院未毕业难题(Camosun College)文凭购买、毕业证购买、大学文凭购买、大学毕业证购买、买文凭、日韩文凭、英国大学文凭、美国大学文凭、澳洲大学文凭、加拿大大学文凭(q薇1954292140)新加坡大学文凭、新西兰大学文凭、爱尔兰文凭、西班牙文凭、德国文凭、教育部认证,买毕业证,毕业证购买,买大学文凭,购买日韩毕业证、英国大学毕业证、美国大学毕业证、澳洲大学毕业证、加拿大大学毕业证(q薇1954292140)新加坡大学毕业证、新西兰大学毕业证、爱尔兰毕业证、西班牙毕业证、德国毕业证,回国证明,留信网认证,留信认证办理,学历认证。从而完成就业。
主营项目:
1、真实教育部国外学历学位认证《加拿大毕业文凭证书快速办理卡莫森学院文凭购买》【q薇1954292140】《论文没过卡莫森学院正式成绩单》,教育部存档,教育部留服网站100%可查.
2、办理CC毕业证,改成绩单《CC毕业证明办理卡莫森学院购买毕业证流程》【Q/WeChat:1954292140】Buy Camosun College Certificates《正式成绩单论文没过》,卡莫森学院Offer、在读证明、学生卡、信封、证明信等全套材料,从防伪到印刷,从水印到钢印烫金,高精仿度跟学校原版100%相同.
3、真实使馆认证(即留学人员回国证明),使馆存档可通过大使馆查询确认.
4、留信网认证,国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书,留信网存档可查.
《卡莫森学院录取通知书加拿大毕业证书办理CC成绩单用纸》【q薇1954292140】学位证1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。
挂科处理解决方案加拿大文凭卡莫森学院成绩单【q薇1954292140】复刻成绩单加拿大卡莫森学院毕业证(CC毕业证书)研究生offer在线制作 卡莫森学院毕业证办理,办成绩单加拿大卡莫森学院文凭办理,加拿大卡莫森学院成绩单办理和真实留信认证、留服认证、卡莫森学院学历认证。学院文凭定制,卡莫森学院原版文凭补办,扫描件文凭定做,100%文凭复刻。【q薇1954292140】Buy Camosun College Diploma购买美国毕业证,购买英国毕业证,购买澳洲毕业证,购买加拿大毕业证,以及德国毕业证,购买法国毕业证(q薇1954292140)购买荷兰毕业证、购买瑞士毕业证、购买日本毕业证、购买韩国毕业证、购买新西兰毕业证、购买新加坡毕业证、购买西班牙毕业证、购买马来西亚毕业证等。包括了本科毕业证,硕士毕业证。
留信认证的作用:
1. 身份认证:留信认证可以证明你的留学经历是真实的,且你获得的学历或学位是正规且经过认证的。这对于一些用人单位来说,尤其是对留学经历有高度要求的公司(如跨国公司或国内高端公司),这是非常重要的一个凭证。
专业评定:留信认证不仅认证你的学位证书,还会对你的所学专业进行评定。这有助于展示你的学术背景,特别是对于国内公司而言,能够清楚了解你所学专业的水平和价值。
国家人才库入库:认证后,你的信息将被纳入国家人才库,并且可以在国家人才网等平台上展示,供包括500强公司等大型公司挑选和聘用人才。这对于回国找工作特别是进入大公司,具有非常积极的作用。
2. 留信认证对就业的好处
提高竞争力:通过留信认证,尤其是对你所学专业的认证,可以大大提高你在国内求职时的竞争力。许多公司对留学生背景和所学专业有很高的要求,认证后的信息能够帮助公司快速识别符合条件的候选人。Day 1 Seminar_Environment Workshop presentation_FINAL_web.pptx



Day 1 Seminar_Environment Workshop presentation_FINAL_web.pptxmhutttch
?
Nature and Planning What's Next?Wildlife Day 2025: Celebrating Nature and Conservation Efforts



Wildlife Day 2025: Celebrating Nature and Conservation Effortssun web solutionss
?
Join us as we celebrate Wildlife Day 2025! This 狠狠撸Share presentation explores the fascinating world of wildlife and highlights the importance of conservation efforts. From majestic elephants to endangered species, we delve into the unique behaviors and habitats of various animals and discuss how we can contribute to protecting these incredible creatures. Discover the beauty of biodiversity and learn about the crucial role we all play in preserving our natural world. Let's come together to make every day a Wildlife DayKamil Pyciak, A Name Making Waves in the Digital World



Kamil Pyciak, A Name Making Waves in the Digital Worldkamilpyciakinfo1
?
Kamil Pyciak, based in the USA, is a passionate explorer and nature lover who connects with a Polish audience through an international platform. Surrounded by America’s breathtaking landscapes, he ventures into national parks, capturing the essence of the wilderness through his lens. Despite being miles away from Poland, Kamil’s digital presence transcends borders, uniting a global community of outdoor enthusiasts. Through striking photography and engaging storytelling, he fosters a shared admiration for nature, proving that the love for the great outdoors is a universal language that brings people together across continents.Anisfeld Water Management Chapter 2.pptx



Anisfeld Water Management Chapter 2.pptxShimon Anisfeld
?
狠狠撸show based on Chapter 2 of Water Management: Prioritizing Justice and Sustainability (Island Press, 2024)Multi_Tester_Presentation.pttx. grade 11 electrical installation and maintenance



Multi_Tester_Presentation.pttx. grade 11 electrical installation and maintenanceTyroneSedillo1
?
electrical installation and maintenanceImproving castor (Ricinus communis) productivity through different sowing sch...



Improving castor (Ricinus communis) productivity through different sowing sch...Open Access Research Paper
?
Field experiment was conducted at Tapioca and Castor Research Station during 2014 -15 on evaluation of different sowing schedules (August, September, October and November) and varieties/ hybrids (DCS -107, DCH – 177, GCH – 7 and YRCH – 1) in castor. Among the sowing dates, sowing of castor at 2nd fortnight of August has recorded significantly higher kernel yield (705.8kg/ha) followed by September (497.0kg/ha) over October and November sown plots due to deficit in rainfall. Among the varieties/hybrids tested GCH7 has recorded significantly higher mean kernel yield (597.7kg/ha) in all dates of sowing over other genotypes. GCH7 and DCH 177 have recorded significantly higher kernel yield by taking sowing during 2nd fortnight of August (1046 and 927.6kg/ha).
Sostenibilidad en SEAT - Maria Tarrés #SImposioFunseam



Sostenibilidad en SEAT - Maria Tarrés #SImposioFunseamFunseam - Fundación para la Sostenibilidad Energética y Ambiental
?
Presentación de Maria Tarrés, responsable de Estrategia de Sostenibilidad de SEAT, en el marco del XIII Simposio Empresarial Internacional, organizado por Funseam el pasado 3 de febrero de 2025, en Barcelona.
Más información en: https://funseam.com/xiii-simposio-empresarial-internacional-funseam-2025/VENTILATION SYSTEM IN ANIMAL HOUSES.pptx



VENTILATION SYSTEM IN ANIMAL HOUSES.pptxRishiChaudhary20
?
VENTILATION SYSTEM IN ANIMAL HOUSE
WHY DO WE need VENTILATION?
To keep Air movement
To keep cooling
To keep control relative humidity
To improve air quality for confined animals.
Air distribution
To remove moisture, gases, dust, odors and pathogens
For livestock productivity.
To limit carbon dioxide & methane buildup.
Day 2 Seminar Local Government Reorganisation and Planning Seminar_web.pptx



Day 2 Seminar Local Government Reorganisation and Planning Seminar_web.pptxmhutttch
?
Prepare for the impact of devolution and local government reorganisation! This workshop explores how these changes will affect planning and how local authorities can adapt smoothly. Hear insights from those in newly formed and combined authoritiesDay 2 Seminar_Innovation and Bold Leadership_web.pptx



Day 2 Seminar_Innovation and Bold Leadership_web.pptxmhutttch
?
How can planning services stay resilient while embracing bold leadership? This session explores managing change, tackling challenges, and daring to do things differently. Hear real-world insights, devise “unthinkable” solutions, and leave with a challenge to take one bold step.
Day 2 Seminar_Going Digital PAS conference Feb 2025_web.pptx



Day 2 Seminar_Going Digital PAS conference Feb 2025_web.pptxmhutttch
?
We hear from MHCLG’s digital team on the progress so far, and one of the councils who has been part of Open Digital Planning for years. We will share some ideas about what might be next, and how leaders of services can prepare for a more digital future. If you can feel the potential that better ICT and use of data can bring but don’t know where to start this session is for you.
Comparative study of foliar application of various beer products and sakkara ...



Comparative study of foliar application of various beer products and sakkara ...Open Access Research Paper
?
Cucumber (Cucumis sativus) is an important vegetable crop in the tropics. Beer brewing is an intricate process encompassing mixing and further elaboration of four essential raw materials. “Sakkara”, Sri Lankan name for jiggery made by sugar cane stem extract. Sakkara Brewing (SBr) is also an intricate process like beer. It has reported that foliar application of beer and SBr resulted in significant growth stimulation in plants. The objectives of the present study were to compare the effects of five commercially available beer products and SBr on growth, flowering and fruit setting of cucumber plants. The study was conducted at farmer’s poly tunnel in a Completely Randomize Design with seven treatments randomized in five replicates. The treatments were T1 – Carlsberg Special Brew (8.8% Ethanol), T2 – Carlsberg (4.8% Ethanol), T3 – Lion Strong (8.8% Ethanol), T4 – Lion Stout (8.8% Ethanol), T5- Lion Larger (4.8% Ethanol), T6 – SBr (2.2% ethanol, 4% methanol, 2.4 x 104 yeast cells per 1mm3 and PH= 3.36) and T7 – Control (without spraying). Plants were established in pots and standard crop management practices were done. Products were sprayed to the seedlings 15 days after sowing and continued 6 times at 10 days intervals. Measurements were taken on growth, flowering and Fruit setting stages. The higher values of plant growth, reproductive and yield parameters were observed in beer and SBr applied treatments compared to control. SBr is very low cost product compared to commercially available beer. So, it can be recommended for vegetable cultivation as economically feasible and eco-friendly organic product.
Considerations for appropriate assessment of efficacy of biopesticides in the...



Considerations for appropriate assessment of efficacy of biopesticides in the...OECD Environment
?
The OECD Seminar on Different aspects of efficacy evaluation of biopesticides, held on 28-29 June 2021, covered the similarities and differences of the efficacy evaluation of the different categories of biopesticides, new application techniques, efficacy evaluation of biopesticides based on plant defence inducers (PDI), comparison of efficacy requirements for biostimulants vs. biopesticides, how to evaluate different Integrated Pest Management (IPM) modules, and registration pathways with limited or no evaluation of efficacy. The event facilitated exchanges between policy makers, academia, and industry. Water Pollution.pdf Akash Mahakur



Water Pollution.pdf Akash MahakurAkash Mahakur
?
Water pollution occurs when harmful substances contaminate a body of water, making it toxic to humans and the environment.
Causes
Point source pollution: Pollution from specific sources like sewage treatment plants or factories
Diffuse pollution: Pollution from widespread sources like farming and power plants
Oil spills: Accidental spills, transportation, runoff, and intentional dumping
Industrial wastewater: Heavy metals, dyes, and other pollutants released into water bodies
Agricultural runoff: Fertilizers, pesticides, and salt
Improving castor (Ricinus communis) productivity through different sowing sch...



Improving castor (Ricinus communis) productivity through different sowing sch...Open Access Research Paper
?
Sostenibilidad en SEAT - Maria Tarrés #SImposioFunseam



Sostenibilidad en SEAT - Maria Tarrés #SImposioFunseamFunseam - Fundación para la Sostenibilidad Energética y Ambiental
?
Comparative study of foliar application of various beer products and sakkara ...



Comparative study of foliar application of various beer products and sakkara ...Open Access Research Paper
?





