Why and how to teach collocations
- 2. Lexical Approach Choosing our words carefully in certain situations is more important than choosing grammatical structures (Harmer 1991). We cannot use structures correctly if we do not have enough vocabulary knowledge. Collocation describes the relationship between words that often appear together. They include structural patterns that resemble traditional grammar and combinations of words that simply go together.
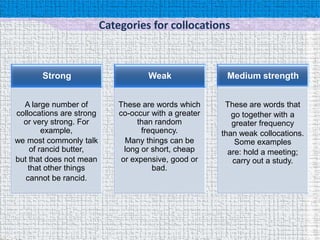
- 4. Categories for collocations Strong Weak Medium strength A large number of These are words which These are words that collocations are strong co-occur with a greater go together with a or very strong. For than random greater frequency example, frequency. than weak collocations. we most commonly talk Many things can be Some examples of rancid butter, long or short, cheap are: hold a meeting; but that does not mean or expensive, good or carry out a study. that other things bad. cannot be rancid.
- 5. Learners’ difficulties with collocations 1. Learners may have intralingual problems. For example, instead of many thanks, they might incorrectly use several thanks. 2. Learners may make negative transfer from their mother tongue. For example, become lovers instead of fall in love. 3. When students learn words through definitions or in isolation, their chances of using appropriate collocations or remembering the words decrease. 4. When students read texts, they may not recognize collocations as meaningful phrases, which would inhibit their understanding of the text.
- 6. Teaching collocations Make students aware of collocations. Teaching individual collocations. Storing collocations.
- 7. Activities to raise students’ awareness of collocations 1. Ask 2. After they have read a learners to text, learners can be given a set of underline incomplete phrases taken from the chunks they text and asked to complete them by can find in a scanning the text again. This can be text. done at any level. 5. Give 3. To 4. After they students encourage have seen phrases in student certain their native autonomy, collocations in language and have a text, learners equivalent students do can be asked phrases in dictionary to find pairs of English, and work to find collocations ask students certain arranged to match the collocations. randomly. phrases.
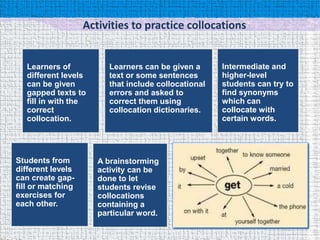
- 8. Activities to practice collocations Learners of Learners can be given a Intermediate and different levels text or some sentences higher-level can be given that include collocational students can try to gapped texts to errors and asked to find synonyms fill in with the correct them using which can correct collocation dictionaries. collocate with collocation. certain words. Students from A brainstorming different levels activity can be can create gap- done to let fill or matching students revise exercises for collocations each other. containing a particular word.