Why study java script
- 1. Why Study JavaScript? JavaScript is one of the 3 languages all web developers must learn: 1. HTML to define the content of web pages 2. CSS to specify the layout of web pages 3. JavaScript to program the behavior of web pages This tutorial is about JavaScript, and how JavaScript works with HTML and CSS. JavaScript Assignment Operators Assignment operators are used to assign values to JavaScript variables. Operator Example Same As = x = y x = y += x += y x = x + y -= x -= y x = x - y *= x *= y x = x * y /= x /= y x = x / y %= x %= y x = x % y
- 2. JavaScript Arithmetic Operators Arithmetic operators are used to perform arithmetic between variables and/or values. Operator Description + Addition - Subtraction * Multiplication / Division % Modulus ++ Increment -- Decrement The addition operator (+) adds a value: JavaScript Data Types JavaScript variables can hold many data types: numbers, strings, arrays, objects and more: var length = 16; // Number var lastName = "Johnson"; // String var cars = ["Saab", "Volvo", "BMW"]; // Array var x = {firstName:"John", lastName:"Doe"}; // Object JavaScript Booleans Booleans can only have two values: true or false. Example
- 3. var x = true; var y = false; JavaScript Arrays JavaScript arrays are written with square brackets. Array items are separated by commas. The following code declares (creates) an array called cars, containing three items (car names): Example var cars = ["Saab", "Volvo", "BMW"]; JavaScript Objects JavaScript objects are written with curly braces. Object properties are written as name:value pairs, separated by commas. Example var person = {firstName:"John", lastName:"Doe", age:50, eyeColor:"blue"}; onClick: <INPUT TYPE="submit" NAME="mysubmit" VALUE="Submit" onClick="return confirm(`Are you sure you want to submit the form?')"> <SCRIPT> function valid(form) { var input = form.data.value; alert("Hello " + input + " ! Welcome..."); } </SCRIPT> </HEAD>
- 4. <BODY> <H3> Example of onClick Event Handler </H3> Click on the button after inputting your name into the text box:<BR> <FORM> <INPUT TYPE="text" NAME="data"> <INPUT TYPE="button" VALUE="Click Here" onClick="valid(this.form)"> </FORM> </BODY> </HTML> onFocus: <BODY BGCOLOR="#ffffff" onFocus="document.bgcolor='#000000'"> HTML> <HEAD><TITLE>Example of onFocus Event Handler</TITLE></HEAD> <BODY> <H3>Example of onFocus Event Handler</H3> Click your mouse in the text box:<BR> <FORM> <INPUT TYPE="text" onFocus='alert("You focused in the textbox!!")'> </FORM> </BODY> </HTML> In the above example, when you put your mouse on the text box, an alert() message displays a message. onLoad: <IMG SRC=/slideshow/why-study-java-script/48333281/"images/object.gif" NAME="jsobjects" onLoad="alert('You loaded myimage')"> <HTML> <HEAD> <TITLE>Example of onLoad Event Handler</TITLE> <SCRIPT>
- 5. function hello() { alert("Hello there...nnThis is an example of onLoad."); } </SCRIPT> </HEAD> <BODY onLoad="hello()"> <H3>Example of onLoad Event Handler</H3> </BODY> </HTML> The exampl onMouseOver: <MAP NAME="mymap"> <AREA NAME="FirstArea" COORDS="0,0,49,25" href="mylink.html" onMouseOver="self.status='This will take you to mylink.html'; return true"> </MAP> HTML> <HEAD><TITLE>Example of onMouseOver Event Handler</TITLE></HEAD> <BODY> <H3>Example of onMouseOver Event Handler</H3> Put your mouse over <A href="javascript:void('');" onMouseOver="window.status='Hello! How are you?'; return true;"> here </A> and look at the status bar (usually at the bottom of your browser window). </BODY> </HTML> onSubmit:
- 6. <HTML> <HEAD><TITLE> Example of onSubmit Event Handler </TITLE></HEAD> <BODY> <H3>Example of onSubmit Event Handler </H3> Type your name and press the button<BR> <FORM NAME="myform" onSubmit="alert('Thank you ' + myform.data.value +'!')"> <INPUT TYPE="text" NAME="data"> <INPUT TYPE="submit" VALUE="Submit this form"> </FORM> </BODY> <HTML> onUnload: <SCRIPT> function goodbye() { alert("Thanks for Visiting!"); } </SCRIPT> </HEAD> <BODY onUnLoad="goodbye();"> <H3>Example of onUnload Event Handler</H3> Look what happens when you try to leave this page... </BODY> </HTML> EVENT HANDLER USED WITH onAbort image onBlur select, text, text area onChange select, text, textarea onClick button, checkbox, radio, link, reset, submit, area onError image
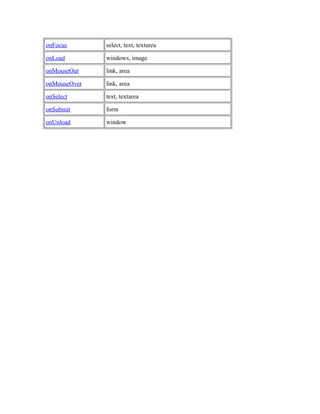
- 7. onFocus select, text, textarea onLoad windows, image onMouseOut link, area onMouseOver link, area onSelect text, textarea onSubmit form onUnload window

![JavaScript Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators are used to perform arithmetic between variables
and/or values.
Operator Description
+ Addition
- Subtraction
* Multiplication
/ Division
% Modulus
++ Increment
-- Decrement
The addition operator (+) adds a value:
JavaScript Data Types
JavaScript variables can hold many data types: numbers, strings,
arrays, objects and more:
var length = 16; // Number
var lastName = "Johnson"; // String
var cars = ["Saab", "Volvo", "BMW"]; // Array
var x = {firstName:"John", lastName:"Doe"}; // Object
JavaScript Booleans
Booleans can only have two values: true or false.
Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whystudyjavascript-150519125558-lva1-app6892/85/Why-study-java-script-2-320.jpg)
![var x = true;
var y = false;
JavaScript Arrays
JavaScript arrays are written with square brackets.
Array items are separated by commas.
The following code declares (creates) an array called cars, containing
three items (car names):
Example
var cars = ["Saab", "Volvo", "BMW"];
JavaScript Objects
JavaScript objects are written with curly braces.
Object properties are written as name:value pairs, separated by commas.
Example
var person = {firstName:"John", lastName:"Doe", age:50,
eyeColor:"blue"};
onClick:
<INPUT TYPE="submit" NAME="mysubmit" VALUE="Submit"
onClick="return confirm(`Are you sure you want to submit the form?')">
<SCRIPT>
function valid(form) {
var input = form.data.value;
alert("Hello " + input + " ! Welcome...");
}
</SCRIPT>
</HEAD>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whystudyjavascript-150519125558-lva1-app6892/85/Why-study-java-script-3-320.jpg)