WordPress Development Environments
- 1. Ohad Raz WordPress Consultant WordCamp Jerusalem 2013
- 2. WordPress Development Environments Ohad Raz WordPress Consultant WordCamp Jerusalem 2013
- 3. Who Am I? ŌĆó Father and husband. ŌĆó Ohad Raz (aka Bainternet). ŌĆó WordPress Consultant Developer and Designer ŌĆó Plugin developer 18 published plugins with over 132,000 downloads. ŌĆó Core Contributor as of 3.5 ŌĆó Moderator and Editor @ WordPress Answers And I also fight crime at night
- 4. What's this about? ŌĆó Development Environments. ŌĆó Development Environments Workflow. ŌĆó Tips and Tricks: ŌĆó Server. ŌĆó Domain. ŌĆó Files. ŌĆó Database. ŌĆó Some Version Control.
- 5. Environments Local / Development Staging / Testing Live / Production
- 6. Development Environment Development usually refers to your local machine where you have your web server, database, IDE, and related tools installed. Its where you actually develop your project.
- 7. Staging Environment The Staging Environment is a server the resembles where the project is actually going to live and where you upload your work for testing. Its mostly used for testing and showing off your work.
- 8. Live Environment The live environment is where the project is live on the web with real content and where users actually interact with your work ItŌĆÖs the actual site.
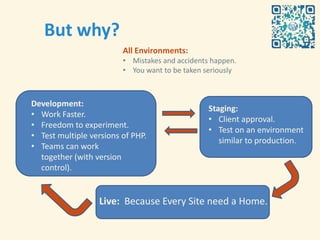
- 9. But why? All Environments: ŌĆó Mistakes and accidents happen. ŌĆó You want to be taken seriously Development: Staging: ŌĆó Work Faster. ŌĆó Client approval. ŌĆó Freedom to experiment. ŌĆó Test on an environment ŌĆó Test multiple versions of PHP. similar to production. ŌĆó Teams can work together (with version control). Live: Because Every Site need a Home.
- 10. Development Environment Server WAMP MAMP XAMPP Windows Mac X any platform Apache Apache Apache MySQL MySQL MySQL PHP PHP PHP Perl
- 11. Development Environment Server Install WordPress Locally : 1. Download WordPress. 2. Extract the downloaded zip file. 3. Create a database. 4. Configure wp-config.php 5. Run WordPress Setup Or do it all at once with WordPress Auto Installer This script will download the latest copy of WordPress, extract the files to the directory you named, create a new database and take you straight to where all you have to do is set you sites name, your username and pass and you have a new WordPress Installation ready to roll.
- 12. Domain Issue Live: domain.com Dev: domain.dev This way you can use a simple Search and Replace on files and database dump. Or use real domain name Using the hosts file. Live & Dev: domain.com # Point domain.com to your computer 127.0.0.1 domain.com Windows: C:WINDOWSsystem32driversetchosts Mac/Linux: /etc/hosts
- 13. Domain Issue Create A Virtual Host <VirtualHost 127.0.0.1> DocumentRoot "C:/wamp/www/WordCamp/local" ServerName domain.dev <Directory "C:/wamp/www/WordCamp/local"> Options FollowSymLinks Indexes MultiViews AllowOverride All Order deny,allow Allow from all Allow from 127.0.0.1 </Directory> </VirtualHost> [wamp] c:wampbinapacheApacheVERSIONconfhttpd.conf [mamp] /private/etc/apache2/httpd.conf [xampp] ..apacheconfextrahttpd-vhosts.conf
- 14. Files Sync FTP sync Only copy changed files based on size or date FileZilla - http://filezilla-project.org/ Command line Rsync - http://rsync.samba.org/ Wget - http://www.gnu.org/software/wget/ Capistrano* - http://capistranorb.com/ Version control Git - http://git-scm.com/ SVN - http://subversion.apache.org/ HG - http://mercurial.selenic.com/
- 15. Files Sync wp-config.php One level above the WordPress Root Directory in all environments and ignored in version control. Or a separate file per each environment: //dev-config.php /* Development Environment */ define('WP_ENV', 'local'); define('WP_DEBUG', true); define('DB_NAME', 'local_db_name'); define('DB_USER', 'local_db_user'); define('DB_PASSWORD', 'local_db_password'); define('DB_HOST', 'local_db_host'); //stage-config.php /* Staging Environment */ define('WP_ENV', 'stage'); define('WP_DEBUG', true); define('DB_NAME', 'stage _db_name'); define('DB_USER', 'stage _db_user'); define('DB_PASSWORD', 'stage _db_password'); define('DB_HOST', 'stage _db_host');
- 16. Files Sync wp-config.php //First we check for development env if ( file_exists( dirname( __FILE__ ) . '/dev-config.php' ) ) { include( dirname( __FILE__ ) . '/dev-config.php' ); } elseif ( file_exists( dirname( __FILE__ ) . '/stage-config.php' ) ) { //then we check for staging env include( dirname( __FILE__ ) . '/stage-config.php' ); }else { //if we got here then we are at production env. define('WP_ENV', 'production'); define('WP_DEBUG', false); define( 'DB_NAME', 'production_db' ); define( 'DB_USER', 'production_user' ); define( 'DB_PASSWORD', 'production_password' ); define( 'DB_HOST', 'production_db_host' ); } } ŌĆ”
- 17. Database Sync Native Export Import It's best to import into Dev then move the database over to production because when you import it will download all the new media files from production.
- 18. Database Sync Database Management tools: Export & import the database using PHPMyAdmin or alternative. Use ŌĆØadd drop tablesŌĆØ This will delete the old tables when you import. Use the ŌĆØINSERT IGNORE INTOŌĆØ MySQL command to add the new tables from dev. or the ŌĆØREPLACEŌĆØ command to overwrite duplicate rows in the same table.
- 19. Database Sync Use A plugin: WP Migrate DB Which takes care of serialized data Ex: s:9:ŌĆ£domin.dev" Becomes: s:11:ŌĆ£domain.info"
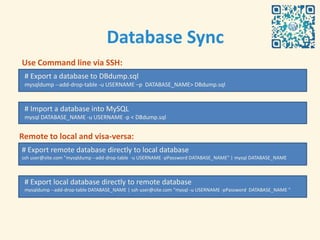
- 20. Database Sync Use Command line via SSH: # Export a database to DBdump.sql mysqldump --add-drop-table -u USERNAME ŌĆōp DATABASE_NAME> DBdump.sql # Import a database into MySQL mysql DATABASE_NAME -u USERNAME -p < DBdump.sql Remote to local and visa-versa: # Export remote database directly to local database ssh user@site.com "mysqldump --add-drop-table -u USERNAME -pPassword DATABASE_NAME" | mysql DATABASE_NAME # Export local database directly to remote database mysqldump --add-drop-table DATABASE_NAME | ssh user@site.com "mysql -u USERNAME -pPassword DATABASE_NAME "
- 21. All Around Solutions Server / Stack: Bitnami - simple stack with WordPress bundled in. Instant WordPress - The easiest and quickest way to install WordPress! DesktopServer - Another easy way with virtual servers and deploy capability. Plugins: BackupBuddy - Back up, restore and move WordPress. Duplicator ŌĆō ŌĆ£ability to migrate a site from one location to another location in 3 steps.ŌĆØ
- 22. Version Control Version Control - track your files over time. But Why? ŌĆó Easily un-break your code. ’āś Feel free to experiment. ’āś No more of this: ’üČ Logo.png ’üČ Logo_final.png ’üČ Logo_last.png ’üČ Logo_last2.png ŌĆó Never. Lose. Anything. ’āś If You Ever ’üČ Lost a file ’üČ Written over a file ’üČ Made a change that broke your code
- 23. Version Control Some More reasons ŌĆó One canonical version. ’āś There is a clear place to go for the primary copy of the code. ŌĆó Collaboration ’āś Track changes For teams ’üČ See what others have done ’üČ Ability to reject / avoid bad changes ’āś Simultaneous editing ’āś Merge ŌĆó Deployment!!!
- 24. Version Control Methods: ŌĆó Version Control the entire WordPress environment ŌĆó Version Control only the WP-Content Directory ŌĆó Version Control only a specific Theme or Plugin
- 25. Version Control Simple git commands: ŌĆó git init - initializes a git repository ’āś git init - initializes a git repository in current folder ’āś git init foldername - initializes a git repository in foldername ŌĆó git add ŌĆō tell git to keep track. ’āś git add . - add everything. ’āś git add somefile.php ŌĆō add somefile.php ŌĆó git commit - stage files / stores a version of the current code ’āś git commit -m "commit messageŌĆ£ ŌĆó git status - allows you to see the current state of your code. ŌĆó git pull ŌĆō pull updates ŌĆó git push ŌĆō push updates
- 26. Version Control On Local Host: ŌĆó Download and Install WordPress. ŌĆó Create a new repository. ŌĆó Tell git to ignore wp-config.php ŌĆó Add and commit changes. git init . touch .gitignore | echo wp-config.php >>.gitignore git add . git commit ŌĆōmŌĆØinitial WordPress CommitŌĆØ
- 27. Version Control Repository Hosts GITHUB - web-based hosting service for software development projects that use the Git revision control system. BitBucket - web-based hosting service for projects that use either the Mercurial or Git revision control systems
- 28. Version Control Create a new BitBucket Repository
- 29. Version Control Create a new BitBucket Repository
- 30. Version Control On Local Host: ŌĆó Add Bitbucket as remote repository ŌĆó Push to Bitbucket. git remote add origin https://bitbucket.org/bainternet/some-wordpress-project.git git push
- 31. Version Control On Stage/Production: ŌĆó Clone Bitbucket Repository. ŌĆó Run WordPress install once. git clone https://bitbucket.org/bainternet/some-wordpress-project.git
- 32. Version Control Workflow: On local On Server git pull git pull git checkout -b dev //make some changes git commit -m "made dev changes" git checkout master git merge dev git commit -m ŌĆ£merged dev changes" git push
- 33. Version Control On local On Server git pull git checkout -b feature-x git pull //make some changes git commit -m ŌĆ£started feature-x " git checkout master git checkout -b bug-y //fix bug y git commit -m ŌĆ£Fixed bug y" git checkout master git merge bug-y git commit -m ŌĆ£merged bug y fix" git push git checkout feature-x //finish working on feature x git commit -m ŌĆ£finished feature-x " git checkout master git merge dev git commit -m ŌĆ£merged dev changes" git push
- 34. Questions???
- 35. Thank You!











![Domain Issue
Create A Virtual Host
<VirtualHost 127.0.0.1>
DocumentRoot "C:/wamp/www/WordCamp/local"
ServerName domain.dev
<Directory "C:/wamp/www/WordCamp/local">
Options FollowSymLinks Indexes MultiViews
AllowOverride All
Order deny,allow
Allow from all
Allow from 127.0.0.1
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
[wamp] c:wampbinapacheApacheVERSIONconfhttpd.conf
[mamp] /private/etc/apache2/httpd.conf
[xampp] ..apacheconfextrahttpd-vhosts.conf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-130220153458-phpapp01/85/WordPress-Development-Environments-13-320.jpg)