Ads overview-en
- 1. Microsoft Active Directory An Overview
- 2. What is Active Directory? ’ü« MicrosoftŌĆśs new Directory Service ’ü« Called: ADS, NTDS ’ü« Successor to LAN Manager Domains ’ü« Goals ŌĆó Open Standards ŌĆó High Scalability ŌĆó Simplified Administration ŌĆó Compatibility to existing Windows NT systems and applications
- 3. Open Standards ’ü« LDAP ŌĆó Low-Level API to Active Directory ’ü« X.500 ŌĆó Active Directory Structure ŌĆó Not fully standard-compliant ’ü« DNS ŌĆó Resource Location ŌĆó Extensions, e. G. ŌĆ×Dynamic DNSŌĆ£ ’ü« Kerberos ŌĆó Authentication
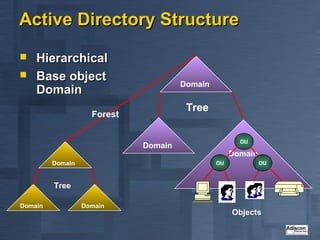
- 4. Active Directory Structure ’ü« Hierarchical ’ü« Base object Domain Domain Tree Forest OU Domain Domain Domain OU OU Tree Domain Domain Objects
- 5. Which objects does Active Directory contain? ’ü« ŌĆ×old Friends ŌĆ£ ŌĆó User ŌĆó Group ŌĆó Computer ’ü« New Elements ŌĆó Distribution Lists ŌĆó System Policies ’ü« Application defined custom objects ’ü« Described in the Schema
- 6. What is the Schema? ’ü« Definition of all AD ŌĆó Object-Types (Classes) ŌĆó Attributes ŌĆó Data-Types (Syntaxes) ’ü« Can be compared to a Database Schema ’ü« ONE consistent Schema inside a single Forest ’ü« Extensible
- 7. What is a Domain? ’ü« AD Base Element (Building Block) ’ü« NT 4 Compatible ’ü« Physically Implemented on Domain Controllers (DC) ’ü« Border for ŌĆó Replication Traffic Firma.de ŌĆó System Policies ŌĆó Administration
- 8. What is an Organizational Unit (OU)? ’ü« Implements a Structure inside a Domain ’ü« Can be nested as needed ’ü« Can not be assigned any rights ’ü« Typically used for Administrative Reasons ŌĆó e.g. System Policies LA New York Admin Sales Admin Sales
- 9. What is a Tree? ’ü« Hierarchical Domain Structure inside a single Namespace ŌĆó adiscon.com adiscon.com ŌĆó la.adiscon.com Tree ŌĆó ny.adiscon.com la.adiscon.com ny.adiscon.com ’ü« Transitive Trusts created automatically ’ü« Sub-Domain must be added to Root- Domain ŌĆō otherwise there will be no tree!
- 10. What is a Forest? ’ü« Combination of Trees ’ü« Disjunct Namespaces ŌĆó adiscon.de ŌĆó adiscon.com ’ü« Transitive Trusts created automatically ’ü« There is one single tree-root! ’ü« Sub-Tree must be added to Root-Tree, otherwise no Forest will be created
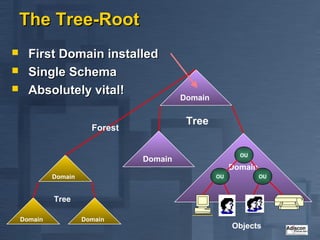
- 11. The Tree-Root ’ü« First Domain installed ’ü« Single Schema ’ü« Absolutely vital! Domain Tree Forest OU Domain Domain Domain OU OU Tree Domain Domain Objects
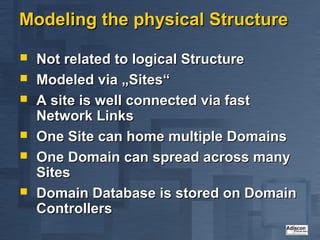
- 12. Modeling the physical Structure ’ü« Not related to logical Structure ’ü« Modeled via ŌĆ×SitesŌĆ£ ’ü« A site is well connected via fast Network Links ’ü« One Site can home multiple Domains ’ü« One Domain can spread across many Sites ’ü« Domain Database is stored on Domain Controllers
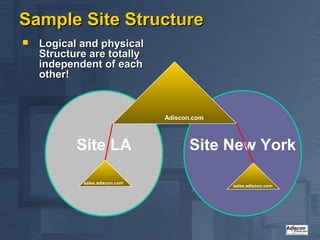
- 13. Sample Site Structure ’ü« Logical and physical Structure are totally independent of each other! Adiscon.com Site LA Site New York sales.adiscon.com sales.adiscon.com
- 14. Which Role can a Server have? ’ü« Member Server ’ü« Domain Controller ’ü« Global Catalog ’ü« FSMO ŌĆó Special Roles carried out by only a limited set of Servers ŌĆó e.g. PDC Emulator ŌĆó e.g. Schema Master
- 15. What is a Domain-Controller? ’ü« Stores a physical Copy of the Active Directory Database ŌĆó Currently a single Domain per DC supported! ŌĆó ESE95 Database (MS Exchange) ’ü« Logon Services ŌĆó Kerberos ŌĆó LAN Manager Authentication ’ü« Recommendation: always have at least 2 Domain Controllers!
- 16. What is a Global Catalog Server? ’ü« Answers AD Search Queries ’ü« Must be present to successfully logon ’ü« Holds a copy of all Objects of the whole ForestŌĆ” ’ü« ...but holds only a subset of the Attributes ŌĆó User definable ’ü« Recommendation: at least one GC per (larger) Site
- 17. Multi Master Replication ’ü« Updates can be applied to ANY Domain Controller ’ü« Will be Replicated to each other Domain Controls (inside that Domain) within 15 Minutes ’ü« Optimized Algorithm reduces Replication Traffic ’ü« Not time based (triggered on demand, only)!
- 18. Intra-Sites Replication ’ü« All Domain Databases involved ’ü« Changes are transmitted compressed ’ü« via IP (RPC) or SMTP ŌĆó SMTP not within a single domain! ’ü« Time Replication occurs can be configured ’ü« Volume of Replication Traffic can not be restricted! ’ü« Have an Eye on GCs!
- 19. Mixed vs. Native Mode? ’ü« Mixed Mode supports Coexistence with NT4 ŌĆó Default ŌĆó NT 4 BDCs continue to work ŌĆó Enables ŌĆ£Fallback ScenarioŌĆØ during Migration ’ü« Only Native Mode supports all AD Features ŌĆó More than 40 MB Domain Database Size ŌĆó Mostly problem-free ŌĆ×MoveTreeŌĆ£ ŌĆó Universal Groups, Group nesting ’ü« Once you have switched to Native Mode, there is no way back to Mixed Mode!
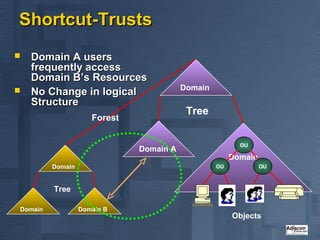
- 20. Are there still Trusts available? ’ü« Old fashioned NT 4 Trusts can still be used ŌĆó Work like always ŌĆó No additional functionality ’ü« Most be used to connect different Forests ŌĆó Be careful ŌĆō no common Global Catalog! ’ü« Shortcut-Trusts ŌĆó Connect frequently used Domains to each other (Performance Optimization)
- 21. Shortcut-Trusts ’ü« Domain A users frequently access Domain BŌĆÖs Resources Domain ’ü« No Change in logical Structure Tree Forest OU Domain A Domain Domain OU OU Tree Domain Domain B Objects
- 22. Vital for AD: DNS! ’ü« DNS is Active DirectoryŌĆÖs Locator Service ’ü« Without correctly configured DNS no working Active Directory! ŌĆó Currently TOP 1 Trouble spot ’ü« Can be hosted on non MS-DNS ŌĆó Minimum BIND Version 8.1.2 ŌĆó No special Characters in Computer Names ŌĆó Not really an option ŌĆó Recommendation: delegate a separate ŌĆ£AD- ZoneŌĆØ on non-MS DNS and use MS-DNS for that zone ŌĆō saves lots of Trouble!
- 23. Who is using Active Directory? ’ü« Windows 2000 ŌĆó Authentication ŌĆó System Policies ’ü« Directory Enabled Applications ŌĆó Please do not overlook them when planning your AD!
- 24. What are Directory-Enabled Applications? ’ü« Applications directly using and accessing the Active Directory ŌĆó e.g. Exchange 2000 ŌĆó Many more expected! ’ü« Typically extend the Schema ’ü« May dramatically change usage pattern for Active Directory Resources ŌĆó Replication Traffic (new Objects, Attributes) ŌĆó AD Queries (GCs!)
- 25. Active Directory Security ’ü« Improved Authentication ’ü« Permissions applied via ACLs ŌĆó To Objects as whole ŌĆó To specific Attributes ’ü« Fine-Tuning of Access Permissions possible ’ü« Tool-Support to visualize Security Settings currently weak (try Visio!)
- 26. What is Kerberos? ’ü« ŌĆ×age-oldŌĆ£ Internet-Standard - mature ’ü« Commonly used under Unix ’ü« Secure Authentication thanks to Encryption ’ü« Standard-Authentication Model under Windows 2000 ’ü« Microsoft Kerberos not fully compatible to other Kerberos Implementations
- 27. Delegation of Administration ’ü« Admin rights can be delegated to Users or Groups ŌĆó NOT to OUs! ’ü« Delegation via Wizards ’ü« Currently ŌĆ£Admin NightmareŌĆØ ŌĆō very hard to detect who has rights ŌĆó All objects must be viewed separately and manually ŌĆó Currently no good tools ŌĆō but expected to be available in the future ŌĆó Microsoft itself also plans to provide additional tools
- 28. Inheritance in Active Directory ’ü« From Top to Bottom ’ü« Inheritance can only be blocked completely ŌĆó No IRF like Novell
- 29. Groups ’ü« Basically, like under NT 4 ŌĆó Local Groups are assigned Permissions ŌĆó Global Groups contain Users ’āś From a single Domain ’āś Global Groups are members in Local Groups for Permission assignment ’ü« New: Universal Groups ŌĆó Can be used everywhere in every Domain (Permissions, Members) ŌĆó Implemented via GC ’āś Replication traffic limits usability
- 30. Active Directory Problem Spots ’ü« DNS Dependency ’ü« No ŌĆ×Merge-TreeŌĆ£ ’ü« No Partitioning (only a single Domain per Domain Controller) ’ü« Limited Tool-Support ’ü« Forest Global Schema ’ü« Schema-Modifications can not be undone ’ü« Issues will be addressed over time by Microsoft (keep in mind AD is Version 1.0!)
- 31. Importance of AD for MicrosoftŌĆÖs Strategy ’ü« Most important Product ’ü« All new Microsoft Products need or at least work better with Active Directory ŌĆó Exchange 2000 ŌĆó SQL Server 2000 ŌĆó ... ’ü« Bill Gates: ŌĆ×We have bet Microsoft on Active Directory.ŌĆ£
- 32. Questions? ’ü« rgerhards@adiscon.com ’ü« www.windows-expert.net