D dimer
- 1. D-Dimer Blood Test Submitted by Mr.A.Ajith Bsc . Microbiology DMLT
- 2. D ÔÇô Dimer Blood Test ´üÁ D-DimerTest ´üÁ A D-dimer test looks for D-dimer in blood.D-dimer is a protein fragment (small piece) that's made when a bloodclot dissolves in your body. ´üÁ Blood clottingis an important process that prevents you from losing too much blood when you are injured. Normally, your body will dissolve the clot once your injury has healed. With a blood clottingdisorder, clots can form when you don't have an obvious injury or don't dissolve when they should. These conditionscan be very serious and even life-threatening. AD-dimer test can show if you have one of these conditions. ´üÁ Other names: fragment D-dimer, fibrin degradation fragment ´üÁ USED FOR ´üÁ A D.DIMER test is most oftern used to find out the whetheryou have blood clot disorder. These disorder include
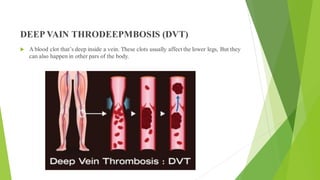
- 3. DEEP VAIN THRODEEPMBOSIS (DVT) ´üÁ A blood clot thatÔÇÖs deep inside a vein. These clots usually affect the lower legs, But they can also happen in other pars of the body.
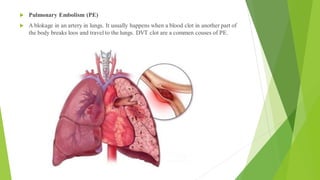
- 4. ´üÁ Pulmonary Embolism (PE) ´üÁ A blokage in an artery in lungs. It usually happens when a blood clot in another part of the body breaks loos and travel to the lungs. DVT clot are a commen couses of PE.
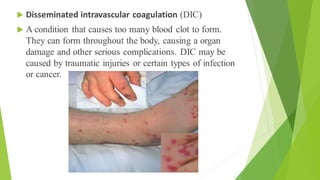
- 5. ´üÁ Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) ´üÁ A condition that causes too many blood clot to form. They can form throughout the body, causing a organ damage and other serious complications. DIC may be caused by traumatic injuries or certain types of infection or cancer.
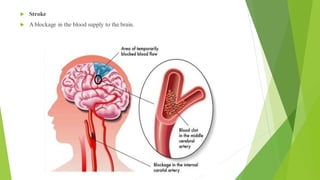
- 6. ´üÁ Stroke ´üÁ A blockage in the blood supply to the brain.
- 7. ´üÁ Risks Factors D-dimertest ´üÁ You may have slight pain or bruising at the spot where the needlewas put in, but most symptoms go away quickly. ´üÁ results mean ´üÁ If your results show low or normal D-dimer levels in the blood, it means you probablydon't have a clottingdisorder. ´üÁ If your results show higher than normal levels of ´üÁ D-dimer, it may mean you have a clotting disorder. ´üÁ ´üÁ But it cannot show where the clot is located or what type of clottingdisorder you have. Also, high D-dimer levels are not always caused by clotting problems. Other conditionsthat can cause high D-dimerlevels includepregnancy, heart disease, and recent surgery. If your D-dimer results were not normal, your provider will probablyorder more tests to make a diagnosis. ´üÁ If you have questionsabout your results, talk to your health care provider. ´üÁ Learn more about laboratorytests, reference ranges, and understandingresults.
- 8. ´üÁ Testing Purpose ´üÁ Blood clotting disorder, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or a pulmonary embolism (PE). ´üÁ Symptoms of DVT include: ´üÁ Leg pain or tenderness ´üÁ Leg swelling ´üÁ Redness or red streaks on the legs ´üÁ Symptoms of PE include: ´üÁ Trouble breathing ´üÁ Cough ´üÁ Chest pain ´üÁ Rapid heartbeat
- 9. ´üÁ Risks Factors D-dimer test ´üÁ You may have slight pain or bruising at the spot where the needle was put in, but most symptoms go away quickly. ´üÁ results mean ´üÁ If your results show low or normal D-dimer levels in the blood, it means you probably don't have a clotting disorder. ´üÁ If your results show higher than normal levels of ´üÁ D-dimer, it may mean you have a clotting disorder. ´üÁ ´üÁ But it cannot show where the clot is located or what type of clotting disorder you have. Also, high D-dimer levels are not always caused by clotting problems. Other conditions that can cause high D-dimer levels include pregnancy, heart disease, and recent surgery. If your D-dimer results were not normal, your provider will probably order more tests to make a diagnosis. ´üÁ If you have questions about your results, talk to your health care provider. ´üÁ Learn more about laboratory tests, reference ranges, and understanding results. ´üÁ
- 10. ´üÁ Is there anything else I need to know about a D-dimer test? ´üÁ If your D-dimer test results were not normal, your provider may order one or more imaging tests to find out if you have a clotting disorder. These include: ´üÁ Doppler ultrasound, a test that uses sound waves to create images of your veins. ´üÁ CT angiography. In this test, you are injected with a special dye that helps your blood vessels show up on a special type of x- ray machine. ´üÁ Ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scan. These are two tests that may be done separately or together. They both use small amounts of radioactive substances to help a scanning machine see how well air and blood move through your lungs. ´üÁ
- 11. ´üÁThank you A.AJITH Bsc.Microbiology. DMLT.,