Essential Features Of Maps ( class- 6 )
- 2. Maps ? A map is a symbolic representation of selected characteristics of a place, usually drawn on a flat surface. ? Two essential features of maps are: ? Title ? Direction
- 3. Title ? The map title tells us what kind of information is provided in it.
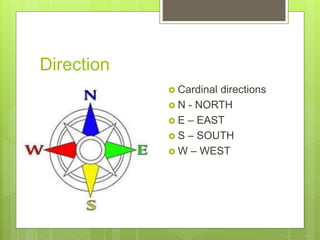
- 4. Direction ? Cardinal directions ? N - NORTH ? E ©C EAST ? S ©C SOUTH ? W ©C WEST
- 5. Intermediate directions ? The directions in between the cardinal directions are the intermediate directions. ? North-east(NE) ? North-west(NW) ? South-east(SE) ? South-west(SW)
- 6. Scale ? Verbal scale ? States the ratio ? One inch equal five miles ? Linear scale ? Helps in direct measurement. |---------|---------|---------| ? Representative fraction scale ? Shows as a ratio or fraction. 12:22 or 12/22 ? 1 inch (on the map)and 24000 inches (on the earth)
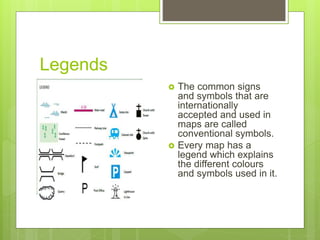
- 7. Legends ? The common signs and symbols that are internationally accepted and used in maps are called conventional symbols. ? Every map has a legend which explains the different colours and symbols used in it.
- 8. Geographical features ? River ? Meanders ? Tributaries ? Distributaries ? Delta ? Fold mountain ? Block mountain
- 9. River ? A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river.
- 10. Meanders ? A meander is a curve in a river. Meanders form a snake-like pattern as the river flows across a fairly flat valley floor. The position of the curves changes over time.
- 11. Tributaries ? A tributary is a river or stream that feeds into a larger body of water.
- 12. Distributaries ? A branch of a river that does not return to the main stream after leaving it.
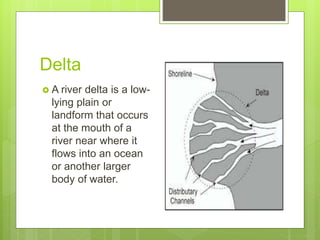
- 13. Delta ? A river delta is a low- lying plain or landform that occurs at the mouth of a river near where it flows into an ocean or another larger body of water.
- 14. Fold mountain ? Fold mountains are mountains that form mainly by the effects of folding on layers within the upper part of the Earth's crust.
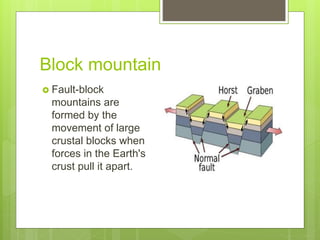
- 15. Block mountain ? Fault-block mountains are formed by the movement of large crustal blocks when forces in the Earth's crust pull it apart.
- 16. Grid ? A network formed by the criss-crossing of vertical and horizontal lines on a map or a globe to locate a place.
- 17. Two types of grid: ? Parallels of latitude: imaginary circular lines drawn horizontally between the two poles and parallel to each other. ? Meridians of longitude : imaginary lines drawn vertically from the north pole to south pole.