Accounting glossery word.docx
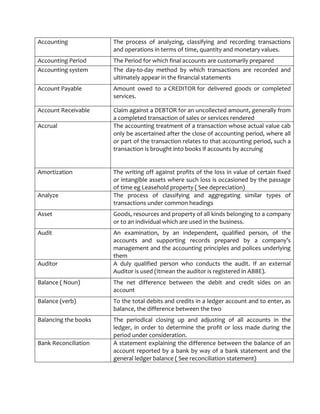
- 1. Accounting The process of analyzing, classifying and recording transactions and operations in terms of time, quantity and monetary values. Accounting Period The Period for which final accounts are customarily prepared Accounting system The day-to-day method by which transactions are recorded and ultimately appear in the financial statements Account Payable Amount owed to a CREDITOR for delivered goods or completed services. Account Receivable Claim against a DEBTOR for an uncollected amount, generally from a completed transaction of sales or services rendered Accrual The accounting treatment of a transaction whose actual value cab only be ascertained after the close of accounting period, where all or part of the transaction relates to that accounting period, such a transaction is brought into books if accounts by accruing Amortization The writing off against profits of the loss in value of certain fixed or intangible assets where such loss is occasioned by the passage of time eg Leasehold property ( See depreciation) Analyze The process of classifying and aggregating similar types of transactions under common headings Asset Goods, resources and property of all kinds belonging to a company or to an individual which are used in the business. Audit An examination, by an independent, qualified person, of the accounts and supporting records prepared by a company’s management and the accounting principles and polices underlying them Auditor A duly qualified person who conducts the audit. If an external Auditor is used (Itmean the auditor is registered in ABBE). Balance ( Noun) The net difference between the debit and credit sides on an account Balance (verb) To the total debits and credits in a ledger account and to enter, as balance, the difference between the two Balancing the books The periodical closing up and adjusting of all accounts in the ledger, in order to determine the profit or loss made during the period under consideration. Bank Reconciliation A statement explaining the difference between the balance of an account reported by a bank by way of a bank statement and the general ledger balance ( See reconciliation statement)
- 2. Book of Accounts A set of books, which record the business transactions of a firm, company, entity etc (See bookkeeping). Capital The money Supplied by the proprietors of a business in order to acquired the resources (assets) with which to operate the business Cash Book A book in which an account( record ) is kept of ll receipts and payments of money, by cash or cheque Cast ( Verb) To add up a column of figures Credit (noun) An entry on the right hand side of a ledger account Credit Note Document sent to a person, firm, etc stating that his account is credited( reduced) with the amount stated( eg when goods are returned by that person, firm etc or allowance is made to that person, firm etc) Creditor One to whom money is owned for goods , service etc Current Asset The group of assets in cash or near cash state (eg cash. Debtors, stock). Debit(Noun) An entry on theleft hand side of a ledger account Debit (verb) To debit an account to make an entry on the left hand side. Debit Note Document sent to a person , company etc stating that his account is debited (increased ) with the amount started (eg as a result of price change or invoice with an oversight error) Debtor One who owes money for goods, services supplied Depreciation The measure of the estimated loss in money value of a fixed asset owing to use, obsolescence or passage of time. Discount Allowance deducted from an invoice price, account etc Fixed Asset An asset which is in permanent use within a business 9eg Land, Building, furniture, plant, machinery, etc) as defined in an applicable accounting standard Intangible asset Asset, which is neither fixed nor current yet, possesses a value (eg Goodwill, investment). Inventory The stock—in-trade and work in progress, etc of a business as defined in an applicable accounting standard.
- 3. Invoice A documentary showing the character, quantity, price, terms, nature of delivery and other particulars of goods sold or services rendered Journal A collection of accounts Ledger The principal book of accounts In which the entries from all the other books are summarized divided into cash book, bought Ledger, sales Ledger and Nominal Ledger Ledger account A record in the ledger showing one of the two aspects of each transaction or groups of transactions( see also Account) Liabilities A term denoting the combined debt owed by an entity as defined by a applicable accounting standard Liquidity The excess cash or near cash assets over current liabilities Personal Account An account showing transactions with a particular person, firm or company as distinct from a nominal account. Petty Cash Book A book subsidiary to the cashbook, in which are recorded all small cash payments Posting The transfer of entries from the books of prime entry to their separate accounts in the ledgers Prepayment A payment made in the current accounting period of which part or all relates to a future period Profit & Loss Account A Summary account of all revenue and expense accounts showing as its balance, the profit(or loss) for the period under consideration Reconciliation A statement showing the process whereby the balance of two accounts, independently written up in respect of the same transactions, which show an apparent discrepancy, re brought into agreement, The most common reconciliation statement is that used to bring into agreement with the general ledger bank account balance and bank statement balance (see bank reconciliation) Revenue Income received from any source Sales Day Book A book of prime entry used to list, analyze and summarize all the invoices for credit sales transactions Sales Ledger A detailed list of items, on a properly headed working paper, totaled to agree with the figure that is being analyzed or supported and cross- referenced.
- 4. Schedule A detailed list of items, on a properly headed working paper, totaled to agree with the figure that is being analyzed or supported and cross-referenced.