Rhythm recognition
- 1. Rhythm Recognition Andey bin Rahman
- 2. Tachyarrhythmia Narrow complex Regular ? SVT ? Sinus tachycardia ? Atrial flutter ? Junctional rhythm Irregular ? Atrial fibrillation ? Atrial flutter with variable block ? Multifocal atrial tachycardia Wide complex Regular ? Ventricular tachycardia ? SVT with aberancy Irregular ? Atrial fibrillation with preexcitation ? AF with aberrancy ? Ventricullar fibrillation ? Torsades de pointes
- 4. Sinus Rhythm
- 6. Atrial Flutter Rate A: 300 V:<150 Rhythm Regular QRS Narrow Feature sawtooth
- 7. Supraventricular Tachycardia Rate >150 Rhythm Regular QRS Narrow Feature P not visible
- 8. Junctional rhythm Rate 40-60 Rhythm Regular QRS Narrow Feature P not visible, inverted or after QRS
- 9. Atrial fibrillation Rate A: 600 V:variable Rhythm irregular QRS Narrow Feature Irregularly irregular
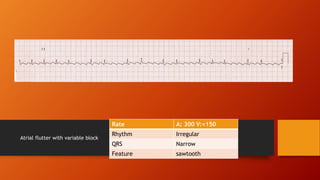
- 10. Atrial flutter with variable block Rate A: 300 V:<150 Rhythm Irregular QRS Narrow Feature sawtooth
- 11. Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Rate Variable Rhythm Irregular QRS Narrow Feature 3 or more P waves that differ in polarity (up/down), shape, and size
- 12. Wide complex
- 13. Ventricular Tachycardia Rate >150 Rhythm Regular QRS wide Feature No visible p
- 15. Ventricular fibrillation Rate Very fast Rhythm Irregular QRS bizarre Feature no recognizable P, QRS, or T waves
- 16. Torsades de pointes Rate V: 150-200 Rhythm Irregular QRS QRS complexes display ˇ°spindle-nodeˇ± pattern Feature no recognizable P &T waves, prolong QT before occurence
- 17. Bradyarrhythmia
- 18. Bradyarrhythmia Sinus Bradycardia 1st degree Heart block 2nd degree Heart block (Mobitz 1) 2nd degree Heart block (Mobitz 2) 3rd degree Heart block
- 20. 1st degree Heart block ? P-R Interval > 200msec (5 small box) ? No dropped beat
- 21. 2nd degree heart block , Mobitz 1 (Wenckebach) ? Progressive prolongation of P-R intervals ? P-P intervals constant ? Dropped beat ? PR interval is longest immediately before the dropped beat ? PR interval is shortest immediately after the dropped beat
- 22. 2nd degree HB Mobitz II ? Intermittent non-conducted P waves without progressive prolongation of the PR interval ? PR interval in the conducted beats remains constant ? P-P constant ? RR interval surrounding the dropped beat(s) is an exact multiple of the preceding RR interval
- 23. 3rd degree HB (complete HB) ? complete absence of AV conduction (AV dissociation) ? Perfusing rhythm is maintained by a junctional or ventricular escape rhythm
- 24. Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA) ? presence of coordinated electrical activity in myocardium but no detectable cardiac output ? formerly known as EMD (electromechanical dissociation)
- 25. Asystole
- 26. Arrest rhythm ? VF ? VT ? PEA ? Asystole
- 27. Thank you