Memory basic concept hierarchy and cache memory 1
Download as PPTX, PDF2 likes438 views
In these slides the basic concept of memory have been explained. Furthermore the concept of cache memory has also explained in detail with the add of animation so that readers may understand the concept easily.
1 of 21
Downloaded 31 times




















Recommended
Unit 3 ca-memory



Unit 3 ca-memoryBBDITM LUCKNOW
╠²
This document discusses memory technologies and hierarchy. It begins by distinguishing between the brain and memory, then outlines what will be covered, including memory technologies, hierarchical organization, locality principle, and memory design analysis. It covers semiconductor memory types like ROM, RAM, DRAM and flash. It describes the memory hierarchy from fastest/smallest to slowest/largest, and data transfer between levels. Locality principles of temporal and spatial are defined. Examples of direct mapped, set associative and fully associative caches are provided.The Happiness Advantage 



The Happiness Advantage Rosa Smith-Montanaro - Trainer, Career Coach, Recruiter
╠²
This was our topic for discussion last week. The Seven Principles of Happiness based on the book by Shawn Achor Semiconductor memories and auxiliary memories

Semiconductor memories and auxiliary memoriesAsif Iqbal
╠²
In these slides the concept of semiconductor memories have been explained in detail. With the clear dramatisation of CMOS logics. Auxiliary memories and its type have also been discussed.Powerpoint memory



Powerpoint memoryCMoondog
╠²
Memory has three main processes: sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Sensory memory only lasts a second, short-term memory lasts a few seconds unpracticed, and long-term memory can last a lifetime. There are five main types of memory: episodic, semantic, working, procedural, and implicit. Memories are not static but change over time based on beliefs and new information. Factors like stress, alcohol, head injuries, and PTSD can impact memory formation and recall.Memory Organization



Memory OrganizationKamal Acharya
╠²
This slide contain the introduction to memory , hierarchy, types, virtual memory,associative memory and cache memory.Memory



MemoryCMoondog
╠²
This document discusses different types of memory including short-term memory, long-term memory, procedural memory, priming memory, episodic memory, and semantic memory. It describes key aspects of memory such as encoding, storage, and retrieval. Different causes of memory loss are also outlined including alcohol blackout, dissociative fugue, Korsakoff's psychosis, post-traumatic amnesia, and repressed memory.Psychology Memory and Learning Power Point



Psychology Memory and Learning Power PointMrTimBradley
╠²
This document provides an overview of memory and learning concepts. It discusses the three stages of memory (encoding, storage, and retrieval). It describes the different types of memory like sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. It also discusses how learning occurs through classical and operant conditioning, and how cognitive factors like latent learning, cognitive maps, insight, learned helplessness, and observational learning impact the learning process. Key terms and concepts related to memory and different types of learning are defined and explained with examples.Human Memory (Psychology)



Human Memory (Psychology)Shara Mae Reloj
╠²
Sensory memory briefly stores perceptions and passes them to short-term memory. Short-term memory stores recently acquired information through working memory. Long-term memory securely stores information for long periods through explicit (declarative) memory of facts and episodic memory of experiences, and implicit (procedural) memory of skills. The three processes of memory are encoding, which converts information into a storable form; storage, where information resides in the brain over time; and retrieval, where the brain recalls previously learned information.Memory powerpoint



Memory powerpointCMoondog
╠²
1) The document discusses memory formation and processes in the human brain.
2) It explains that memory is encoded, stored, and recalled throughout the entire brain in bits and pieces.
3) The main processes of memory include encoding specific networks of neurons that are triggered by conscious or random stimuli to recall experiences.Memory PowerPoint



Memory PowerPointKRyder
╠²
Memory is the capacity to retain and retrieve information. There are three main types of memory - sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Memories can be implicit (unconscious) or explicit (conscious recollection). Factors like rehearsal, encoding, interference and state-dependence affect how and what we remember versus forget over time. Recovered memories from early childhood or recovered through suggestive techniques should be questioned due to concerns over accuracy.Human Memory - Psychology



Human Memory - PsychologyRyan Braganza
╠²
There are three main types of memory: sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Memory theories propose that information is encoded, stored, and retrieved in different stages. The most widely accepted theory is the information processing theory proposed by Atkinson and Shiffrin, which describes a multi-stage model of memory involving input, sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Better processing and elaboration of information leads to stronger long-term memories according to levels of processing theories.Psychology- Memory



Psychology- MemoryMya007
╠²
1. The multi-store model of memory proposes that memory consists of three main stores: sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory.
2. Sensory memory briefly stores sensory information, short-term memory can hold information for seconds to minutes, and long-term memory stores information indefinitely.
3. The working memory model updated the multi-store model by proposing two slave systems - the phonological loop and visuospatial sketchpad - that actively maintain information in short-term memory under the control of a central executive.Introductory Psychology: Memory



Introductory Psychology: MemoryBrian Piper
╠²
lecture 20 from a college level introduction to psychology course taught Fall 2011 by Brian J. Piper, Ph.D. (psy391@gmail.com) at Willamette University, Loftus, eyewitness memoryRaspberryPI PPT WITH ALL THE DETAILS OF PROGRAMMING



RaspberryPI PPT WITH ALL THE DETAILS OF PROGRAMMINGAsif Iqbal
╠²
RaspberryPI PPT WITH ALL THE DETAILS OF PROGRAMMING first day presentation related to iot.pptx



first day presentation related to iot.pptxAsif Iqbal
╠²
gsdfgsfdgdsfgdfgfgsfdgdfgsgdfsgsfdgdfsgdfsgdsfgssdfgfdsgsfgsfgfsdgdfgsdfgsdfgdfsgfddffdgdfgdsfgdfgdfgfdgsgsdfgsfgdfsgfgdb smb s fs d bvcb s fgsdfg fsdfgsd5415Microprocessor-Lecture-11.pdf



5415Microprocessor-Lecture-11.pdfAsif Iqbal
╠²
THIS IS NOT MY PRESENTATION..THE NAME OF THE AUTHOER IS MENTIONED IN THE PPT. I M JUST UPLOADING IT TO DOWNLOAD THE CONTNET11815939.ppt



11815939.pptAsif Iqbal
╠²
This document describes the design of small directive antennas for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. It outlines the introduction to IoT and wireless sensor networks (WSN), discusses antenna theory including common parameters and array designs, and presents the practical work done to design directive antennas operating at 868MHz and 2400MHz. Miniaturization techniques were used to reduce the antenna size. The results showed the designed antennas met requirements for gain, front-to-back ratio, and matching while providing knowledge in IoT, WSN, antenna fundamentals, and design optimization software.Chandrayaan 3.pptx



Chandrayaan 3.pptxAsif Iqbal
╠²
Chandrayaan-3 is India's third lunar mission to soft land on the lunar south pole region in order to conduct scientific experiments studying the lunar geology, atmosphere, and environment. The mission objectives are to demonstrate a safe soft landing on the lunar surface, conduct rover operations, and on-site surface experiments. Chandrayaan-3 was successfully launched on July 14, 2023 and is expected to land on the lunar surface between August 23-24, 2023. The mission advances India's space exploration capabilities and promotes international cooperation in space.Memory unit 6



Memory unit 6Asif Iqbal
╠²
In this presentation, all kind of computer Memories are explained.
These PPTs are better presentable in ║▌║▌▀Ż Show, that's not possible here, the Explanatory Videos are available at
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCaVNvNzkb01ZMT1GDeITM9winstruction 



instruction Asif Iqbal
╠²
these presentations covers the second unit of NCS- 505 Computer Architecture, taught in CSE third year of AKTU affiliated colleges. OPTICAL COMMUNICATION Unit 5



OPTICAL COMMUNICATION Unit 5Asif Iqbal
╠²
The document discusses digital transmission systems and coherent optical communications. It covers the following key points:
1) It describes the components and operation of optical receivers, including the challenges of detecting weak signals and making decisions on transmitted data. Error sources like intersymbol interference are also discussed.
2) Bit error rate and probability of error are defined, and formulas for calculating BER under Gaussian noise are provided.
3) Eye diagrams are introduced as a way to visualize signal quality over time. Factors like timing jitter and noise amplitude are described.
4) Coherent optical receivers are overviewed, including their advantages for high data rates and constellations. Challenges in carrier recovery using optical phase-lockedOPTICAL COMMUNICATION Unit 4



OPTICAL COMMUNICATION Unit 4Asif Iqbal
╠²
The document discusses optical coupling between light sources and optical fibers. It defines coupling efficiency as the ratio of power coupled into the fiber to power emitted from the source. Radiance and radiation patterns of different light sources are described. Expressions are provided for calculating the power coupled from a source to a fiber based on the source and fiber parameters. Methods to improve coupling efficiency such as lensing are also discussed. The document also covers topics like fiber-to-fiber coupling loss, mechanical misalignment loss, and fiber end defects.optical communication Unit 3



optical communication Unit 3Asif Iqbal
╠²
Optical sources convert electrical signals to optical signals for data transmission through fiber optic cables. They include LEDs, ELEDs, SLEDs, and laser diodes (LDs). LEDs produce incoherent light while laser diodes produce coherent light. Incoherent light sources are used for multimode fiber systems while laser diodes are used for single mode systems. Laser diodes must operate above the lasing threshold to produce coherent light, otherwise they function as ELEDs. Tunable lasers can produce coherent light of a controlled variable wavelength, allowing them to replace multiple light sources in multi-wavelength transmission systems.OPTICAL COMMUNICATION Unit 2



OPTICAL COMMUNICATION Unit 2Asif Iqbal
╠²
This document discusses optical waveguides and fiber optic modes. It begins by describing the mode patterns seen in the end faces of small diameter fibers. It then discusses multimode propagation and explains that many modes are excited, resulting in complex field and intensity patterns. Finally, it summarizes the key parameters and solutions used to determine the modes in cylindrical optical fibers.OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION UNIT-1



OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION UNIT-1Asif Iqbal
╠²
This document provides information about light propagation through optical fibers. It begins by defining an optical fiber as a cylindrical waveguide made of glass that uses total internal reflection to transmit light. It then discusses the fiber's core and cladding layers and the conditions needed for total internal reflection. The key points covered include:
- Light propagation is guided through the fiber core by total internal reflection at the core-cladding interface.
- Only rays entering the fiber core within the acceptance angle will continue propagating through total internal reflection.
- Electromagnetic mode theory is needed to fully understand light propagation in fibers. Discrete modes exist that are solutions to Maxwell's equations.
- The evanescent field that penetrates the clSynchronous Sequential Logic Unit 4



Synchronous Sequential Logic Unit 4Asif Iqbal
╠²
These slides contain the basic of sequential logic, and includes a detailed and animated description of Flip-Flop and latches, it includes shift registers and counters also. It covers the fourth unit of Digital Logic DesignMore Related Content
Viewers also liked (8)
Memory



MemoryCMoondog
╠²
This document discusses different types of memory including short-term memory, long-term memory, procedural memory, priming memory, episodic memory, and semantic memory. It describes key aspects of memory such as encoding, storage, and retrieval. Different causes of memory loss are also outlined including alcohol blackout, dissociative fugue, Korsakoff's psychosis, post-traumatic amnesia, and repressed memory.Psychology Memory and Learning Power Point



Psychology Memory and Learning Power PointMrTimBradley
╠²
This document provides an overview of memory and learning concepts. It discusses the three stages of memory (encoding, storage, and retrieval). It describes the different types of memory like sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. It also discusses how learning occurs through classical and operant conditioning, and how cognitive factors like latent learning, cognitive maps, insight, learned helplessness, and observational learning impact the learning process. Key terms and concepts related to memory and different types of learning are defined and explained with examples.Human Memory (Psychology)



Human Memory (Psychology)Shara Mae Reloj
╠²
Sensory memory briefly stores perceptions and passes them to short-term memory. Short-term memory stores recently acquired information through working memory. Long-term memory securely stores information for long periods through explicit (declarative) memory of facts and episodic memory of experiences, and implicit (procedural) memory of skills. The three processes of memory are encoding, which converts information into a storable form; storage, where information resides in the brain over time; and retrieval, where the brain recalls previously learned information.Memory powerpoint



Memory powerpointCMoondog
╠²
1) The document discusses memory formation and processes in the human brain.
2) It explains that memory is encoded, stored, and recalled throughout the entire brain in bits and pieces.
3) The main processes of memory include encoding specific networks of neurons that are triggered by conscious or random stimuli to recall experiences.Memory PowerPoint



Memory PowerPointKRyder
╠²
Memory is the capacity to retain and retrieve information. There are three main types of memory - sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Memories can be implicit (unconscious) or explicit (conscious recollection). Factors like rehearsal, encoding, interference and state-dependence affect how and what we remember versus forget over time. Recovered memories from early childhood or recovered through suggestive techniques should be questioned due to concerns over accuracy.Human Memory - Psychology



Human Memory - PsychologyRyan Braganza
╠²
There are three main types of memory: sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Memory theories propose that information is encoded, stored, and retrieved in different stages. The most widely accepted theory is the information processing theory proposed by Atkinson and Shiffrin, which describes a multi-stage model of memory involving input, sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Better processing and elaboration of information leads to stronger long-term memories according to levels of processing theories.Psychology- Memory



Psychology- MemoryMya007
╠²
1. The multi-store model of memory proposes that memory consists of three main stores: sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory.
2. Sensory memory briefly stores sensory information, short-term memory can hold information for seconds to minutes, and long-term memory stores information indefinitely.
3. The working memory model updated the multi-store model by proposing two slave systems - the phonological loop and visuospatial sketchpad - that actively maintain information in short-term memory under the control of a central executive.Introductory Psychology: Memory



Introductory Psychology: MemoryBrian Piper
╠²
lecture 20 from a college level introduction to psychology course taught Fall 2011 by Brian J. Piper, Ph.D. (psy391@gmail.com) at Willamette University, Loftus, eyewitness memoryMore from Asif Iqbal (20)
RaspberryPI PPT WITH ALL THE DETAILS OF PROGRAMMING



RaspberryPI PPT WITH ALL THE DETAILS OF PROGRAMMINGAsif Iqbal
╠²
RaspberryPI PPT WITH ALL THE DETAILS OF PROGRAMMING first day presentation related to iot.pptx



first day presentation related to iot.pptxAsif Iqbal
╠²
gsdfgsfdgdsfgdfgfgsfdgdfgsgdfsgsfdgdfsgdfsgdsfgssdfgfdsgsfgsfgfsdgdfgsdfgsdfgdfsgfddffdgdfgdsfgdfgdfgfdgsgsdfgsfgdfsgfgdb smb s fs d bvcb s fgsdfg fsdfgsd5415Microprocessor-Lecture-11.pdf



5415Microprocessor-Lecture-11.pdfAsif Iqbal
╠²
THIS IS NOT MY PRESENTATION..THE NAME OF THE AUTHOER IS MENTIONED IN THE PPT. I M JUST UPLOADING IT TO DOWNLOAD THE CONTNET11815939.ppt



11815939.pptAsif Iqbal
╠²
This document describes the design of small directive antennas for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. It outlines the introduction to IoT and wireless sensor networks (WSN), discusses antenna theory including common parameters and array designs, and presents the practical work done to design directive antennas operating at 868MHz and 2400MHz. Miniaturization techniques were used to reduce the antenna size. The results showed the designed antennas met requirements for gain, front-to-back ratio, and matching while providing knowledge in IoT, WSN, antenna fundamentals, and design optimization software.Chandrayaan 3.pptx



Chandrayaan 3.pptxAsif Iqbal
╠²
Chandrayaan-3 is India's third lunar mission to soft land on the lunar south pole region in order to conduct scientific experiments studying the lunar geology, atmosphere, and environment. The mission objectives are to demonstrate a safe soft landing on the lunar surface, conduct rover operations, and on-site surface experiments. Chandrayaan-3 was successfully launched on July 14, 2023 and is expected to land on the lunar surface between August 23-24, 2023. The mission advances India's space exploration capabilities and promotes international cooperation in space.Memory unit 6



Memory unit 6Asif Iqbal
╠²
In this presentation, all kind of computer Memories are explained.
These PPTs are better presentable in ║▌║▌▀Ż Show, that's not possible here, the Explanatory Videos are available at
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCaVNvNzkb01ZMT1GDeITM9winstruction 



instruction Asif Iqbal
╠²
these presentations covers the second unit of NCS- 505 Computer Architecture, taught in CSE third year of AKTU affiliated colleges. OPTICAL COMMUNICATION Unit 5



OPTICAL COMMUNICATION Unit 5Asif Iqbal
╠²
The document discusses digital transmission systems and coherent optical communications. It covers the following key points:
1) It describes the components and operation of optical receivers, including the challenges of detecting weak signals and making decisions on transmitted data. Error sources like intersymbol interference are also discussed.
2) Bit error rate and probability of error are defined, and formulas for calculating BER under Gaussian noise are provided.
3) Eye diagrams are introduced as a way to visualize signal quality over time. Factors like timing jitter and noise amplitude are described.
4) Coherent optical receivers are overviewed, including their advantages for high data rates and constellations. Challenges in carrier recovery using optical phase-lockedOPTICAL COMMUNICATION Unit 4



OPTICAL COMMUNICATION Unit 4Asif Iqbal
╠²
The document discusses optical coupling between light sources and optical fibers. It defines coupling efficiency as the ratio of power coupled into the fiber to power emitted from the source. Radiance and radiation patterns of different light sources are described. Expressions are provided for calculating the power coupled from a source to a fiber based on the source and fiber parameters. Methods to improve coupling efficiency such as lensing are also discussed. The document also covers topics like fiber-to-fiber coupling loss, mechanical misalignment loss, and fiber end defects.optical communication Unit 3



optical communication Unit 3Asif Iqbal
╠²
Optical sources convert electrical signals to optical signals for data transmission through fiber optic cables. They include LEDs, ELEDs, SLEDs, and laser diodes (LDs). LEDs produce incoherent light while laser diodes produce coherent light. Incoherent light sources are used for multimode fiber systems while laser diodes are used for single mode systems. Laser diodes must operate above the lasing threshold to produce coherent light, otherwise they function as ELEDs. Tunable lasers can produce coherent light of a controlled variable wavelength, allowing them to replace multiple light sources in multi-wavelength transmission systems.OPTICAL COMMUNICATION Unit 2



OPTICAL COMMUNICATION Unit 2Asif Iqbal
╠²
This document discusses optical waveguides and fiber optic modes. It begins by describing the mode patterns seen in the end faces of small diameter fibers. It then discusses multimode propagation and explains that many modes are excited, resulting in complex field and intensity patterns. Finally, it summarizes the key parameters and solutions used to determine the modes in cylindrical optical fibers.OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION UNIT-1



OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION UNIT-1Asif Iqbal
╠²
This document provides information about light propagation through optical fibers. It begins by defining an optical fiber as a cylindrical waveguide made of glass that uses total internal reflection to transmit light. It then discusses the fiber's core and cladding layers and the conditions needed for total internal reflection. The key points covered include:
- Light propagation is guided through the fiber core by total internal reflection at the core-cladding interface.
- Only rays entering the fiber core within the acceptance angle will continue propagating through total internal reflection.
- Electromagnetic mode theory is needed to fully understand light propagation in fibers. Discrete modes exist that are solutions to Maxwell's equations.
- The evanescent field that penetrates the clSynchronous Sequential Logic Unit 4



Synchronous Sequential Logic Unit 4Asif Iqbal
╠²
These slides contain the basic of sequential logic, and includes a detailed and animated description of Flip-Flop and latches, it includes shift registers and counters also. It covers the fourth unit of Digital Logic DesignCombinational Logic Unit 2



Combinational Logic Unit 2Asif Iqbal
╠²
The document discusses multiplexers, encoders, and decoders. It can be summarized as follows:
1) A multiplexer has N control inputs and 2^N data inputs, and selects one of the data inputs to pass to its single output based on the state of the control inputs.
2) Encoders convert numeric inputs into binary codes, while decoders convert binary codes into a single numeric output.
3) Common encoders include binary-coded decimal encoders that convert decimal numbers into 4-bit BCD codes to represent each digit.Unit-1 Digital Design and Binary Numbers:



Unit-1 Digital Design and Binary Numbers:Asif Iqbal
╠²
these slides contains general discerption about digital signals, binary numbers, digital numbers, and basic logic gates. it covers the first unit of AKTU syllabus. voltage regulater



voltage regulaterAsif Iqbal
╠²
These slides contain a descriptive and animated presentation of voltage regulators, in order to let the students understand the thing better. special diode



special diodeAsif Iqbal
╠²
The document discusses different types of special-purpose diodes used in electronics. It explains the construction and working of n-type and p-type semiconductors by doping silicon with different impurity atoms. The depletion region that forms when an n-type and p-type material are joined is also described. Different diodes are then explained, including light-emitting diodes, varactor diodes, tunnel diodes, Schottky barrier diodes, and photodiodes. Their key characteristics and applications are provided in brief. Circuit diagrams demonstrate how diodes can be used as switches and in tuning networks.oscillator unit 3 



oscillator unit 3 Asif Iqbal
╠²
these slides contain basic principal of oscillators, and a brief discussion of various type of oscillatorsNunit 2 feedback



Nunit 2 feedbackAsif Iqbal
╠²
these slides discuss the basic properties of negative feedback, with example of basic feedback amplifiers. Recently uploaded (20)
Industrial Valves, Instruments Products Profile



Industrial Valves, Instruments Products Profilezebcoeng
╠²
WeŌĆÖre excited to share our product profile, showcasing our expertise in Industrial Valves, Instrumentation, and Hydraulic & Pneumatic Solutions.
We also supply API-approved valves from globally trusted brands, ensuring top-notch quality and internationally certified solutions. LetŌĆÖs explore valuable business opportunities together!
We specialize in:
ŌĆó Industrial Valves (Gate, Globe, Ball, Butterfly, Check)
ŌĆó Instrumentation (Pressure Gauges, Transmitters, Flow Meters)
ŌĆó Pneumatic Products (Cylinders, Solenoid Valves, Fittings)
As authorized partners of trusted global brands, we deliver high-quality solutions tailored to meet your industrial needs with seamless support.decarbonization steel industry rev1.pptx



decarbonization steel industry rev1.pptxgonzalezolabarriaped
╠²
Webinar Decarbonization steel industryStructural QA/QC Inspection in KRP 401600 | Copper Processing Plant-3 (MOF-3)...



Structural QA/QC Inspection in KRP 401600 | Copper Processing Plant-3 (MOF-3)...slayshadow705
╠²
This presentation provides an in-depth analysis of structural quality control in the KRP 401600 section of the Copper Processing Plant-3 (MOF-3) in Uzbekistan. As a Structural QA/QC Inspector, I have identified critical welding defects, alignment issues, bolting problems, and joint fit-up concerns.
Key topics covered:
Ō£ö Common Structural Defects ŌĆō Welding porosity, misalignment, bolting errors, and more.
Ō£ö Root Cause Analysis ŌĆō Understanding why these defects occur.
Ō£ö Corrective & Preventive Actions ŌĆō Effective solutions to improve quality.
Ō£ö Team Responsibilities ŌĆō Roles of supervisors, welders, fitters, and QC inspectors.
Ō£ö Inspection & Quality Control Enhancements ŌĆō Advanced techniques for defect detection.
¤ōī Applicable Standards: GOST, KMK, SNK ŌĆō Ensuring compliance with international quality benchmarks.
¤ÜĆ This presentation is a must-watch for:
Ō£ģ QA/QC Inspectors, Structural Engineers, Welding Inspectors, and Project Managers in the construction & oil & gas industries.
Ō£ģ Professionals looking to improve quality control processes in large-scale industrial projects.
¤ōó Download & share your thoughts! Let's discuss best practices for enhancing structural integrity in industrial projects.
Categories:
Engineering
Construction
Quality Control
Welding Inspection
Project Management
Tags:
#QAQC #StructuralInspection #WeldingDefects #BoltingIssues #ConstructionQuality #Engineering #GOSTStandards #WeldingInspection #QualityControl #ProjectManagement #MOF3 #CopperProcessing #StructuralEngineering #NDT #OilAndGasAI, Tariffs and Supply Chains in Knowledge Graphs



AI, Tariffs and Supply Chains in Knowledge GraphsMax De Marzi
╠²
How tarrifs, supply chains and knowledge graphs combine.Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdf



Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdfWater Industry Process Automation & Control
╠²
Welcome to the March 2025 issue of WIPAC Monthly the magazine brought to you by the LinkedIn Group WIPAC Monthly.
In this month's edition, on top of the month's news from the water industry we cover subjects from the intelligent use of wastewater networks, the use of machine learning in water quality as well as how, we as an industry, need to develop the skills base in developing areas such as Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence.
Enjoy the latest editionUS Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...



US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...Thane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
╠²
Preface: The ReGenX Generator innovation operates with a US Patented Frequency Dependent Load Current Delay which delays the creation and storage of created Electromagnetic Field Energy around the exterior of the generator coil. The result is the created and Time Delayed Electromagnetic Field Energy performs any magnitude of Positive Electro-Mechanical Work at infinite efficiency on the generator's Rotating Magnetic Field, increasing its Kinetic Energy and increasing the Kinetic Energy of an EV or ICE Vehicle to any magnitude without requiring any Externally Supplied Input Energy. In Electricity Generation applications the ReGenX Generator innovation now allows all electricity to be generated at infinite efficiency requiring zero Input Energy, zero Input Energy Cost, while producing zero Greenhouse Gas Emissions, zero Air Pollution and zero Nuclear Waste during the Electricity Generation Phase. In Electric Motor operation the ReGen-X Quantum Motor now allows any magnitude of Work to be performed with zero Electric Input Energy.
Demonstration Protocol: The demonstration protocol involves three prototypes;
1. Protytpe #1, demonstrates the ReGenX Generator's Load Current Time Delay when compared to the instantaneous Load Current Sine Wave for a Conventional Generator Coil.
2. In the Conventional Faraday Generator operation the created Electromagnetic Field Energy performs Negative Work at infinite efficiency and it reduces the Kinetic Energy of the system.
3. The Magnitude of the Negative Work / System Kinetic Energy Reduction (in Joules) is equal to the Magnitude of the created Electromagnetic Field Energy (also in Joules).
4. When the Conventional Faraday Generator is placed On-Load, Negative Work is performed and the speed of the system decreases according to Lenz's Law of Induction.
5. In order to maintain the System Speed and the Electric Power magnitude to the Loads, additional Input Power must be supplied to the Prime Mover and additional Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft.
6. For example, if 100 Watts of Electric Power is delivered to the Load by the Faraday Generator, an additional >100 Watts of Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft by the Prime Mover.
7. If 1 MW of Electric Power is delivered to the Load by the Faraday Generator, an additional >1 MW Watts of Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft by the Prime Mover.
8. Generally speaking the ratio is 2 Watts of Mechanical Input Power to every 1 Watt of Electric Output Power generated.
9. The increase in Drive Shaft Mechanical Input Power is provided by the Prime Mover and the Input Energy Source which powers the Prime Mover.
10. In the Heins ReGenX Generator operation the created and Time Delayed Electromagnetic Field Energy performs Positive Work at infinite efficiency and it increases the Kinetic Energy of the system.Unit II: Design of Static Equipment Foundations



Unit II: Design of Static Equipment FoundationsSanjivani College of Engineering, Kopargaon
╠²
Design of Static Equipment, that is vertical vessels foundation.How to Build a Maze Solving Robot Using Arduino



How to Build a Maze Solving Robot Using ArduinoCircuitDigest
╠²
Learn how to make an Arduino-powered robot that can navigate mazes on its own using IR sensors and "Hand on the wall" algorithm.
This step-by-step guide will show you how to build your own maze-solving robot using Arduino UNO, three IR sensors, and basic components that you can easily find in your local electronics shop.Wireless-Charger presentation for seminar .pdf



Wireless-Charger presentation for seminar .pdfAbhinandanMishra30
╠²
Wireless technology used in chargerIntegration of Additive Manufacturing (AM) with IoT : A Smart Manufacturing A...



Integration of Additive Manufacturing (AM) with IoT : A Smart Manufacturing A...ASHISHDESAI85
╠²
Combining 3D printing with Internet of Things (IoT) enables the creation of smart, connected, and customizable objects that can monitor, control, and optimize their performance, potentially revolutionizing various industries. oT-enabled 3D printers can use sensors to monitor the quality of prints during the printing process. If any defects or deviations from the desired specifications are detected, the printer can adjust its parameters in real time to ensure that the final product meets the required standards.google_developer_group_ramdeobaba_university_EXPLORE_PPT



google_developer_group_ramdeobaba_university_EXPLORE_PPTJayeshShete1
╠²
EXPLORE 6 EXCITING DOMAINS:
1. Machine Learning: Discover the world of AI and ML!
2. App Development: Build innovative mobile apps!
3. Competitive Programming: Enhance your coding skills!
4. Web Development: Create stunning web applications!
5. Blockchain: Uncover the power of decentralized tech!
6. Cloud Computing: Explore the world of cloud infrastructure!
Join us to unravel the unexplored, network with like-minded individuals, and dive into the world of tech!Air pollution is contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any ch...



Air pollution is contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any ch...dhanashree78
╠²
Air pollution is contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere.
Household combustion devices, motor vehicles, industrial facilities and forest fires are common sources of air pollution. Pollutants of major public health concern include particulate matter, carbon monoxide, ozone, nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide. Outdoor and indoor air pollution cause respiratory and other diseases and are important sources of morbidity and mortality.
WHO data show that almost all of the global population (99%) breathe air that exceeds WHO guideline limits and contains high levels of pollutants, with low- and middle-income countries suffering from the highest exposures.
Air quality is closely linked to the earthŌĆÖs climate and ecosystems globally. Many of the drivers of air pollution (i.e. combustion of fossil fuels) are also sources of greenhouse gas emissions. Policies to reduce air pollution, therefore, offer a win-win strategy for both climate and health, lowering the burden of disease attributable to air pollution, as well as contributing to the near- and long-term mitigation of climate change.
Env and Water Supply Engg._Dr. Hasan.pdf



Env and Water Supply Engg._Dr. Hasan.pdfMahmudHasan747870
╠²
Core course, namely Environment and Water Supply Engineering. Full lecture notes are in book format for the BSc in Civil Engineering program. Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdf



Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdfWater Industry Process Automation & Control
╠²
US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...



US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...Thane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
╠²
Memory basic concept hierarchy and cache memory 1
- 1. MEMORY UNIT-3 Mohammad Asif Iqbal Assistant Professor, Deptt of ECE, JETGI, Barabanki
- 3. WHAT WE WILL LEARN IN THIS LECTURE ’ü▒Memory technologies ’ü▒Hierarchal organization ’ü▒Principle of locality ’ü▒Analysis of hierarchy ’ü▒Simple case organizations
- 4. TYPICAL SPECIFICATIONS OF COMPUTERS TODAY
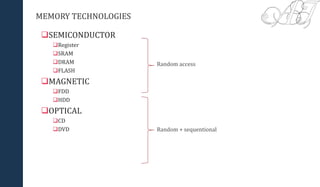
- 5. MEMORY TECHNOLOGIES ’ü▒SEMICONDUCTOR ’ü▒Register ’ü▒SRAM ’ü▒DRAM ’ü▒FLASH ’ü▒MAGNETIC ’ü▒FDD ’ü▒HDD ’ü▒OPTICAL ’ü▒CD ’ü▒DVD Random access Random + sequentional
- 6. HIERARCHAL STRUCTURE SPEED CPU SIZE COST/ BIT Fastest Memory Slowest Highest Fastest Memory Memory Biggest Lowest
- 7. DATA TRANSFER BETWEEN LEVELS
- 8. PRINCIPLE OF LOCALITY ’ü▒Temporal locality ’ü▒References repeated in time ’ü▒The concept that a resource that is referenced at one point in time will be referenced again sometime in the near future. ’ü▒Spatial locality ’ü▒Reference repeated in space ’ü▒Special case: sequential locality ’ü▒The concept that likelihood of referencing a resource is higher if a resource near it was just referenced.
- 10. CACHE ACCESS EXAMPLE. Before the reference to Xn After the reference to Xn X4 X4 X1 X1 Xn-2 Xn-2 Xn-1 Xn-1 X2 X2 X3 X3
- 13. CACHE WITH 4 WORD BLOCKS
- 14. QUESTIONS MM SIZE CACHE SIZE BLOCK SIZE TAG BITS TAG DIRECTOR Y 128 KB 16KB 256 B ------- ------- 32 GB 32KB 1KB ------- ------- ------- 512 KB 1 KB 7 -------
- 15. MORE FLEXIBLE BLOCK ARRANGEMENT
- 16. FULLY ASSOCIATIVE CACHE Question:- MM:- 32 GB BLOCK:- 32 KB TAG= ? Propagation Delay Of Comparator=10 K ns PD of OR Gate= 10 ns HL=?
- 17. SET ASSOCIATIVE CACHE MM SIZE CACHE SIZE BLOCK SIZE TAG BITS TAG DIRESTOR Y SET ASSOCIATIV E 128 KB 16KB 256B ----- ----- 2-WAY 32GB 32KB 1KB ----- ----- 4-WAY ----- 512KB 1KB 7 ------ 8-WAY
- 18. 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 52 53 54 55 40 41 42 43 12 13 14 15 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 01 11 10 00 01 00 11 01 11 11 11 01 01 10 10 11 MORE EXAMPLE OF DIRECT MAPPING TAG LINE BO
- 19. MORE EXAMPLE OF SET ASSOCIATIVE MAPPING 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0,4 1,5 2,6 3,7 TAG SET BO
- 20. MORE EXAMPLE OF FULLY ASSOCIATIVE MAPPING 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 TAG BO
- 21. THANK YOU!
Editor's Notes
- #3: ŌĆ£Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) studies artificial systems that take inspiration from the behavior of real ant colonies and which are used to solve discrete optimization problems.ŌĆØ











