Cardiovascular system
Download as pptx, pdf2 likes70 views
Cardiovascular system presented by pradeep banjare from apollo college of pharmacy anjora, durg
1 of 30
Download to read offline









Ad
Recommended
tobacoo 792013edit.pptx
tobacoo 792013edit.pptxPradeep Banjare
╠²
Tobacco has killed over 60 million people in developed countries since 1950, more than died in World War II. If current trends continue, tobacco will kill over 100 million people in the first two decades of the 21st century and 500 million people alive today. Tobacco kills over 1,200 people per day in the country from various cancers, respiratory and heart diseases. Quitting smoking has immediate and long term health benefits as risks of cancers and heart disease drop significantly within a few years of quitting. Tobacco contains over 4,000 chemicals, including 40 known cancer-causing agents and is highly addictive due to nicotine.Reasoning practice-book for SSC exam preparation
Reasoning practice-book for SSC exam preparationPradeep Banjare
╠²
The document presents a classification and analogy reasoning test, which assesses the ability to differentiate items or identify relationships based on common qualities or characteristics among groups. It includes various types of questions, such as word classification, alphabet classification, and number classification, along with answers and explanations for each question. It also contains sections for training on analogies, noting various relationships between workers and products, tools, actions, and materials.General science
General science Pradeep Banjare
╠²
The document appears to be a repetitive mention of 'scanned by camscanner,' indicating that it may contain numerous scanned pages or images but lacks substantive content or coherent information.GK FOR SSC EXAM PREPARATION 2
GK FOR SSC EXAM PREPARATION 2Pradeep Banjare
╠²
GK FOR SSC EXAM PREPARATION 2
Presented by pradeep banjare
from apollo college of pharmacy anjora, durgGK FOR SSC EXAM PREPARATION 1
GK FOR SSC EXAM PREPARATION 1Pradeep Banjare
╠²
9000+ question hindi
presented by pradeep banjare
from apollo collge of pharmacy anjora, durgUrinary system
Urinary systemPradeep Banjare
╠²
The urinary system, also known as the renal system or urinary tract, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. It eliminates waste from the body, regulates blood volume and pressure, and controls electrolyte and metabolite levels to maintain blood pH.Respiratory system
Respiratory system Pradeep Banjare
╠²
Respiratory system
presented by pradeep banjare
from apollo college of pharmacy anjora, durgAlkaloids
AlkaloidsPradeep Banjare
╠²
This document discusses two methods of classifying alkaloids: biosynthetic classification and chemical classification. Biosynthetic classification is based on the precursor compounds that alkaloids are derived from during plant biosynthesis, such as tryptophan, lysine, ornithine, and tyrosine. Chemical classification is based on the presence of the basic heterocyclic nucleus and lists examples of alkaloid classes including piperidine, pyrrolidine, quinoline, isoquinoline, indole, and steroidal alkaloids.Phamakokinetics & pharmacodynamics
Phamakokinetics & pharmacodynamicsPradeep Banjare
╠²
The document is a collection of multiple-choice questions and answers focusing on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics for exam preparation in pharmacy. It covers various aspects of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and mechanisms of action, along with key terminology relevant to the field. Additionally, it includes questions on drug interactions and effects related to dose response.Phamacology mcq 2
Phamacology mcq 2Pradeep Banjare
╠²
This document provides a list of 30 multiple choice pharmacology questions along with answers about various drugs and their properties. It also includes a short self-assessment section with 5 additional multiple choice questions. The questions cover topics such as antibiotics, antifungals, anticancer drugs, antimalarials, endocrine pharmacology, and more. The document is presented by Pradeep Banjare from Apollo College of Pharmacy in Durg, India as a study aid and exam preparation for pharmacology.Top 100 pharmacology mcq & ans
Top 100 pharmacology mcq & ansPradeep Banjare
╠²
The document contains a collection of 100 multiple choice questions and answers focusing on pharmacology principles, drug interactions, metabolism, and therapeutic monitoring. It covers key topics such as drug absorption, protein binding, first-pass metabolism, and the effects of various drugs on the body, along with examples and exceptions. This compilation serves as a resource for students and professionals in the field of pharmacology to assess their knowledge and understanding.Digestive system
Digestive system Pradeep Banjare
╠²
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract and accessory organs including the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder. The digestive system works to convert food into energy and nutrients through a multi-step process beginning in the mouth and involving the breakdown of food and absorption of nutrients through a long tube called the alimentary canal before the excretion of wastes. Key functions include ingestion, secretion, mixing, digestion, absorption, and excretion to process food through the body.Gpate & pharmacist Sort note
Gpate & pharmacist Sort notePradeep Banjare
╠²
Bacteria are single-celled organisms that can be inhibited through the use of vaccines. Pradeep Banjare from Apollo College of Pharmacy in Durg presented information on bacterial cells and inhibitors. Vaccines can help inhibit bacteria and prevent the spread of disease.Skeletal system
Skeletal system Pradeep Banjare
╠²
The skeletal system consists of 206 bones and a network of tissues that connect them. It performs vital functions of support, movement, protection of organs, blood cell production, calcium storage, and hormone regulation. The skeletal system includes the skull, spinal cord, rib cage, shoulders, hips, and bones in the hands and feet. Cartilage cushions the ends of bones at joints like knees, elbows, and vertebrae. Ligaments and tendons connect bones to other bones and muscles to facilitate movement. The skeletal system enables the human body to survive through these various structural and functional roles.Knowledge of Antibiotics and classifications
Knowledge of Antibiotics and classificationsPradeep Banjare
╠²
The document defines antibiotics as substances that destroy or inhibit the growth of bacteria and are used to treat infections. It discusses the classification and types of bacteria, including Gram-positive and Gram-negative, and how antibiotics work by inhibiting bacterial cell functions or killing bacteria. The document also provides lists of common infections treated with antibiotics, examples of generic and brand name antibiotics, and discusses antibiotic resistance and anti-infective drugs.More Related Content
More from Pradeep Banjare (8)
Alkaloids
AlkaloidsPradeep Banjare
╠²
This document discusses two methods of classifying alkaloids: biosynthetic classification and chemical classification. Biosynthetic classification is based on the precursor compounds that alkaloids are derived from during plant biosynthesis, such as tryptophan, lysine, ornithine, and tyrosine. Chemical classification is based on the presence of the basic heterocyclic nucleus and lists examples of alkaloid classes including piperidine, pyrrolidine, quinoline, isoquinoline, indole, and steroidal alkaloids.Phamakokinetics & pharmacodynamics
Phamakokinetics & pharmacodynamicsPradeep Banjare
╠²
The document is a collection of multiple-choice questions and answers focusing on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics for exam preparation in pharmacy. It covers various aspects of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and mechanisms of action, along with key terminology relevant to the field. Additionally, it includes questions on drug interactions and effects related to dose response.Phamacology mcq 2
Phamacology mcq 2Pradeep Banjare
╠²
This document provides a list of 30 multiple choice pharmacology questions along with answers about various drugs and their properties. It also includes a short self-assessment section with 5 additional multiple choice questions. The questions cover topics such as antibiotics, antifungals, anticancer drugs, antimalarials, endocrine pharmacology, and more. The document is presented by Pradeep Banjare from Apollo College of Pharmacy in Durg, India as a study aid and exam preparation for pharmacology.Top 100 pharmacology mcq & ans
Top 100 pharmacology mcq & ansPradeep Banjare
╠²
The document contains a collection of 100 multiple choice questions and answers focusing on pharmacology principles, drug interactions, metabolism, and therapeutic monitoring. It covers key topics such as drug absorption, protein binding, first-pass metabolism, and the effects of various drugs on the body, along with examples and exceptions. This compilation serves as a resource for students and professionals in the field of pharmacology to assess their knowledge and understanding.Digestive system
Digestive system Pradeep Banjare
╠²
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract and accessory organs including the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder. The digestive system works to convert food into energy and nutrients through a multi-step process beginning in the mouth and involving the breakdown of food and absorption of nutrients through a long tube called the alimentary canal before the excretion of wastes. Key functions include ingestion, secretion, mixing, digestion, absorption, and excretion to process food through the body.Gpate & pharmacist Sort note
Gpate & pharmacist Sort notePradeep Banjare
╠²
Bacteria are single-celled organisms that can be inhibited through the use of vaccines. Pradeep Banjare from Apollo College of Pharmacy in Durg presented information on bacterial cells and inhibitors. Vaccines can help inhibit bacteria and prevent the spread of disease.Skeletal system
Skeletal system Pradeep Banjare
╠²
The skeletal system consists of 206 bones and a network of tissues that connect them. It performs vital functions of support, movement, protection of organs, blood cell production, calcium storage, and hormone regulation. The skeletal system includes the skull, spinal cord, rib cage, shoulders, hips, and bones in the hands and feet. Cartilage cushions the ends of bones at joints like knees, elbows, and vertebrae. Ligaments and tendons connect bones to other bones and muscles to facilitate movement. The skeletal system enables the human body to survive through these various structural and functional roles.Knowledge of Antibiotics and classifications
Knowledge of Antibiotics and classificationsPradeep Banjare
╠²
The document defines antibiotics as substances that destroy or inhibit the growth of bacteria and are used to treat infections. It discusses the classification and types of bacteria, including Gram-positive and Gram-negative, and how antibiotics work by inhibiting bacterial cell functions or killing bacteria. The document also provides lists of common infections treated with antibiotics, examples of generic and brand name antibiotics, and discusses antibiotic resistance and anti-infective drugs.Cardiovascular system
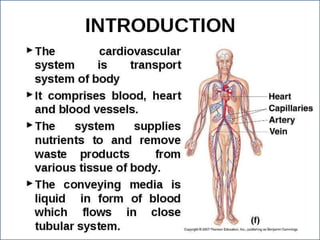
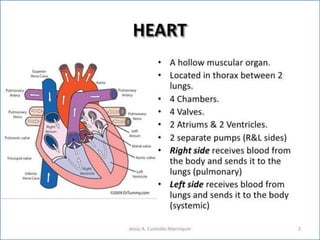
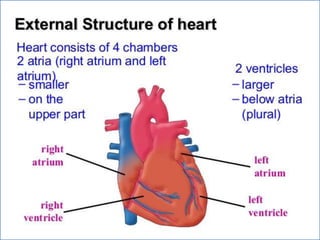
- 1. PRESENTED BY- PRADEEP BANJARE APOLLO COLLEGE OF PHARMACY ANJORA, DURG
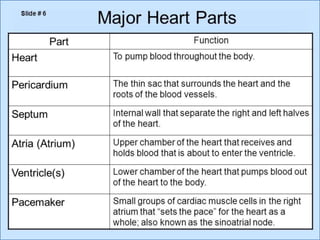
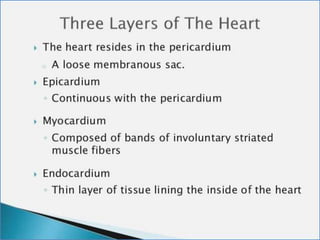
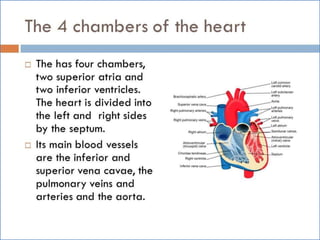
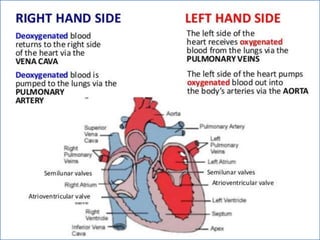
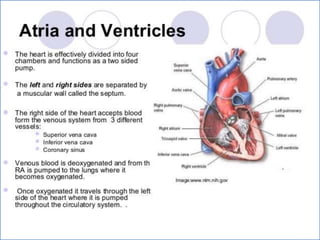
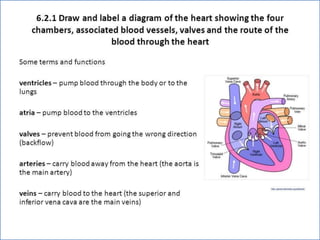
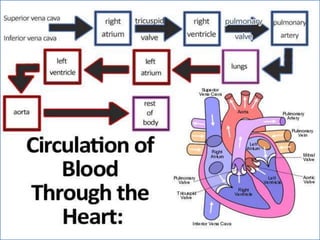
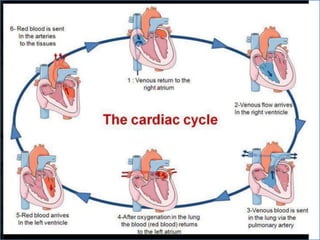
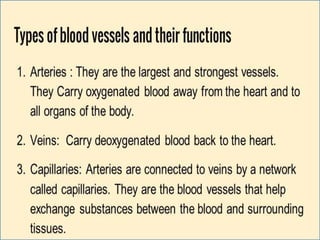
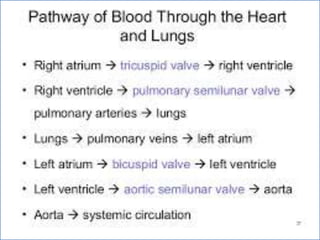
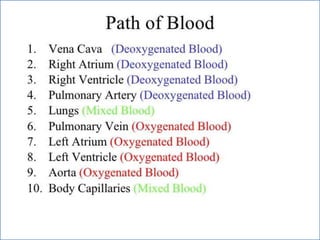
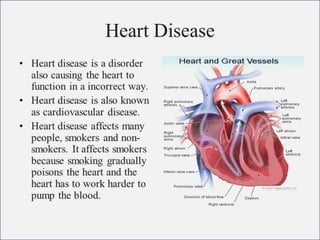
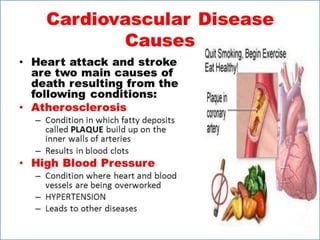
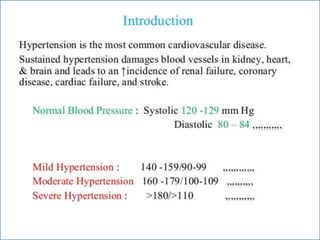
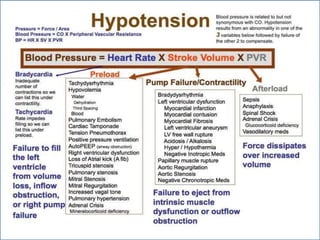
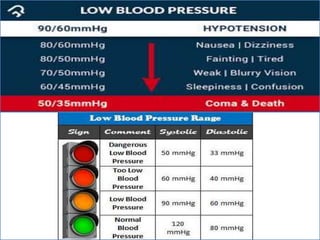
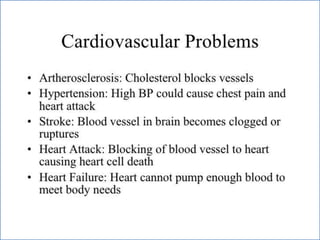
- 2. -: CONTENT :- 1. INRODUCTION 2. HEART- INTERNAL & ETERNAL STRUCTURE 3. LOCATION OF THE HEART 4. FUNCTION OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYS. 5. MAJOR PART OF HEART 6. LAYER & CHAMBER OF HEART 7. ATRIA & VENTRICLES 8. CIRCULATION OF BLOOD & CARDIOC CYCLE 9. PATHWAY OF BLOOD 10. HEART DISEASE- HYPER & HYPOTENSION 11. PROBLEM OF HEART
