Fatty acid Biosynthesis
- 1. Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Prof. C. S. Nirghude Assistant Professor K. K. Wagh College of Agril. Biotechnology, Nashik
- 2. ïĩ Lipids play a variety of cellular roles ïĩ They are the principal form of stored energy in most organisms and major constituents of cellular membranes. ïĩ The dietary carbohydrates and amino acids, when consumed in excess, can be converted to fatty acids and stored as triacylglycerol
- 3. Location ïĩ Denovo (new) synthesis of fatty acids occurs predominantly in liver, kidney, adipose tissue and lactating mammary glands ïĩ The enzyme machinery for fatty acid production is located in the cytosomal fraction of the cell.
- 4. Steps ïĩ The fatty acid synthesis may be accomplished in 3 stages ïĩ I.Production of acetyl CoA and NADPH ïĩ ll. Conversion of acetyl CoA to malonyl CoA ïĩ lll. Reactions of fatty acid synthase complex
- 5. l. Production of acetyl CoA ANd NADPH ïĩ Acetyl CoA is produced in the mitochondria by the oxidation of pyruvate and fatty acids. ïĩ Mitochondria, however, are not permeable to acetyl CoA ïĩ An alternate or a bypass arrangement is made for the transfer of acetyl CoA to cytosol.
- 7. Formation of Malonyl CoA ïĩ Malonyl CoA formed from Acetyl CoA and bicarbonate in the presence of enzyme Acetyl CoA carboxylase.
- 8. Fatty acid synthase complex ïĩ Enzyme Consist of seven polypeptide ïĩ 1. Aceyl Carrier Protein (ACP) ïĩ 2. Acetyl CoA ACP transacetylase (AT) ïĩ 3. Malonyl CoA ACP Transferase (MT) ïĩ 4. Îē- Keto aceyl ACP synthase(KS) ïĩ 5. Îē- Keto aceyl ACP reductase (KR) ïĩ 6. Îē- Hydroxyl acyl ACP dehydratase(HD) ïĩ 7. Enoyl ACP reductase (ER)
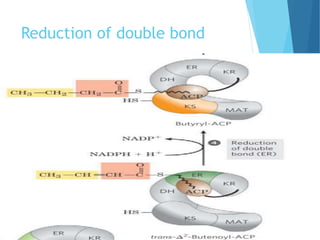
- 9. Mechanism ïĩ Fatty acid synthesis catalyzed in four reaction 1. Condensation 2. Reduction of carbonyl group 3. Dehydration 4. Reduction of double bond
- 10. Condensation
- 11. Reduction of carbonyl group
- 12. Dehydration
- 13. Reduction of double bond
- 15. Overall Reaction