Third Party Supply of Offsets: Offset Market
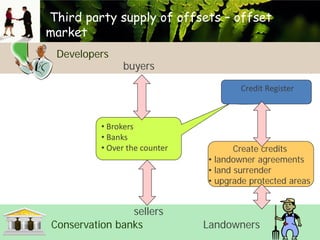
- 1. Third party supply of offsets ŌĆō offset market Developers buyers Credit Register ŌĆó Brokers ŌĆó Banks ŌĆó Over the counter sellers Conservation banks Create credits ŌĆó landowner agreements ŌĆó land surrender ŌĆó upgrade protected areas Landowners
- 2. Like-for-like and offset supply Risk to supplier increases Different credit types Demand high and certain Aggregated offsets & banks Demand low and uncertain Bespoke trades thruŌĆÖ brokers Like-for-like rules (including trading up) determine market segmentation: ŌĆó Low segmentation ŌåÆ banks and landscape solutions ŌĆó High segmentation ŌåÆ bespoke and individual site solutions
- 3. Market facilitation ŌĆō Over The Counter Over The Counter - ŌĆó a bank of credits available at price pre-set by the landowner ŌĆó based on ŌĆśtrading upŌĆÖ to higher biodiversity importance ŌĆó offset specified in the permit condition ŌĆó offset plan provided at time of purchase ŌĆó walk in and buy - feels like ŌĆśin lieu paymentŌĆÖ
- 4. Endangered grasslands ŌĆó Plains Grassland - Victorian Volcanic Plain
- 5. Offset bank & protected area ŌĆó A 15,000 ha reserve through the purchase and surrender of freehold land ŌĆó Will provide offsets for 15 years of urban development in MelbourneŌĆÖs west ŌĆó Designed via a Strategic Assessment Report of future impacts and offsets ŌĆó Land designated under an acquisition overlay ŌĆó Financed through a revolving fund, primed with government funding