Lean Methodology July Monthly
- 1. Lean Methodology Value Creation Joe Kalchbrenner Date 7/25/06
- 2. What is “Lean”? “ Lean Thinking … redefine(s) the work of functions, departments, and firms so they can make a positive contribution to value creation and … speak to the real needs of employees and customers at every point along the stream….” Lean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in your Corporation, Womack,James P.;Jones,Daniel T.
- 3. Why “Lean”? Lean is becoming a CPI buzzword “ Lean manufacturing is key” Process Industries Center for Manufacturing Excellence, PICME, January 2005 reports 20 to 30% cost savings “ Competitive Advantage for the Process Industries” AIChE Nov. 2005 Annual Mtg. Cincinnati OH .
- 4. EEliminate Waste – Reduce Cost FFaster Time To Market - Pull SShorter Lead Time - Flow IImproved Quality – Operator Control IImprove customer responsiveness and satisfaction CCreate A Design, Sales, Order Entry, Procurement, And production System In Each Product/Market LLocate the Value Stream Near Your Internal And External Customers - Location Goals of Lean
- 5. History of Lean, and it’s Main Elements Lean terminology was coined by James Womack and Daniel Jones, in the book: Lean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation” . Lean is based on the Toyota Production System (TPS) that Taiichi Ohno and Shigeo Shingo developed for Toyota after WWII Toyota embraced TPS and used “Material and Information Flow Mapping” to establish flow, eliminate waste and add value “ Material and Information Flow Mapping” – Value Stream Mapping (VSM) – is used to depict the current and future states of the value stream as an early step of developing and implementing lean systems 5S - Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain Kaizen, (continuous improvement) Frederick Taylor c. 1900, time study Kanban, (pull system) for controlling WIP
- 6. Concept of Waste Waste is anything other than the minimum amount of equipment, materials, parts, space, and worker’s time which are absolutely essential to add value to the product
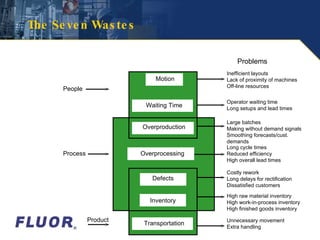
- 7. The Seven Wastes People Process Product Problems Inefficient layouts Lack of proximity of machines Off-line resources Motion Defects Inventory Transportation Overproduct ion Waiting Time Operator waiting time Long setups and lead times Large batches Making without demand signals Smoothing forecasts/cust. demands Long cycle times Reduced efficiency High overall lead times Costly rework Long delays for rectification Dissatisfied customers High raw material inventory High work-in-process inventory High finished goods inventory Unnecessary movement Extra handling Overprocessing
- 8. Does this describe your work area? Space is crowded Unneeded items are stacked between work stations Excess inventory and equipment make it difficult to move, work and improve Equipment is dirty and collection point for miscellaneous materials Lean and You…
- 9. Before 5-S … After 5-S …
- 10. Lean and you… benefits of 5S A place for everything Everything in its place area identification (queue, racks, scrap, etc.) operator facilities (lockers, information boards, etc.) Everything visible location identification (tools, instruction, etc.) Everyone cleans and checks for damage and problems Benefits: Safety/Quality Attacks Waste Develops a Sense of Pride
- 11. Lean and Fluor Enabling methodology for faster, reliable facility start-ups - reduces risks and expedites return on investment for new production. Executed in parallel with FEED/EPC activities to maximize life-cycle value. Proprietary methodology to identify, quantify, and validate plant improvements for existing plants. On-going partnering alliance designed to improve the performance of plant assets in existing plants with substantial on-going cost savings to customers. PlantREADY. Fluor’s suite of total maintenance solutions designed to improve total asset performance.
- 12. Credits Enterprise Services Group O&M Business Lean Manufacturing Mr. Tim Finigan
- 13. Accessorize and Add Value Walk the Walk Talk the Talk