Application of composite materials in aerospace industry (1)
- 1. Presented by: Kanchha Lama (0991904) Parth Patel (0989754) Pramith Varikoti (0988868)
- 2. ’üĮ Introduction : What is composite? ’üĮ Why composite in Aerospace industry? ’üĮ Applications of composite in aerospace ’üĮ Future involvement of composite ’üĮ Conclusion
- 3. o Composite is material consisting of two or more materials, which have different physical and chemical properties, combined together in a proper content and fashion to produce a new material properties that are different from the properties of those individual materials.
- 4. ’üĮ The main aim of the aerospace/aircraft industries is to reduce weight keeping the same or more strength than the regular metals have. ’üĮ This criteria leads to use composite.
- 5. ’āś Light weight ’āś High heat resistance ’āś High strength to weight ratio ’āś Low density ’āś Corrosion resistance ’āś High stiffness ’āś Fatigue resistance
- 7. ’é¦ Fiber glass ’é¦ CFRP ’é¦ QFRP ’é¦ GFRP ’é¦ GLARE
- 8. ’āśFuselage (Bulkhead) ’āśWing flaps ’āśRudder ’āśElevators ’āśRadome ’āśSpoilers ’āśFloor beams and panels ’āśHelicopter main and tail rotor blades ’āśSpace vehicles: Satellites, Missiles, Rockets etc.
- 9. Commercial : o Boeing 777 o Boeing 787 ŌĆ£DreamlinerŌĆØ o Airbus A380 Military: o B-2 Bomber o LCA Tejas (HAL)
- 10. ’āś Components that uses composite structure are: ŌŚ” Horizontal Stabilizer ŌŚ” Vertical Fin ŌŚ” Radom ŌŚ” Wing fairings ŌŚ” Passenger floor beams ŌŚ” Wing Box ŌŚ” Engine Cowlings ŌŚ” Engine fairings ’āś Reduction in weight is over 5800 pounds.
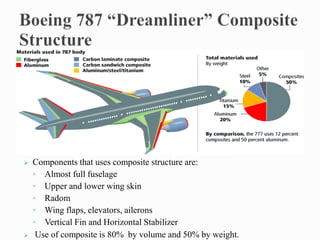
- 11. ’āś Components that uses composite structure are: ŌŚ” Almost full fuselage ŌŚ” Upper and lower wing skin ŌŚ” Radom ŌŚ” Wing flaps, elevators, ailerons ŌŚ” Vertical Fin and Horizontal Stabilizer ’āś Use of composite is 80% by volume and 50% by weight.
- 12. ’āś Components that uses composite structure are: ŌŚ” Horizontal Stabilizer ŌŚ” Vertical Fin ŌŚ” Radom ŌŚ” Wing Fairings ŌŚ” Wing Box ŌŚ” Belly Fairings ŌŚ” Engine Cowlings ŌŚ” Engine fairings ’üĮ Wing box, made of CFRP, has reduced weight up to one and a half tones.
- 13. ’üĮ B-2 Bomber is mostly made of carbon/epoxy materials. ’üĮ The reduction in weight was about 40000 to 50000 pounds. ’üĮ Design material was specially designed to absorb radar waves.
- 14. ’üĮ LCA stands for Light Combat Aircraft which is basically use of composite materials in its structure. ’üĮ Components which are made of composite material are: ŌŚ” Nose ŌŚ” Wing upper surface and leading edge ŌŚ” Exit Nozzle ’üĮ Weight is reduced by 21%
- 15. ’üĮ Used to manufacture Rocket and Missiles motor cases. Materials for this are carbon, aramid and glass. ’üĮ Composites like carbon-carbon are used to manufacture re-entry nose tips and heat shields.
- 16. ’üĮ Use of composite is more challenging to design. ’üĮ NDT test for composite material is much more difficult as compared to metals. ’üĮ Delamination of layers. ’üĮ High cost ’üĮ Damage tolerance. ’üĮ Need specialized repair techniques.
- 17. Honeycomb Structure ’üĮ Honeycomb Structure ’üĮ Hybrid composite materials ’üĮ Advanced Designs through Simulation ’üĮ Investigations into damage tolerance of bonded repairs by test and simulation.
- 18. ’üĮ Since the invention of composite materials, aerospace industry has shown significant use of it in building different parts first to almost most of the structural parts and use of it is rapidly growing. ’üĮ The main aspect we need to keep in mind that strength and stiffness are major considerations for aircrafts whereas stiffness and low coefficient of thermal expansion are major considerations for space applications.
- 19. ’üĮ Composite Materials. Retrieved from http://www.aviation- history.com/theory/composite.htm. ’üĮ Creating a Titan. Retrieved from ’üĮ http://www.flightglobal.com/news/articles/creating-a-titan-199071. ’üĮ Daniel, I. M., Ishai, O.(2005). Engineering mechanics of composite materials. Oxford, New York, 2, 3-4. ’üĮ Holly, R.H. (2013). The great metal tube in the sky. Retrieved from ’üĮ https://arch5541.wordpress.com/2013/01/08/the-great-metal-tube-in-the-sky. ’üĮ Honeycomb structure. Retrieved from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Honeycomb_structure. ’üĮ Hybrid material. Retrieved from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hybrid_material. ’üĮ LCA Tejas Technology. Retrieved from ’üĮ http://www.tejas.gov.in/technology/composite_materials.html. ’üĮ National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Composites. Retrieved from ’üĮ http://www.aeronautics.nasa.gov/pdf/composites_k-12.pdf. ’üĮ Northrop Grumman B-2 Spirit. Retrieved from http://www.military- today.com/aircraft/b2_spirit.htm.
- 20. Thank You