13-itemanalysis-161127124647.pptx
- 1. ITEM ANALYSIS Ann Meredith Garcia, MD
- 2. What is item analysis? ŌĆó Judging the quality of test items by examining the studentsŌĆÖ responses ŌĆó Competent vs. less competent students? ŌĆó Difficulty of items?
- 3. How is item analysis done? Administer the test Check the studentsŌĆÖ responses to separate items Check the total scores
- 4. Tasks of item analysis 1st task: Item discrimination ŌĆó Sort the students who know the topic well from those who do not ŌĆó Correlate performance on a single test item with total test performance ŌĆó (+) Correlation ’āĀ better discrimination 2nd task: Item difficulty
- 5. Electronic item analysis Student Item 1 Score Total Score / 30 A 1 25 B 1 19 C 1 18 D 0 16 E 1 12 F 0 10 ŌĆó Average total score (correct Item 1) = 18.5 ŌĆó Average total score (incorrect Item 1) = 13 ŌĆó Computed correlation coefficient = 0.53 ŌĆó Item is to some extent related to the total score Correct = 1 Incorrect = 0
- 6. Electronic item analysis r = correlation of an option with the total score p = percentage of students who chose that option (n = 65) ŌĆó Correct options should show positive correlations; distractors should show negative correlations Item 1: r = 0.25 ’āĀ low correlation Item 2: r = 0.49 ’āĀ fairly good correlation Item 3: r = 0.34 ’āĀ modest correlation ŌĆó r Ōēż 0.15 ’āĀ course content is not being assessed well ’āĀ eliminate the item (OR revise) Item A B C 1 r = -0.27 p = 13.89 r = 0.25 p = 50.00 r = -0.06 p = 36.11 2 r = -0.46 p = 5.56 r = 0.49 p = 88.86 r = -0.22 p = 5.56 3 r = -0.30 p = 16.67 r = -0.13 p = 27.78 r = 0.34 p = 55.56
- 7. Electronic item analysis r = correlation of an option with the total score p = percentage of students who chose that option (n = 65) ŌĆó Standard error (SE) = 1 / ŌłÜ (number of students ŌĆō 1) = 0.12 ŌĆó Any r > 2(SE) will be accepted as other than a chance relationship between the item and the total score Item 1: r = 0.25 > 0.24 [2(SE)] ’āĀ very marginal but acceptable Item A B C 1 r = -0.27 p = 13.89 r = 0.25 p = 50.00 r = -0.06 p = 36.11 2 r = -0.46 p = 5.56 r = 0.49 p = 88.86 r = -0.22 p = 5.56 3 r = -0.30 p = 16.67 r = -0.13 p = 27.78 r = 0.34 p = 55.56
- 8. Item analysis by hand ŌĆó Step 1: Arrange the studentsŌĆÖ papers according to their test scores (highest to lowest). ŌĆó Step 2: Divide these into ŌĆ£high scorersŌĆØ vs. ŌĆ£low scorersŌĆØ. ŌĆó Step 3: Tabulate the number of students who chose each option in both groups. ŌĆó Step 4: Compute for the discrimination index. Item 1 A B C D Total High scorers 2 4 0 16 22 Low scorers 12 7 0 4 23
- 9. Item analysis by hand ŌĆó Step 4: Compute for the discrimination index (DI). DI = (NumHigh ŌĆō NumLow) Number of students in larger group = (16 ŌĆō 4) / 23 = 0.52 * Ranges from 0 ŌĆō 1.00 * Can also be negative (for distractors) Item 1 A B C D Total High scorers 2 4 0 16 22 Low scorers 12 7 0 4 23
- 10. Item analysis by hand Alternative: Straight difference method ŌĆó Steps 1 ŌĆō 3: Same ŌĆó Step 4: Compute for NumHigh ŌĆō NumLow. ŌĆó If Ōēź 0.10(n) ’āĀ adequate (used across all items) 16 ŌĆō 4 = 12 0.10(45) = 4.5 Item 1 A B C D Total High scorers 2 4 0 16 22 Low scorers 12 7 0 4 23
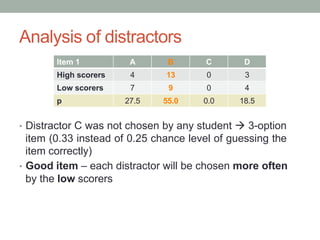
- 11. Analysis of distractors ŌĆó Distractor C was not chosen by any student ’āĀ 3-option item (0.33 instead of 0.25 chance level of guessing the item correctly) ŌĆó Good item ŌĆō each distractor will be chosen more often by the low scorers Item 1 A B C D High scorers 4 13 0 3 Low scorers 7 9 0 4 p 27.5 55.0 0.0 18.5
- 12. Tasks of item analysis 2nd task: Item difficulty ŌĆó Difficulty index/facility index = proportion of students who get an item correctly ŌĆó Step 1: Award a score to each student. ŌĆó Step 2: Arrange the scored tests from highest to lowest. ŌĆó Step 3: Identify the upper and lower 27%. ŌĆó Step 4: Count the response counts in each group. Item 1 A B C D Total High scorers 2 4 0 16 22 Low scorers 11 7 0 4 22
- 13. Tasks of item analysis 2nd task: Item difficulty ŌĆó Difficulty index/facility index = proportion of students who get an item correctly ŌĆó Step 5: Calculate the difficulty index. = H + L N H = no. of students in the high group with a correct answer L = no. of students in the low group with a correct answer N = total no. of students Item 1 A B C D Total High scorers 2 4 0 16 22 Low scorers 11 7 0 4 22
- 14. Tasks of item analysis 2nd task: Item difficulty ŌĆó Difficulty index/facility index = proportion of students who get an item correctly ŌĆó Ranges from 0 ŌĆō 1.00 ŌĆó Best Ōēł 0.50 (0.30 ŌĆō 0.70) ŌĆó Larger index ’āĀ easier item; smaller index ’āĀ more difficult item DI = (16 + 4) / 80 = 0.25 ŌĆó Criteria: ŌĆó Ōēź0.35 = excellent question ŌĆó 0.25 ŌĆō 0.34 = good question ŌĆó 0.15 ŌĆō 0.24 = marginal question ’āĀ revise ŌĆó <0.15 = poor question ’āĀ discard Item 1 A B C D Total High scorers 2 4 0 16 22 Low scorers 11 7 0 4 22
- 15. Item analysis for essay tests ŌĆó Step 1: Identify the upper and lower 25% of the students. ŌĆó Step 2: Compute for the following: Disc. = (Sum of scores for highs ŌĆō sum of score for lows) N x (max. possible score on item) Diff. = (Sum of scores for highs + sum of score for lows) 2N x (max. possible score on item) N = 25% of the number tested Item Score High Group Low Group No. of Students No. of Students x Score No. of Students No. of Students x Score 10 9 90 1 10 8 6 48 0 0 6 2 12 4 24 4 3 12 7 28 2 0 0 8 16 Total 20 162 20 78
- 16. Item analysis for essay tests ŌĆó Step 2: Compute for the following: Disc. = (Sum of scores for highs ŌĆō sum of score for lows) N x (max. possible score on item) = (162 ŌĆō 78) / [(0.25 x 80) x 10] = 0.42 Satisfactory discrimination Item Score High Group Low Group No. of Students No. of Students x Score No. of Students No. of Students x Score 10 9 90 1 10 8 6 48 0 0 6 2 12 4 24 4 3 12 7 28 2 0 0 8 16 Total 20 162 20 78
- 17. Item analysis for essay tests ŌĆó Step 2: Compute for the following: Diff. = (Sum of scores for highs + sum of score for lows) 2N x (max. possible score on item) = (162 + 78) / [(2 x 0.25 x 80) x 10] = 0.60 Satisfactory difficulty Item Score High Group Low Group No. of Students No. of Students x Score No. of Students No. of Students x Score 10 9 90 1 10 8 6 48 0 0 6 2 12 4 24 4 3 12 7 28 2 0 0 8 16 Total 20 162 20 78
- 18. Item response theory and item analysis ŌĆó Calculates the odds of getting an item right ’āĀ converts this number to a natural logarithm ŌĆó Allows faculty to equate the item difficulty scale on one test to the scale of another test and across different student groups ŌĆó Useful system for building item banks
- 19. Thank you! ’üŖ






![Electronic item analysis
r = correlation of an option with the total score
p = percentage of students who chose that option (n = 65)
ŌĆó Standard error (SE) = 1 / ŌłÜ (number of students ŌĆō 1)
= 0.12
ŌĆó Any r > 2(SE) will be accepted as other than a chance
relationship between the item and the total score
Item 1: r = 0.25 > 0.24 [2(SE)] ’āĀ very marginal but acceptable
Item A B C
1 r = -0.27
p = 13.89
r = 0.25
p = 50.00
r = -0.06
p = 36.11
2 r = -0.46
p = 5.56
r = 0.49
p = 88.86
r = -0.22
p = 5.56
3 r = -0.30
p = 16.67
r = -0.13
p = 27.78
r = 0.34
p = 55.56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13-itemanalysis-161127124647-231020015149-03cb51d7/85/13-itemanalysis-161127124647-pptx-7-320.jpg)







![Item analysis for essay tests
ŌĆó Step 2: Compute for the following:
Disc. = (Sum of scores for highs ŌĆō sum of score for lows)
N x (max. possible score on item)
= (162 ŌĆō 78) / [(0.25 x 80) x 10] = 0.42
Satisfactory discrimination
Item Score
High Group Low Group
No. of Students No. of Students
x Score
No. of Students No. of Students
x Score
10 9 90 1 10
8 6 48 0 0
6 2 12 4 24
4 3 12 7 28
2 0 0 8 16
Total 20 162 20 78](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13-itemanalysis-161127124647-231020015149-03cb51d7/85/13-itemanalysis-161127124647-pptx-16-320.jpg)
![Item analysis for essay tests
ŌĆó Step 2: Compute for the following:
Diff. = (Sum of scores for highs + sum of score for lows)
2N x (max. possible score on item)
= (162 + 78) / [(2 x 0.25 x 80) x 10] = 0.60
Satisfactory difficulty
Item Score
High Group Low Group
No. of Students No. of Students
x Score
No. of Students No. of Students
x Score
10 9 90 1 10
8 6 48 0 0
6 2 12 4 24
4 3 12 7 28
2 0 0 8 16
Total 20 162 20 78](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13-itemanalysis-161127124647-231020015149-03cb51d7/85/13-itemanalysis-161127124647-pptx-17-320.jpg)

