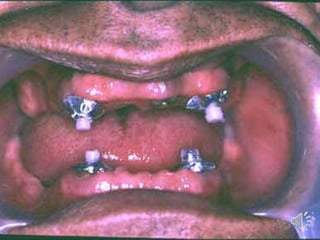
Over denture.ppt
- 5. Requirements For Overdenture Attachments he patients should have low caries index he patients should perform proper home care he patients should have sound periodontal health he patients should have
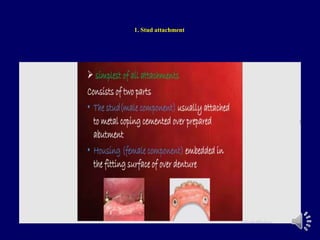
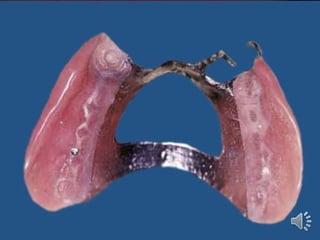
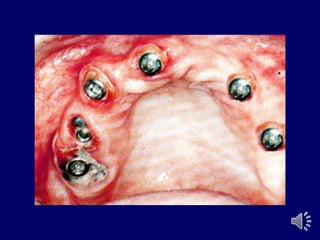
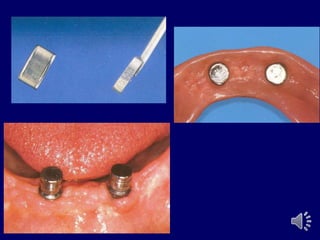
- 6. ABUTMENT WITH ATTACHMENTS Attachments are small precision devices. Objective is to improve retention of denture base. Most attachments are secured to abutment by a cast coping. Consists of two parts o Male o Female
- 7. here additional retention is needed. educed labial flange. educed palatal coverage. plinting. When do we use attachments ?
- 8. Disadvantages of attachments ime consuming ncreased cost of treatment .expensive Plaque control is more difficult ifficult to construct epair is difficult equires careful manipulation by the patient, not recommended for mentally and physically handicapped.
- 9. Types of overdenture attachments tud attachments. ar attachments. agnets.
- 10. Types according to mechanism of action
- 12. Advantages Of Stud Attachments ow profile asy hygiene maintenance nhanced crown/root ratio
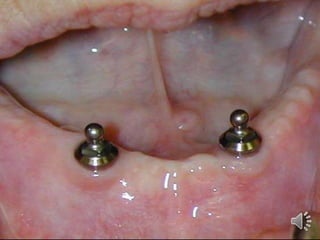
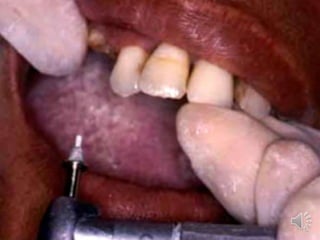
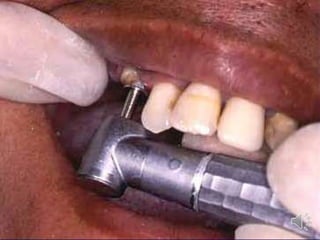
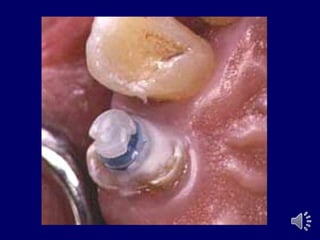
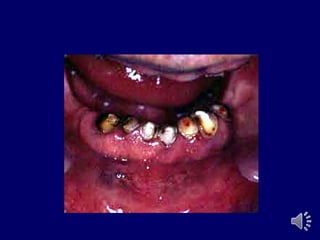
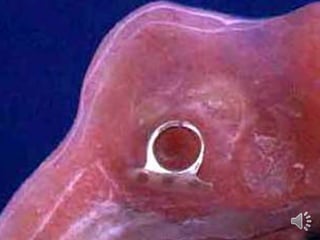
- 13. Extra radicular stud attachment Male element projects from the root surface The stud is attached to the metal coping cemented over the prepared abutment, while the housing is embedded in the fitting surface of the prosthesis
- 14. Extra radicular stud attachment Gerber âĒ eka âĒ otherman
- 15. Stud Attachments est anchor attachment. - Ring attachment. othermann attachment.
- 16. Intra radicular stud attachment he stud is attached to the fitting surface of the denture and the housing is incorporated in the abutment. est anchor attachment. - Ring attachment.
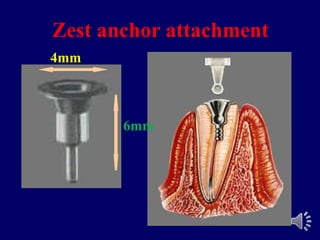
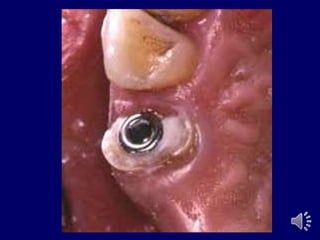
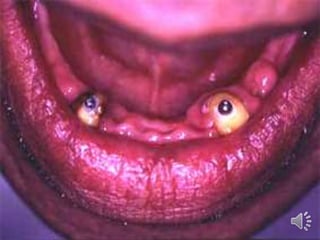
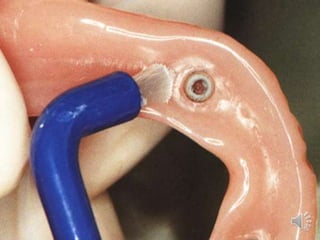
- 17. Zest anchor attachment Nylon Post Metal Sleeve
- 26. Advantages of Zest anchor attachment: t serves well as a temporary fixation for the transitional overdenture. t can be used without metal coping. t can be chair-side procedure.
- 27. Disadvantages of Zest anchor attachment: t requires meticulous cleaning and caring. ylon part needs changing every 3-6m.
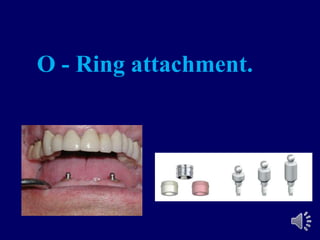
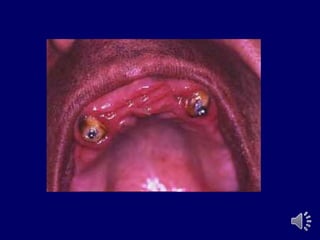
- 29. O - Ring attachment.
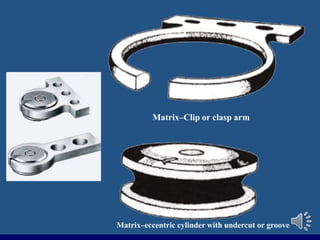
- 39. Rothermann attachment Male part consists of groove Female part (housing) consists of C shaped ring which fits in deeper part of retaining groove
- 40. Matrixâeccentric cylinder with undercut or groove MatrixâClip or clasp arm
- 44. Advantages of the Rothermann attachment: ow in height. t has adequate retention similar to the clasp. he female clip is well retained in the resin.
- 45. Disadvantages of the Rothermann attachment: ufficient denture bulk must be present lingually to secure the female lug. hair-side insertion of the female part is very difficult.
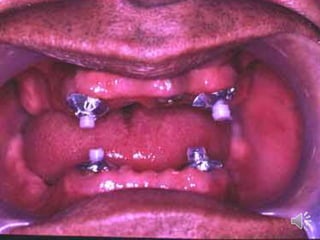
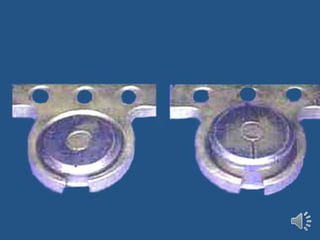
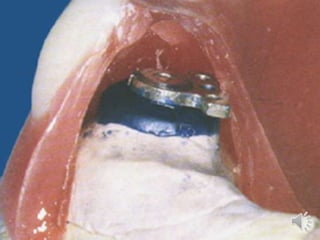
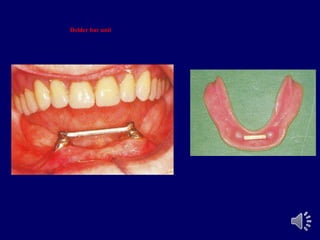
- 46. Bar attachments older bar a- Dolder bar unit. b- Dolder bar joint
- 47. Dolder bar unit
- 48. Dolder bar unit
- 49. Advantages of bar attachments : igidly splint the teeth rovides good retention, stability and support rovides cross arch stabilization
- 50. Disadvantages : ulk of bar laque accumulation earing oldering procedure anual dexterity
- 52. Rare-earth magnets (cobalt-samarium magnets) hey possess a high magnetic field strength hey possess a high intrinsic resistance to demagnetization. agnetic retention is self-limiting; Retentive forces within the range 155â980 g have been reported.
- 54. Advantages of magnet attachment: imple to use. conomical in cost. educe the force transmitted to the abutments. equire little maintenance.
- 55. Attachments Drawbacks. ncreased cost of treatment. aintenance is likely more complicated. ncreased bulk may lead to denture fracture. laque control is more difficult. igher loads is transmitted to abutment.
- 58. Plaque control of the abutment teeth ffective plaque control by the patient rushing root surfaces to be part of the normal oral hygiene program hlorhexidine can be helpful in the control of plaque
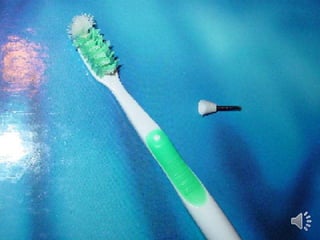
- 60. Plaque control of the denture he overdenture should be brushed after meals with a soft toothbrush articular attention should be paid to the impression surface in the region of the root face depressions ypochlorite solutions are found to be efficient
- 61. Care of the root face opical fluoride applications should be carried out immediately after the root face preparations. he patient should use fluoride, in various form to prevent dentine caries.
- 62. Patient instructions nce a day Brush the overdenture abutment followed with 0.4% stannous fluoride gel atients can expectorate the excess fluoride, but should not rinse or drink for at least 30 min ach morning one drop of 0.4% stannous fluoride gel is placed in to the fitting surface of overdenture