pytagoras theorem.pdf
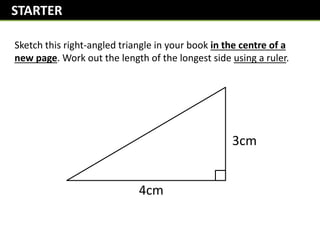
- 1. Sketch this right-angled triangle in your book in the centre of a new page. Work out the length of the longest side using a ruler. 4cm 3cm STARTER
- 2. 3cm 3cm 4cm 4cm 5cm 5cm Area = ? Area = ? Area = ? Now turn each side of the triangle into a square. Can you notice anything about the relationship of the three areas? 32 + 42 = 52 STARTER
- 3. For any right-angled triangle with hypotenuse ð. ð2 + ð2 = ð2 ð ð ð Hypotenuse (the longest side) ! Write this down Pythagorasâ Theorem Bro Note: notice that itâs the longest side thatâs on itâs own on one side of the equation. The (squared) shorter sides are the ones that are added.
- 4. 3 4 ðĨ Step 1: Determine the hypotenuse. Step 2: Form an equation 32 + 42 = ðĨ2 Step 3: Solve the equation to find the unknown side. ðĨ2 = 9 + 16 = 25 ðĨ = 25 =5 The hypotenuse appears on its own. Example Reveal >
- 5. 13 5 ðĨ Step 1: Determine the hypotenuse. Step 2: Form an equation ðĨ2 + 52 = 132 Step 3: Solve the equation to find the unknown side. ðĨ2 = 169 â 25 = 144 ðĨ = 144 =12 The hypotenuse appears on its own. Further Example Reveal >
- 6. 11 ðĨ 6 Step 1: Determine the hypotenuse. Step 2: Form an equation ðĨ2 + 62 = 112 Step 3: Solve the equation to find the unknown side. ðĨ2 = 121 â 36 = 85 ðĨ = 85 =9.22 ( 2 d.p) The hypotenuse appears on its own. Further Example Reveal >
- 7. ðĨ = 85 = 9.22 (2 d.p) A value written as the square root of a number is known as a surd. Sometimes itâs better to leave your answer in surd form (weâll see why later) rather than as a decimal. When we found areas/circumferences of circles, we often left our answer in terms of ð so that it was exact. Similarly, answers in surd form are exact whereas decimal form answers have to be rounded, and are thus not exact. Surd or decimal?
- 8. 6 8 ðĨ 42 55 ðĨ ðĨ 6 4 âTo learn secret way of ninja, find ðĨ you must.â 1 1 ðĨ ðĨ 10 12 1 2 3 4 5 Answer: ð = ðð Answer: ð = ðððð Answer: ð = ð Answer: ð = ðð Answer: ð = ðð Test Your Understanding
- 9. Weâve so far written out the equation ð2 + ð2 = ð2, filled in our information, and rearranged to find the missing side. But itâs helpful to be able to do it in our heads sometimes! If youâre looking for the hypotenuse ï Square root the sum of the squares If youâre looking for another side ï Square root the difference of the squares 3 5 â â = 32 + 52 = 34 ðĨ 4 7 ðĨ = 72 â 42 = 33 Pythagoras Mental Arithmetic
- 10. Pythagoras Game! Everyone stand up. Each of you will be asked, one at a time, and in your head, to find the missing side of the right-angled triangle. Answer must be in exact form. If you get it wrong, you sit down, and the person who last sat down has the opportunity to âstealâ, where they will be able to stand up again if they correct the answer. 3 5 ð 7 2 ðð Test Run: (Note to teacher: You donât need to specifically click on the green boxes. The next answer will be removed by a mouse/right-arrow press anywhere)
- 13. Exercise 1 Find the side marked with the letter (you do not need to copy the diagrams). 4.5 7 1.8 3.6 ð ðĄ 125 98 ð§ ð 19 23 ð 5.1 6.2 9 7 ðĨ ðĶ 2.2 1.4 a b c d e f g Solutions: (to 3sf) (a) 8.32 (b) 3.12 (c) 77.6 (d) 29.8 (e) 5.66 (f) 2.61 (g) 8.03 1 2 To rescue a cat I put a ladder of length 10m against a tree, with the foot of the ladder 2.5m away from the tree. How high up the tree is the cat? 9.68m Alice and Bob want to get from one corner of this rectangular field to the other. Alice walks round the edge of the field. Bob cuts right across. How much further did Alice walk? The length of the shortest diagonal of an octagon is 1. What is the length of the longest diagonal? 240ð 90ð Start Finish 1 Four unit squares are placed edge to edge as shown. What is the length of the line ðð? Solution: ðð 80m 3 4 N Solution: ð (if this were a proof youâd need to justify why itâs right-angled) 1 1 2
- 14. Starter 21 20 29 You may have noticed last lesson that sometimes all three sides of the right-angled triangle were integers. These are known as Pythagorean triples. For example: The sides could be 20, 21 and 29, as 202 + 212 = 292 and thus satisfy Pythagorasâ Theorem. How many Pythagorean triples can you find? (3, 4, 5) (5, 12, 13) (8, 15, 17) (7, 24, 25) (20, 21, 29) (12, 35, 37) (9, 40, 41) (28, 45, 53) (11, 60, 61) (16, 63, 65) (33, 56, 65) (48, 55, 73) (13, 84, 85) (36, 77, 85) (39, 80, 89) (65, 72, 97) Note that you could also have any multiple of any of these triples as the triangles could be scaled in size. So for example (3, 4, 5) could become (6,8,10) and so on. A final note is that if you changed the powers from 2 to 3, or any higher number, then there would never be any solutions. This is known as Fermatâs Last Theorem, which was unproven for hundreds of years before being proven in 1995.
- 15. Harder Questions Thereâs a variety of ways in which Pythagoras questions could get harder: 6 3 ðĨ 4 Multiple triangles chained together. A B Adding lines to form right-angled triangles that werenât originally there. Area? 2 2 2 3 ðĨ 7 9 C Requiring algebraic manipulation. ðĨ â 1 12 2ðĨ + 1
- 16. A :: Multiple Triangles 6 3 ðĨ 4 What should we do first? Find the central length using the right triangle. ð = ðð â ðð = ðð ð Then what? Now we can find ð using the left triangle. ð = ðð + ðð = ðð Notice that 27 2 = 27. This is why itâs often important to leave your answers in surd form.
- 17. Test Your Understanding 4 6 12 ðĨ ðĶ = 42 + 62 = 52 ðĨ = 52 + 144 = 14
- 18. B :: Adding Lines ðĨ 7 4 1 ðĶ = 72 + 42 = 65 ðĨ = 65 â 12 = 8 Sometimes the line(s) you add to form right angled triangle(s) are fairly obviousâĶ ðĶ
- 19. Quickfire Heights! Reminder of Pro Bro Tip: The height of an equilateral triangle is 3 times half the side length. 2 Height = 3 Area = 3 4 Height = 2 3 Area = 4 3 2 3 Height = 3 Area = 3 3 1 Height = 3 2 Area = 3 4
- 20. Test Your Understanding 4 6 Find the height of this isosceles triangle. Solution: ð Medium Difficulty Harder Difficulty An equilateral triangle is cut out of a square of side 2 cm, as shown. What area of the square remains? Solution: ð â ð
- 21. C :: Algebraic Triangles 4ð 3ð 15 3ð 2 + 4ð 2 = 152 9ð2 + 16ð2 = 225 25ð2 = 225 ð2 = 9 ð = ð (You will likely encounter more interesting algebraic Pythagoras problems next year once you cover expanding two brackets)
- 22. Exercise 2 (exercises on provided sheet) 12 4 5 ðĨ Give answers in exact form unless specified. ðĨ = 185 1 ðĶ 2 3 5 ðĶ = 13 1 2
- 23. Exercise 2 (exercises on provided sheet) Two snowmen are back to back, facing in opposite directions. They each walk 3km forward, turn left and then work a further 4km. How far are the snowmen from each other? Solution: 10km 2 1 3 1 ð§ ð§ = 8 â 3 4 6 5 6 6 6 (a) What is the height of this equilateral triangle? Solution: ðð or ð ð (b) The area? Solution: ð ð ðð ð ðð 7 25 25 48 Find the area of this isosceles triangle. Solution: 168 Find the height of this isosceles triangle. Solution: ð ðð = ð ð 6 6 8 8
- 24. Exercise 2 (exercises on provided sheet) 27 ðĨ 2ðĨ Determine ðĨ. ðð + ðð = ððð ððð = ðð ðð = ð ð = ð 9
- 25. Exercise 2 (exercises on provided sheet) N5 ðĨ 9 7 ðĨ Determine ðĨ. Solution: We can find the (square of the) central length in two different ways: ðð + ðð = ðð â ðð ððð = ðð ðð = ðð ð = ð N6 ðĨ 3 27 3ðĨ Determine ðĨ (to 2dp). Solution: Using similar strategy to the previous question: ððð â ðð ð = ðð â ðð ððð â ððð = ðð â ð ðððð = ððð ðð = ððð ðð ð = ð. ðð








































![GRADE_10_MATHEMATICS_GEOMETRY_PERMUTATIO [Repaired].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/grade10mathematicsgeometrypermutatiorepaired-240125012744-43e32e19-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)






























