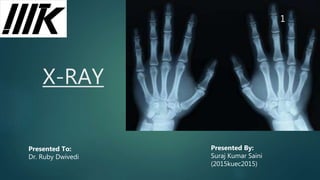
X ray
- 1. X-RAY Presented By: Suraj Kumar Saini (2015kuec2015) Presented To: Dr. Ruby Dwivedi 1
- 2. Table of Content ’üĄ X- Ray ’üĄ Properties of X-ray ’üĄ History ’üĄ Working ’üĄ Application ’üĄ Advantage and Disadvantage 2
- 3. X-Ray ’üĄ X-rays are the electromagnetic waves, they are more energetic so they can penetrate many materials to varying degrees. ’üĄ An X-ray machine is basically like a camera. It uses X-rays to expose the film, instead of visible light. ’üĄ When the X-rays hit the film or sheet, they expose it just as light would. Since bone, fat, muscle, tumors and other masses all absorb X-rays at different levels, the image on the film has different (distinct) structures inside the body because of the different levels of exposure on the film. 3
- 4. Properties of X-Rays ’üĄ X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz (30├Ś1015 Hz to 30├Ś1018 Hz) and energies in the range 100 eV to 100 keV. ’üĄ X- Rays have relatively high penetrating power. ’üĄ They are classified into Hard X-ray and Soft X- Ray: ’üĄ X-ray which have high energy and shorter wavelength is known as Hard X-ray. ’üĄ X-ray which have low energy and longer wavelength is known as Soft X-ray. 4
- 5. History ’üĄ X-ray technology was invented completely by accident. In 1895, a German physicist ŌĆ£Wilhelm RoentgenŌĆØ made the discovery while experimenting with electron beams in a gas discharge tube. ’üĄ Roentgen placed various objects between the tube and the screen, and the screen still glowed. ’üĄ Roentgen found that the X-ray would pass through the tissue of humans leaving the bones and metals visible. One of RoentgenŌĆÖs first experiments late in 1895 was a film of his wife Bertha's hand with a ring on her finger. 5
- 6. Working 6
- 7. ’āś Correct exposure is important to produce a reliable image on the film. Over- or underexposure will result in loss of contrast and therefore possibly in loss of diagnostic information. body film X-Ray source Dark Light 7
- 8. ContinueŌĆ” ’üĄ Calcium in bones is considered a type of metal and when photographic film is placed on the body, this allows the technician to take the picture and an x-ray is developed to solve or analyze the problem. ’üĄ The soft tissue in your body is composed of smaller atoms, and so does not absorb X-ray photons particularly well. The calcium atoms that make up your bones are much larger, so they are better at absorbing X-ray photons. 8
- 9. Applications ’üĄ Medicine: ’üĄ Dentists use them to find complications, cavities and impacted teeth. Soft body tissue are transparent to the waves. Bones also block the rays. ’üĄ Used to detect fractures and formation of stones in human body. 9
- 10. ’üĄ Industry: ’üĄ X-rays are used in industry to inspect products made by various kinds of materials. ’üĄ To identify manufacturing defects in tyres, tennis ball and also used to check defects in diamond 10
- 11. ’üĄ Science: ’üĄ used to analyze the arrangement of atoms in many kinds of substances, particularly crystals. ’üĄ Used in analysis of crystal structure and structure of complex organic molecule. ’üĄ Security: ’üĄ X-ray machines are used in airports to check luggage. 11
- 12. Advantage and disadvantage of X- Ray ’üĄ Advantage: ’üĄ X-ray is the cheapest, the most convenient and widely used method. ’üĄ X-ray are not absorbed very much by air, so the specimen need not be in an evacuated chamber. ’üĄ Disadvantage: ’üĄ They do not interact very strongly with lighter elements. 12
- 13. References ’üĄ https://www.google.co.in/ ’üĄ /Shweta0802/picture-archiving-and- communication-system ’üĄ https://kpmjps.weebly.com/x-rays.html ’üĄ https://xtal.biochem.umass.edu/facility.htm 13
- 14. 14