Fisiologi sistem urinaria
- 1. Oleh: dr. M Faiq Sulaifi Kuliah Ilmu Dasar Keperawatan Program S1 Ilmu Keperawatan STIKES MUHAMMADIYAH LAMONGAN Fisiologi Sistem Urinaria
- 2. Fungsi Ginjal 1. Ekskresi produk sampah metabolik dan bahan kimia asing 2. Mengatur keseimbangan air dan elektrolit 3. Mengatur osmolalitas cairan tubuh dan konsentrasi elektrolit 4. Mengatur tekanan darah 5. Mengatur keseimbangan asam-basa 6. Sekresi, metabolisme dan ekskresi hormon 7. Glukoneogenesis
- 3. Nefron ï Nefron adalah unit fungsional dari ginjal ï 1 nefron terdiri dari: 1. Glomerulus 2. Tubulus yang panjang ï Pada 1 nefron cairan yang tersaring akan menjadi urine
- 5. Proses pada Nefron ï Urinary excretion rate = Filtration rate â Reabsorption rate + Secretion rate
- 7. Filtrasi Glomerulus ï Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) adalah volume total cairan yang difiltrasi oleh glomerulus per unit waktu. GFR = Kf x Net filtration pressure ï Kf: koeffisien filtrasi kapiler glomerulus ï GFR normal (laki-laki) = 125 ml/menit
- 10. Clearance Nutrisi dan Metabolit
- 11. Filtrasi Glomerulus ï Filterabilitas zat yang dapat menembus glomerulus tergantung pada 2 hal: 1. Besar zat 2. Muatan listrik zat (karena glomerulus bermuatan negatif) ï± Semakin besar ukuran zat maka semakin sulit menembus glomerulus ï± Zat dengan muatan listrik negatif lebih sulit menembus dari pada muatan positif
- 12. Kontrol Blood Flow terhadap GFR
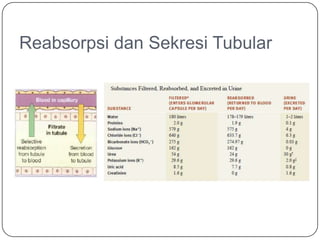
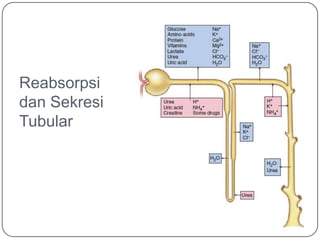
- 13. Reabsorpsi dan Sekresi Tubular
- 16. Reabsorpsi di Loop of Henle Desenden
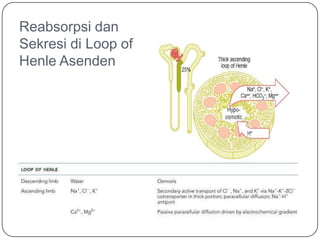
- 17. Reabsorpsi dan Sekresi di Loop of Henle Asenden
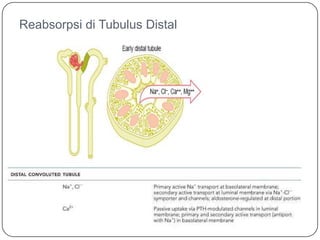
- 18. Reabsorpsi di Tubulus Distal
- 19. Proses di Tubulus Distal Akhir dan Duktus Kolektivus
- 20. Kontrol ADH terhadap Pemekatan Urin
- 21. Sistem Renin Angiotensin Sel Juxtaglomeruler menghasilkan hormon renin yang bekerja pada sistem Renin- Angiotensin
- 23. Pengaruh Renin-Angiotensin pada Pembentukan Urin
- 24. Kontrol Aldosteron terhadap Sekresi Kalium
- 25. Kontrol Aldosteron terhadap Sekresi Natrium
- 26. Keseimbangan Asam-Basa The cells of the renal tubule secrete H+ ions and ammonia into the filtrate and return Na+ ions and HCO3 - ions to the blood in the peritubular capillaries.
- 27. Pembentukan Urin
- 29. Pemekatan Urin (Countercurrent Mechanism) The ability of our kidneys to produce such concentrated urine is critically tied to our ability to survive without water. Water reabsorption that depends on the presence of ADH is called facultative water reabsorption
- 30. Pengenceran Urin When ADH level is low, urine is dilute and has an osmolarity less than the osmolarity of blood
- 31. Resirkulasi Urea
- 32. Ekskresi Volume Cairan 1. Pengaturan ekskresi volume cairan sesuai dengan prinsip âGLOMERULOTUBUL AR BALANCEâ 2. Yaitu: pe GFR pe reabsorpsi tubulus 3. Kecuali pada tubulus distal 4. Pada pasien DM terjadi kegagalan reabsorpsi glukosa diuresis
- 33. Kerja Diuretik
- 34. Kelainan Ginjal
- 35. Hemodialisis During hemodialysis, blood flows through a system of tubes composed of a selectively permeable membrane. Dialysis fluid, the composition of which is similar to that of normal blood, except that the concentration of waste products is very low, flows in the opposite direction on the outside of the dialysis tubes. Waste products, such as urea, diffuse from the blood into the dialysis fluid.
- 36. Nephrolithiasis