Adarsh grid
- 1. Grid Basics Adarsh Patil http://www.adarshpatil.com/
- 2. What is Grid ? It is a volatile heterogeneous distributed system. It is all about sharing resources. It integrates all the heterogeneous resources that are spread across multiple administrative domains (educational institutions, offices, industries) across the world. It gives transparent/collaborative access to these resources and has distributed Job management system. It gives a feeling of Desktop supercomputing - means you are sitting in front of your desktop but you are connected to supercomputer. Grid grows and shrinks dynamically. There is nothing as such you have a static set of resources which we call as Grid. Cluster is not a Grid.
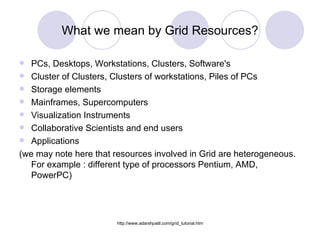
- 3. What we mean by Grid Resources? PCs, Desktops, Workstations, Clusters, Software's Cluster of Clusters, Clusters of workstations, Piles of PCs Storage elements Mainframes, Supercomputers Visualization Instruments Collaborative Scientists and end users Applications (we may note here that resources involved in Grid are heterogeneous. For example : different type of processors Pentium, AMD, PowerPC)
- 4. Why do we need to build Grid? To integrate and aggregate affordable(PC,Desktop,Printers) and unaffordable (clusters,supercomputers,mainframes,giant telescope etc) resources To provide high throughput To build and harvest collaborative boundaries across various communities in research. To give the user feeling of using a most powerful computer. Make fruitful use of the underlying resources and make it as a commodity
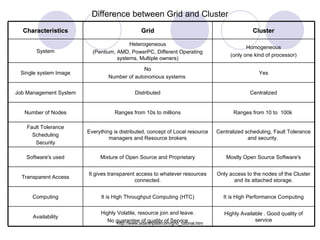
- 5. Difference between Grid and Cluster Highly Available . Good quality of service Highly Volatile, resource join and leave. No guarantee of quality of Service Availability It is High Performance Computing It is High Throughput Computing (HTC) Computing Only access to the nodes of the Cluster and its attached storage. It gives transparent access to whatever resources connected. Transparent Access Mostly Open Source Software's Mixture of Open Source and Proprietary Software's used Centralized scheduling, Fault Tolerance and security. Everything is distributed, concept of Local resource managers and Resource brokers Fault Tolerance Scheduling Security Ranges from 10 to 100k Ranges from 10s to millions Number of Nodes Centralized Distributed Job Management System Yes No Number of autonomous systems Single system Image Homogeneous (only one kind of processor) Heterogeneous (Pentium, AMD, PowerPC, Different Operating systems, Multiple owners) System Cluster Grid Characteristics
- 6. How can we build a Grid? This question has answers within itself . With respect to Grid this question means: How do we take part in the Grid? Or How do we contribute to the Grid ? Or How to we use the Grid? Grid is a social being. Grid is analogous to Electricity Grid. Now if you ask How do we build Electricity Grid? Answers may be Connect to an existing Grid and use it (as a user) and contribute (as a resource). Build a grid using the existing resources using Grid toolkits , Core Middleware's, User Level Middleware's. Getting connected is being part of the Grid.
- 7. Some Terminology Basics Middleware = Resource Broker = Resource Manager . Local Resource Manager - the one which is installed on a standalone PC / Node. Core Level Middleware - the one which controls Local Resource Managers. Grid Computing = large scale Distributed Computing Grid computing superset of Cluster computing, Utility computing, On-demand computing, Metacomputing, P2P computing. Testbed - itâs an infrastructure built out of commodity or proprietary hardware / software to test your research ideas, experiments and activities. Example: Practice court for playing tennis or squash. Virtual Organizations: A community of users having common research interests and testbed supporting their interests. For Example: a group of physicists , a group of chemists , a group of doctors, a group of computer scientists. Each of these groups forms a Virtual Organization (VO). Grid has no standard definition. Everyone has their own definition of Grid. So before jumping into what a person/company says its big into Grid Computing, get to know their definition of Grid. Please keep in mind the basic of everything remains the same but they change the name and attach new letters/words to it Well future is âGridâ
- 8. Credits / Acknowledgements To all the authors/users/administrators/researchers of the Grid Community Please mail me if you want to make changes or have any questions Google and Live are your friends