SCABIES Awajo.pptx
- 2. Scabies ŌĆó Sarcoptes scabei var hominis: specific for humans ŌĆó Sarcoptes scabei var canis: animal mite, rarely causes infection in humans ŌĆó Tramsmission 1. Acquired through direct, prolonged, skin-to-skin contact with an infected person(i.e., same household). 2. Sexual contact. 3. ?Fomite ( infected clothing, bedding)
- 3. ŌĆó Female lifespan 4ŌĆō6 weeks; lays 40ŌĆō50 eggs. ŌĆó Lays 3 eggs per day in tunnels; eggs hatchin 4 days. Burrow 2ŌĆō3 mm daily, usually at night, and lay eggs during the day. ŌĆó Hatched larvae migrate to skin surface and mature into adults. ŌĆó Males and females copulate. Gravid female burrows back under stratum corneum; male falls off skin.
- 4. Epidemiology ŌĆó Estimated at 300 million cases/year worldwide. ŌĆó Epidemics ocured in 15 year cycles, latest 1960 ŌĆó Children (often Ōēż5 years). Nodular scabies more common in children. ŌĆó Young adults (body contact). ŌĆó Elderly and bedridden patients
- 5. Pathogenesis ŌĆó Hypersensitivity of both immediate and delayed types occurs in the development of lesions other than burrows. ŌĆó First infestation: For pruritus to occur, sensitization to S. scabiei must take place -takes several weeks to develop if 1st infestation. ŌĆó Reinfestation: After reinfestation, pruritus may occur within 24 h
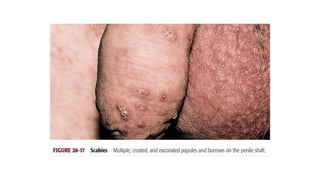
- 6. Clinical features Pruritic papular lesions- Intense, widespread, usually sparing head and neck. Lesions at Site of Infestation ŌĆó Intraepidermal Burrows-grey, slightly elevated ŌĆó Scabietic (Scabious) Nodule ŌĆó Hyperkeratosis/Crusting Psoriasiform Hypersensitivity lesion: ŌĆó Small erythematous papules / papulovesicles ŌĆó Persistent nodular lesions (penis) Secondary changes ŌĆó Pustules: due to secondary infection ŌĆó Eczematised : common infants, children
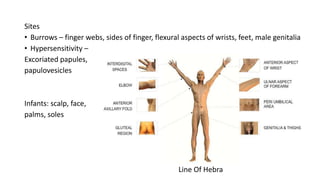
- 7. Sites ŌĆó Burrows ŌĆō finger webs, sides of finger, flexural aspects of wrists, feet, male genitalia ŌĆó Hypersensitivity ŌĆō Excoriated papules, papulovesicles Infants: scalp, face, palms, soles Line Of Hebra
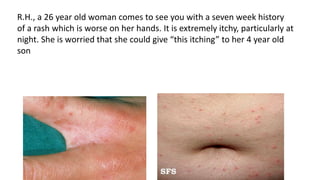
- 8. R.H., a 26 year old woman comes to see you with a seven week history of a rash which is worse on her hands. It is extremely itchy, particularly at night. She is worried that she could give ŌĆ£this itchingŌĆØ to her 4 year old son
- 10. ŌĆó Diagnosis of scabies is made by looking at the burrows or rash. ŌĆó Confirmation of diagnosis Skin scraping papule/ pustule microscopy : mites, eggs, or feces
- 11. Treatment TOPICAL ŌĆó 5% permethrin : apply for 8 hours on days 1 & 8 ŌĆó 1% GBHC: apply for 8 hours on days 1 & 8 ŌĆó 25% Benzyl benzoate: 3 application for 12 hourly ŌĆó 10% Crotamiton: apply for 8 hours on days 1,2,3 & 8 ŌĆó 10% Precipated Sulphur: twice daily for 14 days; DOC in pregnancy ŌĆó 1% Lindane Solution-Apply only once. Wash off in 8 to 12 hours. ORAL ŌĆó Ivermectin 200╬╝g/kg body weight on day 1, 8 and 15
- 12. General principles 1. Apply to whole body below jaw line including genitals, soles, under free edge of nails 2. Treat all family members simultaneously 3. Ordinary laundering of linen 4. Antihistamines: for 4-6 weeks 5. Persistent nodular lesion ŌĆō topical steroid may be required
- 13. Norwegian scabies or crusted scabies ŌĆó Immunocomprised patients ŌĆó Mentally challenged ŌĆó The number of infesting mites may be >1 million. C/F: widespread crusted, hyperkeratotic lesion ŌĆó Innumerable mites (hundreds) ŌĆó Very contagious Treatment - Topical 5% permethrin or topical 5% benzoyl benzoate applied daily for seven days, then twice weekly until cure Keratolytic creams on alternate days to scabicide Oral ivermectin on days 1, 2, 8, 9, and 15 (add days 22, 29 if infestation is severe).
- 14. Animal scabies ŌĆó Mite - Sarcoptes Scabiei var Canis ŌĆó Transmission - Infected animal to human; human to human transmission does not occur ŌĆó Source ŌĆō horses, cattle, dogs, cats; (this infection in animals is called Mange) ŌĆó C/F ŌĆō small, pruritic papules ŌĆ£ temproraryŌĆØ no burrows site - front of trunk, medial aspect of upper extremities ŌĆó Treatment ŌĆō antihistamines ŌĆó specific antiscabetic not required
- 15. THANK YOU