Electronic controllers presentation
3 likes2,628 views
Explain details about Electronic controllers. Error detector, Single mode, proportional mode, integral mode & derivative mode
1 of 9

Recommended
Open Loop and Closed Loop Control System.pptx



Open Loop and Closed Loop Control System.pptxDelower Sumon
╠²
There are two main types of control systems: open-loop and closed-loop. Open-loop systems operate independently of feedback from the output, while closed-loop systems use feedback to automatically adjust the input based on the output. Some key differences are that open-loop systems are simpler and cheaper but less accurate, while closed-loop systems are more complex and costly but provide greater accuracy through feedback correction of errors. Examples of each type are given such as electric hand dryers for open-loop and automatic irons for closed-loop.hall effect and hall effect sensor



hall effect and hall effect sensorADARSH KUMAR
╠²
Hall Effect sensors operate based on the Hall effect, where a voltage difference is produced across a conductor when an electric current passes through it and is exposed to a magnetic field. Hall Effect sensors can detect magnetic fields and produce either linear or digital outputs. They are used in applications like current sensing, speed detection, proximity switching, and position sensing. Some advantages are that they are not affected by ambient conditions and do not have contact with mechanical parts. Some disadvantages include limited range and sensitivity to temperature fluctuations and external magnetic fields.Unit 4 frequency response-Bode plot



Unit 4 frequency response-Bode plotPrajakta Pardeshi
╠²
This document discusses frequency domain analysis and creating Bode plots. Frequency domain analysis examines a system's frequency response by using sinusoidal inputs rather than impulse inputs used in time domain analysis. A Bode plot graphs the magnitude and phase of a system's frequency response on logarithmic and linear scales. It can be used to determine stability margins like gain margin and phase margin. The document provides steps for sketching a Bode plot from a transfer function including identifying poles, zeros and gain. Key aspects of a Bode plot like bandwidth, resonant frequency and cut-off frequency are also defined. Examples of Bode plots for two transfer functions are included.Unit 1 telemetry principles



Unit 1 telemetry principleshiya123jes
╠²
Telemetry is the process of measuring a physical quantity at a remote location and transmitting the data to a central station. This document discusses different types of telemetry systems based on transmission medium (wire, radio, optical fiber), modulation method (DC, AC, pulse), input signal (analog, digital), and number of channels (single, multi). It also describes specific systems including pneumatic, electrical, hydraulic, and pulse telemetry. Common frequency ranges used for telemetry applications are identified.Compensators



Compensatorsjawaharramaya
╠²
The document discusses different types of compensators used in control systems including lag, lead, and lag-lead compensators. It describes the S-plane representation of each compensator and how they can be realized using electrical networks. A lag compensator provides phase lag, improving steady-state performance but slowing the response. A lead compensator increases bandwidth and response speed by providing phase lead. A lag-lead compensator combines the advantages of lag and lead compensation.Telemetry types, frequency,position and multiplexing in telemetry



Telemetry types, frequency,position and multiplexing in telemetrysagheer ahmed
╠²
This document discusses different types of telemetry used in instrumentation systems, including frequency, position, and multiplexing telemetry. Frequency telemetry represents measured values as an alternating current or voltage of varying frequency. Position telemetry relates the signal to the measurement to allow the receiving instrument to display displacement. Multiplexing telemetry allows transmitting multiple measurements over a single channel using either time division or frequency division methods to share the channel. This conserves resources compared to using separate wires for each measurement.Lvdt seminar



Lvdt seminarsrinivas6020
╠²
LVDT is an acronym for Linear Variable Differential Transformer. It is a common type of electromechanical transducer that can convert the rectilinear motion of an object to which it is coupled mechanically into a corresponding electrical signalRecorders.ppt



Recorders.pptANURUPAa
╠²
A recorder records electrical and non-electrical quantities as a function of time to provide a permanent record that can later be examined and analyzed. Recorders are classified as either analog or digital depending on the type of data acquired. Analog recorders include graphic, oscillographic, and magnetic tape recorders. Graphic recorders display a pen-and-ink record on a chart and can be strip chart or X-Y recorders. Strip chart recorders record one or more variables with respect to time in the form of a continuous curve. X-Y recorders plot one variable as a function of another by using two self-balancing potentiometers to move a recording pen.Data Transmission and Telemetry.pdf



Data Transmission and Telemetry.pdfkanizsuburna10
╠²
Telemetry is the automatic measurement and wireless transmission of data from remote sources. In general, telemetry works in the following way: Sensors at the source measure either electrical data, such as voltage and current, or physical data, such as temperature and pressureServomechanism in Control systems engineering



Servomechanism in Control systems engineeringNisarg Amin
╠²
A servomechanism is a closed-loop control system that uses feedback to accurately control a device. It consists of a controlled device, an output sensor, and a feedback system. The feedback system compares the output signal to a reference input and generates a third signal to control the device. This process continues until the output matches the reference input. A servo motor is a type of servomechanism that uses a DC motor, potentiometer, gearing, and control circuitry to rotate a shaft to a desired position based on feedback. It reduces motor speed through gearing while increasing torque. The potentiometer provides feedback of the shaft position to the control circuitry, which drives the motor until the positions match, stoppingTime response of discrete systems 4th lecture



Time response of discrete systems 4th lecturekhalaf Gaeid
╠²
1. The document discusses the time response of discrete-time systems, including their transient and steady-state response. It describes parameters for characterizing transient response such as rise time, delay time, peak time, and settling time.
2. Steady-state errors are also examined for different system types (Type-0, 1, 2 systems) and inputs (step, ramp, parabolic). Examples are provided to calculate steady-state errors.
3. The response of discrete-time systems is derived using impulse response sequences and convolution sums. The time response is broken into zero-input and zero-state responses.Electrical Measurement & Instruments



Electrical Measurement & InstrumentsChandan Singh
╠²
Electrical and electronic measuring equipment. Ammeter. Capacitance meter. Distortionmeter. Electricity meter. Frequency counter. Galvanometer. LCR meter. Microwave power meter.TIME DOMAIN ANALYSIS



TIME DOMAIN ANALYSISSyed Saeed
╠²
presentation slides based on Time Domain Analysis
Reference: automatic control system by s. hasan saeedClassification of transducers



Classification of transducersManash Deka
╠²
Transducers can be classified in several ways:
- Active transducers generate their own power to produce an output signal proportional to the input, like piezoelectric transducers, while passive transducers require an external power source.
- Primary transducers convert a physical input directly into motion, then secondary transducers convert that motion into an electrical signal.
- Transducers can also be categorized by their transduction principle, such as capacitive, electromagnetic, inductive, piezoelectric, photovoltaic, and photoconductive.
- Analog transducers produce a continuous output signal, versus digital transducers which produce a pulse-based 0s and 1sClassical and Modern Control Theory



Classical and Modern Control TheoryQazi Ejaz
╠²
This document outlines the topics to be covered in a course on classical and modern control systems. It includes an introduction, contact information for the instructor, an outline of course topics such as modeling, frequency analysis, time analysis, software, labs, and MATLAB commands. Basic mathematics concepts are reviewed including calculus, linear algebra, Laplace transforms, and differential equations. Electrical and mechanical systems are provided as examples to model control systems.Single Phase Converter



Single Phase ConverterVinod Srivastava
╠²
This document summarizes a seminar on single phase converters. It discusses different types of single phase converters including half wave and full wave rectifiers as well as controlled rectifiers using thyristors. It provides equations for calculating the average output voltage and current for resistive and resistive-inductive loads. The operation and triggering of thyristors in a single phase converter is explained. Graphs of input voltage and output voltage and current are shown. The effect of an output inductor and finite commutation interval are also discussed.Frequency Response Analysis



Frequency Response AnalysisHussain K
╠²
This Presentation explains about the introduction of Frequency Response Analysis. This video clearly shows advantages and disadvantages of Frequency Response Analysis and also explains frequency domain specifications and derivations of Resonant Peak, Resonant Frequency and Bandwidth.Telemetry



TelemetryAnchal bassi
╠²
Telemetry involves measuring values at a remote location and transmitting the data to another location. It involves three steps - measuring a value, converting it to a signal, transmitting the signal, and reconverting it back to the original data. Factors like accuracy, whether the data is analog or digital, error detection/correction, and bandwidth influence telemetry system design. There are two main types - landline systems which use wires/cables over short distances, and radio frequency systems which use radio links from 1km to beyond 50km. Landline systems transmit current or voltage and have simple circuitry but limited range. Radio frequency systems transmit via radio links and are used for long range applications like spacecraft. Modulation schemes include amplitude modulation forA presentation on scada system



A presentation on scada systemIIT INDORE
╠²
SCADA systems are used to monitor and control geographically dispersed industrial processes. A SCADA system consists of field devices like PLCs and RTUs that connect to sensors and convert signals to digital data. This data is communicated to a control center via telemetry where it is processed by a data acquisition server and presented to human operators through an HMI. The system allows operators to monitor and control the industrial process. SCADA has evolved from early monolithic centralized systems to modern distributed and networked systems that utilize open standards and protocols to distribute functionality across a wide area network. SCADA is commonly used in applications like power generation, water treatment, oil and gas pipelines, and more.Nyquist plot



Nyquist plotMrunal Deshkar
╠²
Content covered: Nyquist stability criteria, stability analysis using Nyquist plot, rules for drawing Nyquist plot and its examplesBasics of Sensors & Transducers



Basics of Sensors & TransducersBurdwan University
╠²
This article provides an introduction to the fundamental of Sensors and Transducers. It illustrates the different classifications of sensors and transducers. Explains capacitive, resistive and inductive transducers in brief. Also shows the examples under these types of transducers. Sensor and transducers lect 1



Sensor and transducers lect 1prashant tripathi
╠²
This document provides an introduction to sensors and transducers. It defines a sensor as a device that receives and responds to a signal or stimulus, and a transducer as a device that converts one form of energy into another. The document then discusses different types of sensors classified by their energy form, including displacement, force, pressure, velocity, and level sensors. It provides examples of common sensor types like potentiometers, strain gauges, LVDTs, optical encoders, and piezoelectric sensors. Finally, it covers the topic of signal conditioning, where the signal from the sensor is prepared for use in other parts of a system.Lvdt



LvdtKausik das
╠²
This document discusses transducers and the linear variable differential transformer (LVDT). It defines a transducer as a device that converts one form of energy to another, and classifies transducers based on their principles and whether they are active, passive, primary or secondary. LVDTs are introduced as the most widely used inductive transducer to convert linear motion to an electrical signal. The document proceeds to describe the construction, operating principle, and advantages/disadvantages of LVDTs, and concludes by outlining their applications in measuring small displacements.Need For Modulation in Communication System



Need For Modulation in Communication SystemMyat Myint Zu Thin
╠²
This presentation will explain about the need for modulation in communication system. We made this presentation as our group assignment in Analog and Digital Communication System course in MIIT.CRO



CROvmr1124
╠²
A dual beam oscilloscope can display two signals simultaneously using a CRT that generates and deflects two separate electron beams. It avoids issues with dual trace oscilloscopes that time share a single beam. A dual trace oscilloscope displays two signals by rapidly switching a single beam between the two input channels. Sampling oscilloscopes convert fast signals to low frequency domains by taking samples over successive cycles. Digital storage oscilloscopes digitize input waveforms and store them in memory for display, allowing non-repetitive signals to be observed. Oscilloscope probes come in passive and active varieties, with 1x, 10x, and 100x attenuation ratios for passive probes and integrated circuits in active probes for improved performancePolar Plot



Polar PlotHussain K
╠²
This presentation explains about the introduction of Polar Plot, advantages and disadvantages of polar plot and also steps to draw polar plot. and also explains about how to draw polar plot with an examples. It also explains how to draw polar plot with numerous examples and stability analysis by using polar plot.Stability of Control System



Stability of Control Systemvaibhav jindal
╠²
1. Stability of a system can be determined by observing its time response curve, with stable systems having oscillations that die out quickly or reach steady state fast.
2. Different types of stability include bounded input bounded output stability, asymptotic stability, absolute stability, and relative stability.
3. A system is stable if all poles are in the left half of the s-plane, marginally stable if poles are on the imaginary axis, and unstable if any poles are in the right half plane.Lecture1 measurement & intrumentation



Lecture1 measurement & intrumentationasmawi78
╠²
This lecture introduces measurement and instrumentation. It defines measurement and instrumentation, discusses types of measurements and instruments. It reviews units of measurement, standards of measurement, and calibration. Measurement and instrumentation are used in various applications including home appliances, vehicles, and industrial processes to monitor and control parameters and improve operations.Mechanical steering system



Mechanical steering systemAkshay Dhole
╠²
The document summarizes the basic parts of a steering system. It includes the steering wheel, column and shaft that transmit driver input. The steering gear converts rotational motion to linear motion to turn the wheels. Connecting the steering gear to the wheels are steering linkage components like tie rods and steering arms. Ball joints in the suspension allow for wheel movement during steering.Rfid interfacing & controlling with 8051



Rfid interfacing & controlling with 8051Akshay Dhole
╠²
RFID-
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a generic term that is used to describe a system that transmits the identity (in the form of a unique serial number) of an object or person wireless, using radio waves.
The information on the micro-chip can be read automatically, at a distance, by another wireless machineMore Related Content
What's hot (20)
Data Transmission and Telemetry.pdf



Data Transmission and Telemetry.pdfkanizsuburna10
╠²
Telemetry is the automatic measurement and wireless transmission of data from remote sources. In general, telemetry works in the following way: Sensors at the source measure either electrical data, such as voltage and current, or physical data, such as temperature and pressureServomechanism in Control systems engineering



Servomechanism in Control systems engineeringNisarg Amin
╠²
A servomechanism is a closed-loop control system that uses feedback to accurately control a device. It consists of a controlled device, an output sensor, and a feedback system. The feedback system compares the output signal to a reference input and generates a third signal to control the device. This process continues until the output matches the reference input. A servo motor is a type of servomechanism that uses a DC motor, potentiometer, gearing, and control circuitry to rotate a shaft to a desired position based on feedback. It reduces motor speed through gearing while increasing torque. The potentiometer provides feedback of the shaft position to the control circuitry, which drives the motor until the positions match, stoppingTime response of discrete systems 4th lecture



Time response of discrete systems 4th lecturekhalaf Gaeid
╠²
1. The document discusses the time response of discrete-time systems, including their transient and steady-state response. It describes parameters for characterizing transient response such as rise time, delay time, peak time, and settling time.
2. Steady-state errors are also examined for different system types (Type-0, 1, 2 systems) and inputs (step, ramp, parabolic). Examples are provided to calculate steady-state errors.
3. The response of discrete-time systems is derived using impulse response sequences and convolution sums. The time response is broken into zero-input and zero-state responses.Electrical Measurement & Instruments



Electrical Measurement & InstrumentsChandan Singh
╠²
Electrical and electronic measuring equipment. Ammeter. Capacitance meter. Distortionmeter. Electricity meter. Frequency counter. Galvanometer. LCR meter. Microwave power meter.TIME DOMAIN ANALYSIS



TIME DOMAIN ANALYSISSyed Saeed
╠²
presentation slides based on Time Domain Analysis
Reference: automatic control system by s. hasan saeedClassification of transducers



Classification of transducersManash Deka
╠²
Transducers can be classified in several ways:
- Active transducers generate their own power to produce an output signal proportional to the input, like piezoelectric transducers, while passive transducers require an external power source.
- Primary transducers convert a physical input directly into motion, then secondary transducers convert that motion into an electrical signal.
- Transducers can also be categorized by their transduction principle, such as capacitive, electromagnetic, inductive, piezoelectric, photovoltaic, and photoconductive.
- Analog transducers produce a continuous output signal, versus digital transducers which produce a pulse-based 0s and 1sClassical and Modern Control Theory



Classical and Modern Control TheoryQazi Ejaz
╠²
This document outlines the topics to be covered in a course on classical and modern control systems. It includes an introduction, contact information for the instructor, an outline of course topics such as modeling, frequency analysis, time analysis, software, labs, and MATLAB commands. Basic mathematics concepts are reviewed including calculus, linear algebra, Laplace transforms, and differential equations. Electrical and mechanical systems are provided as examples to model control systems.Single Phase Converter



Single Phase ConverterVinod Srivastava
╠²
This document summarizes a seminar on single phase converters. It discusses different types of single phase converters including half wave and full wave rectifiers as well as controlled rectifiers using thyristors. It provides equations for calculating the average output voltage and current for resistive and resistive-inductive loads. The operation and triggering of thyristors in a single phase converter is explained. Graphs of input voltage and output voltage and current are shown. The effect of an output inductor and finite commutation interval are also discussed.Frequency Response Analysis



Frequency Response AnalysisHussain K
╠²
This Presentation explains about the introduction of Frequency Response Analysis. This video clearly shows advantages and disadvantages of Frequency Response Analysis and also explains frequency domain specifications and derivations of Resonant Peak, Resonant Frequency and Bandwidth.Telemetry



TelemetryAnchal bassi
╠²
Telemetry involves measuring values at a remote location and transmitting the data to another location. It involves three steps - measuring a value, converting it to a signal, transmitting the signal, and reconverting it back to the original data. Factors like accuracy, whether the data is analog or digital, error detection/correction, and bandwidth influence telemetry system design. There are two main types - landline systems which use wires/cables over short distances, and radio frequency systems which use radio links from 1km to beyond 50km. Landline systems transmit current or voltage and have simple circuitry but limited range. Radio frequency systems transmit via radio links and are used for long range applications like spacecraft. Modulation schemes include amplitude modulation forA presentation on scada system



A presentation on scada systemIIT INDORE
╠²
SCADA systems are used to monitor and control geographically dispersed industrial processes. A SCADA system consists of field devices like PLCs and RTUs that connect to sensors and convert signals to digital data. This data is communicated to a control center via telemetry where it is processed by a data acquisition server and presented to human operators through an HMI. The system allows operators to monitor and control the industrial process. SCADA has evolved from early monolithic centralized systems to modern distributed and networked systems that utilize open standards and protocols to distribute functionality across a wide area network. SCADA is commonly used in applications like power generation, water treatment, oil and gas pipelines, and more.Nyquist plot



Nyquist plotMrunal Deshkar
╠²
Content covered: Nyquist stability criteria, stability analysis using Nyquist plot, rules for drawing Nyquist plot and its examplesBasics of Sensors & Transducers



Basics of Sensors & TransducersBurdwan University
╠²
This article provides an introduction to the fundamental of Sensors and Transducers. It illustrates the different classifications of sensors and transducers. Explains capacitive, resistive and inductive transducers in brief. Also shows the examples under these types of transducers. Sensor and transducers lect 1



Sensor and transducers lect 1prashant tripathi
╠²
This document provides an introduction to sensors and transducers. It defines a sensor as a device that receives and responds to a signal or stimulus, and a transducer as a device that converts one form of energy into another. The document then discusses different types of sensors classified by their energy form, including displacement, force, pressure, velocity, and level sensors. It provides examples of common sensor types like potentiometers, strain gauges, LVDTs, optical encoders, and piezoelectric sensors. Finally, it covers the topic of signal conditioning, where the signal from the sensor is prepared for use in other parts of a system.Lvdt



LvdtKausik das
╠²
This document discusses transducers and the linear variable differential transformer (LVDT). It defines a transducer as a device that converts one form of energy to another, and classifies transducers based on their principles and whether they are active, passive, primary or secondary. LVDTs are introduced as the most widely used inductive transducer to convert linear motion to an electrical signal. The document proceeds to describe the construction, operating principle, and advantages/disadvantages of LVDTs, and concludes by outlining their applications in measuring small displacements.Need For Modulation in Communication System



Need For Modulation in Communication SystemMyat Myint Zu Thin
╠²
This presentation will explain about the need for modulation in communication system. We made this presentation as our group assignment in Analog and Digital Communication System course in MIIT.CRO



CROvmr1124
╠²
A dual beam oscilloscope can display two signals simultaneously using a CRT that generates and deflects two separate electron beams. It avoids issues with dual trace oscilloscopes that time share a single beam. A dual trace oscilloscope displays two signals by rapidly switching a single beam between the two input channels. Sampling oscilloscopes convert fast signals to low frequency domains by taking samples over successive cycles. Digital storage oscilloscopes digitize input waveforms and store them in memory for display, allowing non-repetitive signals to be observed. Oscilloscope probes come in passive and active varieties, with 1x, 10x, and 100x attenuation ratios for passive probes and integrated circuits in active probes for improved performancePolar Plot



Polar PlotHussain K
╠²
This presentation explains about the introduction of Polar Plot, advantages and disadvantages of polar plot and also steps to draw polar plot. and also explains about how to draw polar plot with an examples. It also explains how to draw polar plot with numerous examples and stability analysis by using polar plot.Stability of Control System



Stability of Control Systemvaibhav jindal
╠²
1. Stability of a system can be determined by observing its time response curve, with stable systems having oscillations that die out quickly or reach steady state fast.
2. Different types of stability include bounded input bounded output stability, asymptotic stability, absolute stability, and relative stability.
3. A system is stable if all poles are in the left half of the s-plane, marginally stable if poles are on the imaginary axis, and unstable if any poles are in the right half plane.Lecture1 measurement & intrumentation



Lecture1 measurement & intrumentationasmawi78
╠²
This lecture introduces measurement and instrumentation. It defines measurement and instrumentation, discusses types of measurements and instruments. It reviews units of measurement, standards of measurement, and calibration. Measurement and instrumentation are used in various applications including home appliances, vehicles, and industrial processes to monitor and control parameters and improve operations.More from Akshay Dhole (11)
Mechanical steering system



Mechanical steering systemAkshay Dhole
╠²
The document summarizes the basic parts of a steering system. It includes the steering wheel, column and shaft that transmit driver input. The steering gear converts rotational motion to linear motion to turn the wheels. Connecting the steering gear to the wheels are steering linkage components like tie rods and steering arms. Ball joints in the suspension allow for wheel movement during steering.Rfid interfacing & controlling with 8051



Rfid interfacing & controlling with 8051Akshay Dhole
╠²
RFID-
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a generic term that is used to describe a system that transmits the identity (in the form of a unique serial number) of an object or person wireless, using radio waves.
The information on the micro-chip can be read automatically, at a distance, by another wireless machineHttp Introduction



Http IntroductionAkshay Dhole
╠²
HTTP is the most popular application protocol on the internet. It uses the client-server model where an HTTP client sends a request to an HTTP server using a request method like GET or POST. The server then returns a response with a status code and can include a message body. A URL identifies a web resource and includes the protocol, hostname, port, and path. HTTP specifications are maintained by the W3C and the current versions are HTTP/1.0 and HTTP/1.1. The HTTP request and response include a start line, headers, and optional body. Common status codes indicate success, redirection, or client/server errors.Pspice Introduction



Pspice IntroductionAkshay Dhole
╠²
Basics of PSPICE.
SPICE (Simulation Program for Integrated Circuits Emphasis) is a general purpose analog circuit simulator that is used to verify circuit designs and to predict the circuit behavior.
PSpice is a PC version of SPICE and HSpice is a version that runs on workstations and larger computersPLC ARCHITECTURE AND HARDWARE COMPONENTS



PLC ARCHITECTURE AND HARDWARE COMPONENTSAkshay Dhole
╠²
Explains about the basics of PLC ARCHITECTURE AND HARDWARE COMPONENTS.
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a specialized computing system used for control of industrial machines and processes.
A PLC is a computer designed to work in an industrial environment Machine vision in food & beverages



Machine vision in food & beveragesAkshay Dhole
╠²
Explains about how the Machine vision system works in the food and beverages industry. Detail descriptive animation of machine vision systemFIFA 15 Launch 



FIFA 15 Launch Akshay Dhole
╠²
FIFA 15 will focus on emotions and intensity with improved graphics. It will have an official cover featuring Lionel Messi and the most authentic Premier League presentation to date. New features include a street football mode, more realistic crowd emotions and atmospheres, and improved visual catching. FIFA 15 will launch on PlayStation 3, PlayStation 4, Xbox consoles, and be marketed through TV, internet advertisements, and demo versions for mobile and PC.Design of alarm using pir sensor for



Design of alarm using pir sensor forAkshay Dhole
╠²
An╠²alarm device╠²or system of alarm devices gives an audible, visual or other form of╠²alarm signal╠²about a problem or condition. Alarm devices are often outfitted with a╠²siren.
Alarms in an operation and maintenance (O&M) monitoring system, which informs the bad working state of (a particular part of) the system under monitoring. First-out alarm safety alarms, which go off if a dangerous condition occurs.
Temperature controller of hot and cold reservoir



Temperature controller of hot and cold reservoirAkshay Dhole
╠²
Explains about temperature measurement and controlling, temperature sensors & measurement techniques. Open loop and closed loop control systemCounter propagation Network



Counter propagation NetworkAkshay Dhole
╠²
The document summarizes the counterpropagation neural network algorithm. It consists of an input layer, a Kohonen hidden layer that clusters inputs, and a Grossberg output layer. The algorithm identifies the winning hidden neuron that is most activated by the input. The output is then calculated as the weight between the winning hidden neuron and the output neurons, providing a coarse approximation of the input-output mapping.Touch Screen Sensor presentation



Touch Screen Sensor presentationAkshay Dhole
╠²
Explains about touch screen sensor and its operation with the controller, types of touch sensor and its differentiation, advantages & disadvantages and its applications in day today life.Recently uploaded (20)
General Quiz at Maharaja Agrasen College | Amlan Sarkar | Prelims with Answer...



General Quiz at Maharaja Agrasen College | Amlan Sarkar | Prelims with Answer...Amlan Sarkar
╠²
Prelims (with answers) + Finals of a general quiz originally conducted on 13th November, 2024.
Part of The Maharaja Quiz - the Annual Quiz Fest of Maharaja Agrasen College, University of Delhi.
Feedback welcome at amlansarkr@gmail.comHow to Manage Check Out Process in Odoo 17 Website



How to Manage Check Out Process in Odoo 17 WebsiteCeline George
╠²
Checkout process is a final step before processing the purchase. At this step we review the product, add shipping details and confirm the purchase.How to Install Odoo 18 with Pycharm - Odoo 18 ║▌║▌▀Żs



How to Install Odoo 18 with Pycharm - Odoo 18 ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide weŌĆÖll discuss the installation of odoo 18 with pycharm. Odoo 18 is a powerful business management software known for its enhanced features and ability to streamline operations. Built with Python 3.10+ for the backend and PostgreSQL as its database, it provides a reliable and efficient system. Enhancing SoTL through Generative AI -- Opportunities and Ethical Considerati...



Enhancing SoTL through Generative AI -- Opportunities and Ethical Considerati...Sue Beckingham
╠²
This presentation explores the role of generative AI (GenAI) in enhancing the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning (SoTL), using FeltenŌĆÖs five principles of good practice as a guiding framework. As educators within higher education institutions increasingly integrate GenAI into teaching and research, it is vital to consider how these tools can support scholarly inquiry into student learning, while remaining contextually grounded, methodologically rigorous, collaborative, and appropriately public.
Through practical examples and case-based scenarios, the session demonstrates how generative GenAI can assist in analysing critical reflection of current practice, enhancing teaching approaches and learning materials, supporting SoTL research design, fostering student partnerships, and amplifying the reach of scholarly outputs. Attendees will gain insights into ethical considerations, opportunities, and limitations of GenAI in SoTL, as well as ideas for integrating GenAI tools into their own scholarly teaching practices. The session invites critical reflection and dialogue about the responsible use of GenAI to enhance teaching, learning, and scholarly impact.
20250402 ACCA TeamScienceAIEra 20250402 v10.pptx



20250402 ACCA TeamScienceAIEra 20250402 v10.pptxhome
╠²
Team Science in the AI Era: Talk for the Association of Cancer Center Administrators (ACCA) Team Science Network (April 2, 2025, 3pm ET)
Host: Jill Slack-Davis (https://www.linkedin.com/in/jill-slack-davis-56024514/)
20250402 Team Science in the AI Era
These slides: TBD
Jim Twin V1 (English video - Heygen) - https://youtu.be/T4S0uZp1SHw
Jim Twin V1 (French video - Heygen) - https://youtu.be/02hCGRJnCoc
Jim Twin (Chat) Tmpt.me Platform ŌĆō https://tmpt.app/@jimtwin
Jim Twin (English video ŌĆō OpenSource) ŌĆō https://youtu.be/mwnZjTNegXE
Jim Blog Post - https://service-science.info/archives/6612
Jim EIT Article (Real Jim) - https://www.eitdigital.eu/newsroom/grow-digital-insights/personal-ai-digital-twins-the-future-of-human-interaction/
Jim EIT Talk (Real Jim) - https://youtu.be/_1X6bRfOqc4
Reid Hoffman (English video) - https://youtu.be/rgD2gmwCS10Managing Online Signature and Payment with Odoo 17



Managing Online Signature and Payment with Odoo 17Celine George
╠²
Odoo Digital Signature is a feature that allows users to sign documents electronically within the Odoo platform. This functionality streamlines workflows by enabling the creation, distribution, and signing of documents digitally, reducing the need for physical paperwork and speeding up processes.Conrad "Accessibility Essentials: Introductory Seminar"



Conrad "Accessibility Essentials: Introductory Seminar"National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
╠²
This presentation was provided by Lettie Conrad of LibLynx and San Jos├® University during the initial session of the NISO training series "Accessibility Essentials." Session One: The Introductory Seminar was held April 3, 2025.Unit 3: Combustion in Spark Ignition Engines



Unit 3: Combustion in Spark Ignition EnginesNileshKumbhar21
╠²
Stages of combustion, Ignition lag, Flame propagation, Factors affecting flame
speed, Abnormal combustion, Influence of engine design and operating
variables on detonation, Fuel rating, Octane number, Fuel additives, HUCR,
Requirements of combustion chambers of S.I. Engines and its types.Chapter 6. Business and Corporate Strategy Formulation.pdf



Chapter 6. Business and Corporate Strategy Formulation.pdfRommel Regala
╠²
This integrative course examines the strategic decision-making processes of top management,
focusing on the formulation, implementation, and evaluation of corporate strategies and policies.
Students will develop critical thinking and analytical skills by applying strategic frameworks,
conducting industry and environmental analyses, and exploring competitive positioning. Key
topics include corporate governance, business ethics, competitive advantage, and strategy
execution. Through case studies and real-world applications, students will gain a holistic
understanding of strategic management and its role in organizational success, preparing them to
navigate complex business environments and drive strategic initiatives effectively. Design approaches and ethical challenges in Artificial Intelligence tools for...



Design approaches and ethical challenges in Artificial Intelligence tools for...Yannis
╠²
The recent technology of Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) has undeniable advantages, especially with regard to improving the efficiency of all stakeholders in the education process.
At the same time, almost all responsible international organisations and experts in the field of education and educational technology point out a multitude of general ethical problems that need to be addressed. Many of these problems have already arisen in previous models of artificial intelligence or even in systems based on learning data, and several are appearing for the first time.
In this short contribution, we will briefly review some dimensions of ethical problems, both (a) the general ones related to trust, transparency, privacy, personal data security, accountability, environmental responsibility, bias, power imbalance, etc., and (b) the more directly related to teaching, learning, and education, such as students' critical thinking, the social role of education, the development of teachers' professional competences, etc.
In addition, the categorizations of possible service allocation to humans and AI tools, the human-centered approach to designing AI tools and learning data, as well as the more general design of ethics-aware applications and activities will be briefly presented. Finally, some short illustrative examples will be presented to set the basis for the debate in relation to ethical and other dilemmas.Different Facets of Knowledge on different View.pptx



Different Facets of Knowledge on different View.pptxNrapendraVirSingh
╠²
Knowledge is a fundamental aspect of human understanding, evolving through different dimensions and perspectives. The nature of knowledge varies depending on its scope, application, and contextual relevance. In this lecture, we explore four key distinctions in knowledge: Particular vs. Universal, Concrete vs. Abstract, Practical vs. Theoretical, and Textual vs. Contextual. Each of these dichotomies helps us comprehend how knowledge is categorized, interpreted, and applied across different fields of study.
UTI Quinolones by Mrs. Manjushri Dabhade



UTI Quinolones by Mrs. Manjushri DabhadeDabhade madam Dabhade
╠²
UTI quinolones by Mrs. Manjushri Dabhade3. AI Trust Layer, Governance ŌĆō Explainability, Security & Compliance.pdf



3. AI Trust Layer, Governance ŌĆō Explainability, Security & Compliance.pdfMukesh Kala
╠²
AI Trust Layer, Governance ŌĆō Explainability, Security & ComplianceDifferent perspectives on dugout canoe heritage of Soomaa.pdf



Different perspectives on dugout canoe heritage of Soomaa.pdfAivar Ruukel
╠²
Sharing the story of haabjas to 1st-year students of the University of Tartu MA programme "Folkloristics and Applied Heritage Studies" and 1st-year students of the Erasmus Mundus Joint Master programme "Education in Museums & Heritage". Pass SAP C_C4H47_2503 in 2025 | Latest Exam Questions & Study Material



Pass SAP C_C4H47_2503 in 2025 | Latest Exam Questions & Study MaterialJenny408767
╠²
Pass SAP C_C4H47_2503 with expert-designed practice tests & real questions. Start preparing today with ERPPrep.com and boost your SAP Sales Cloud career! Analysis of Conf File Parameters in Odoo 17



Analysis of Conf File Parameters in Odoo 17Celine George
╠²
In this slide, we will analyse the configuration file parameters in Odoo 17. The odoo.conf file plays a pivotal role in configuring and managing the Odoo 17 server. It contains essential parameters that control database connections, server behaviour, logging, and performance settings.Conrad "Accessibility Essentials: Introductory Seminar"



Conrad "Accessibility Essentials: Introductory Seminar"National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
╠²
Electronic controllers presentation
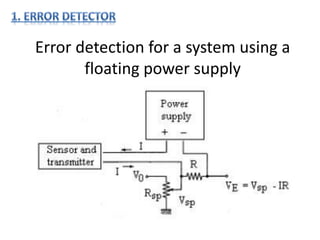
- 2. Error detection for a system using a floating power supply
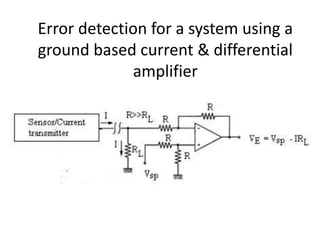
- 3. Error detection for a system using a ground based current & differential amplifier
- 4. Mercury switch on a bimetal strip temperature controller
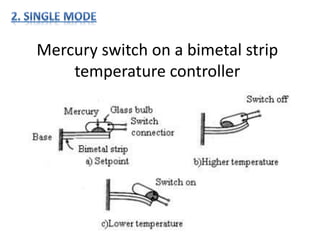
- 5. Two position controller with neutral zone made from op amps & comparator
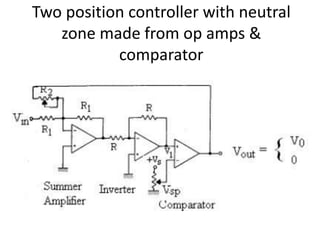
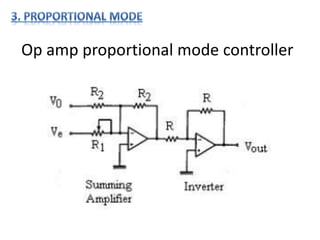
- 6. Op amp proportional mode controller
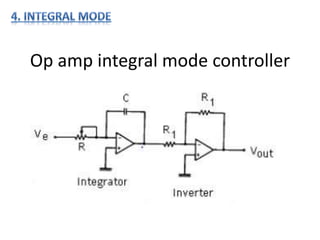
- 7. Op amp integral mode controller
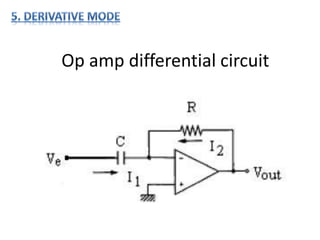
- 8. Op amp differential circuit
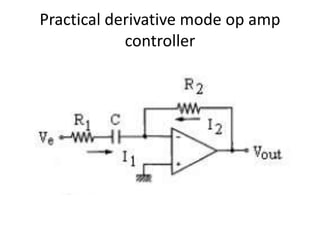
- 9. Practical derivative mode op amp controller




